目录
切换1. Introduction
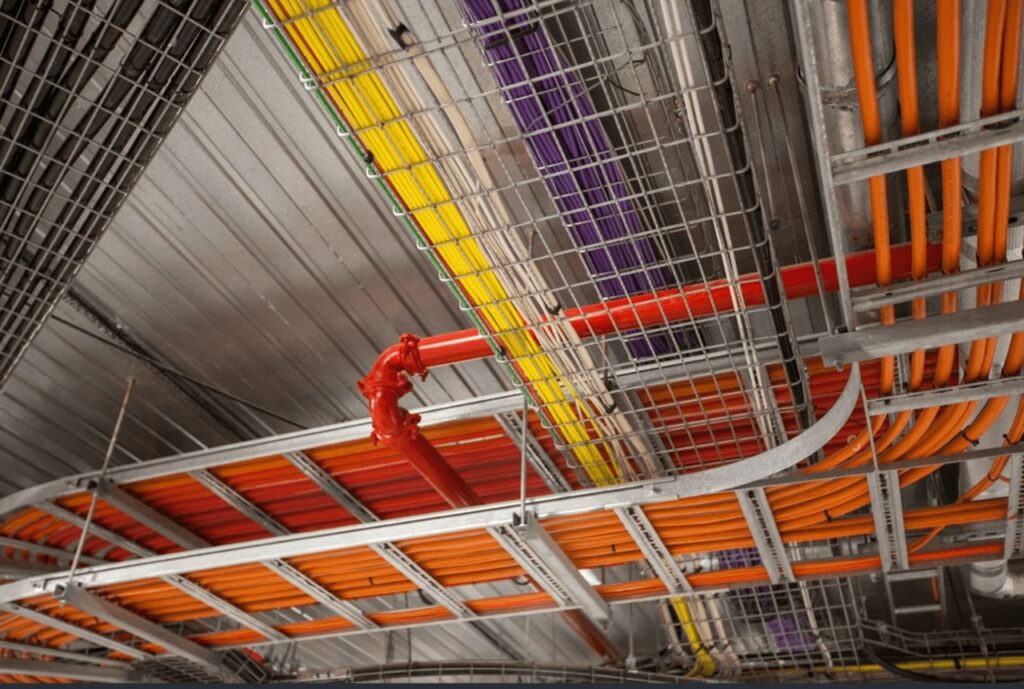

Understanding the differences between electrical raceways and conduits is essential when planning electrical systems for a construction project. Each system has its advantages depending on factors like the type of building, environmental conditions, and specific electrical needs.
By understanding these differences and considering factors like safety, compliance, cost, installation ease, and the specific demands of your project, you can make a more informed decision on which system will best protect and organize your electrical wiring.
In the following post, we will dive deeper into the details of raceways and conduits, exploring their types, benefits, and specific applications to help you choose the right solution for your electrical system.
2. What is an Electrical Raceway?
2.1 Definition and Basic Function
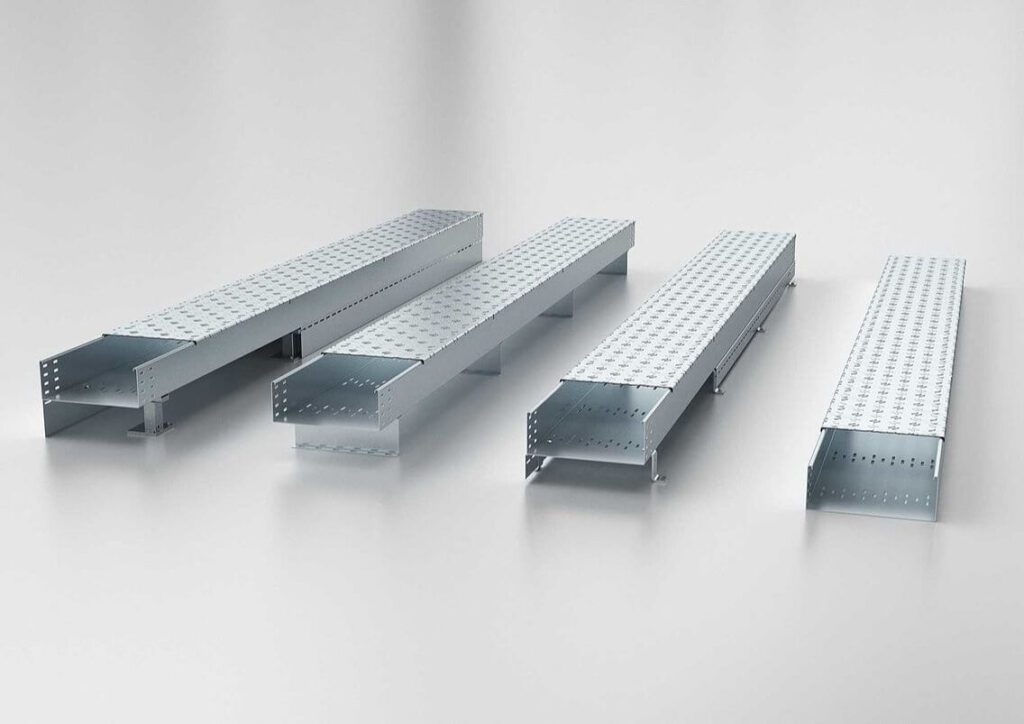

An electrical cable raceway is a system that serves as a pathway for electrical cables, providing a structure to route and organize multiple wires. They differ from conduits because they are usually open and not completely enclosed around the cables. Raceways can be mounted on surfaces, or sometimes underneath floors, to manage cable runs efficiently. They help keep cables neatly organized while offering protection from dust, debris, and physical damage.

2.2 Key Functions of Electrical Cable Raceways:
Cable Organization: Cable raceways allow multiple cables to be routed together in an orderly manner, making it easier to maintain and modify wiring configurations when needed.
Physical Protection: While not fully enclosed, raceways still provide a degree of protection against environmental factors like dust, dirt, and light impacts, depending on the design.
Safety and Compliance: By keeping cables from tangling or being exposed to physical damage, raceways help prevent potential electrical hazards, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
Easy Modification: Because raceways are typically open or partially enclosed, they allow for easy access to the cables, making it easier to modify or add new wiring without needing to dismantle large sections.
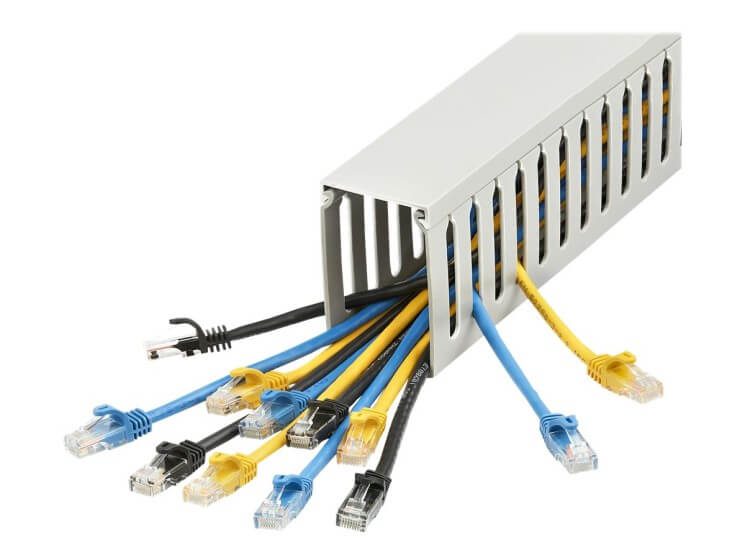

2.3 How Electrical Raceways Work?
Cable raceways work by providing a track or channel along which cables can be routed and organized. The cables typically rest inside or along the raceway, often secured by brackets or clips.
Installation: Cable raceways are often installed on the surface of walls, ceilings, or along floors. They may be mounted with clips, screws, or adhesive, depending on the type and design of the raceway.
Routing Cables: Once installed, the cables are arranged within the raceway, following the path designated by the raceway system. They may be secured using clips or other fasteners to prevent movement or tangling.
Accessibility: Since raceways are typically open or only partially enclosed, cables can be accessed easily for repairs, upgrades, or future modifications. Raceways that mount to the surface allow for easy access without disassembling or removing large parts of the installation.
Protection from Hazards: While not completely enclosed like a conduit, a raceway still provides some protection from dust, dirt, moisture, and light impact. It helps to prevent cables from being exposed to environmental hazards, reducing the risk of wear and tear over time.
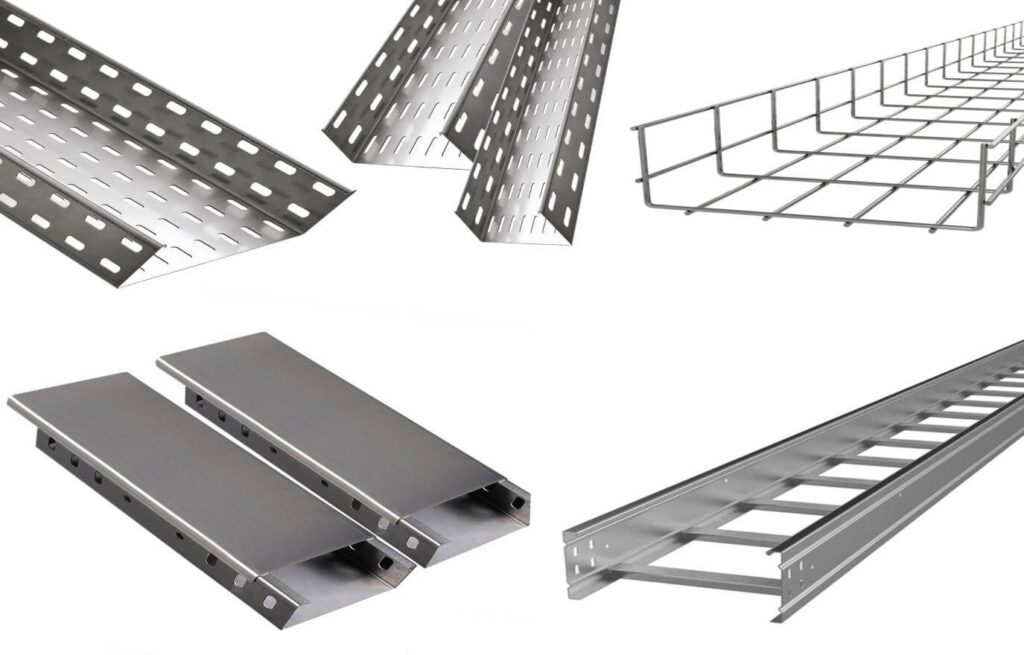

2.4 Types of Electrical Raceways
Here are some common types of non-enclosed electrical raceways used for cable management:
Cable Trays:
Description: Cable trays are open channels or trays used to route large groups of cables. These trays are often mounted along ceilings or walls and allow cables to be laid out in a neat and organized manner.
Common Types: Ladder, ventilated, or solid-bottom trays.
Applications: Frequently used in industrial and commercial settings, such as factories, power plants, or data centers, where large volumes of cables need to be managed over long distances.
Surface-Mounted Raceway (Wiremold):
Description: Surface-mounted raceways are typically plastic or metal channels that run along walls or ceilings to route electrical wires. They are commonly used for low-voltage wiring, such as data cables or phone lines.
Applications: Used in residential or commercial spaces where cables need to be organized but are not embedded within walls. Often seen in home offices or entertainment systems.
Raceway Ducts:
Description: These are narrow, open ducts often used to house multiple cables along walls or ceilings. Unlike traditional conduit, raceway ducts don’t fully encase the cables, providing quick access for changes or additions.
Applications: Commonly used for low-voltage applications like telecommunications or audio/visual cables in commercial environments.
Open Cable Ladder Trays:
Description: Ladder trays are open design systems with horizontal rungs that support cables, similar to a ladder. These trays allow easy routing of cables while providing ample space for airflow to prevent heat buildup.
Applications: Typically used in data centers or industrial facilities where extensive cabling needs to be organized over large areas.
Cable Busways:
Description: Cable busways are modular, open raceway systems used for power distribution, consisting of aluminum or copper busbars housed in an open track.
Applications: These are commonly used for high-voltage and high-current applications in industrial or power generation settings.
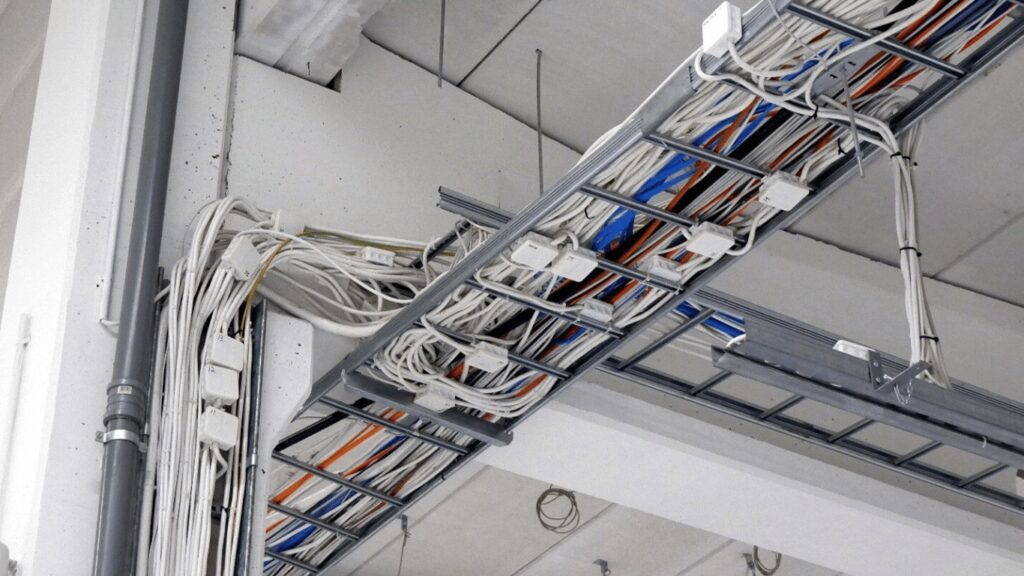

2.5 Why Use an Electrical Raceway?
Electrical raceways are used for several important reasons, particularly for organizing, protecting, and simplifying cable management systems:
Simplified Cable Management: Raceways help reduce cable clutter by grouping wires together in an organized manner. This makes it easier to manage multiple cables and ensures that systems remain clean and orderly.
Protection from Environmental Factors: Raceways provide a basic level of protection from dust, moisture, physical impact, and accidental abrasion, reducing the risk of damage to cables and prolonging their lifespan.
Safety and Compliance: Properly managing cables with raceways ensures compliance with safety regulations, reducing the risk of electrical hazards like fires or electrical shorts.
Accessibility: Since raceways are often open or partially enclosed, they provide easy access for cable modifications or replacements. This is particularly useful in spaces that need frequent changes or maintenance.
Aesthetic Considerations: Raceways help to maintain a clean and aesthetically pleasing environment by keeping cables hidden from view, especially in residential or commercial spaces.
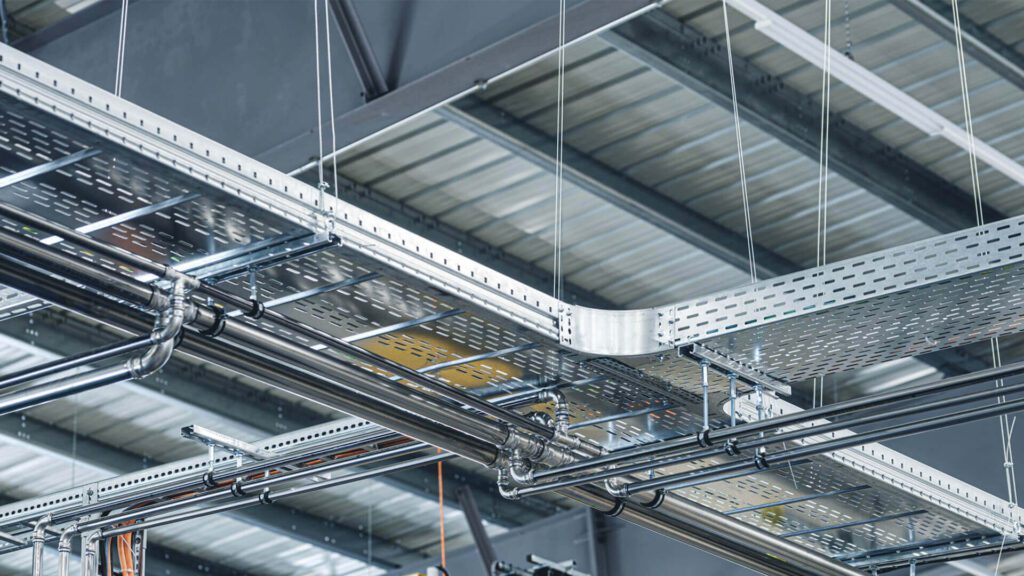

2.6 Applications of Electrical Raceway
Electrical raceways are commonly used in a variety of settings for both low-voltage and high-voltage systems. Some of the typical applications include:
Residential and Commercial Buildings: Raceways are often used in homes and offices to organize and protect low-voltage wiring like data and phone cables, ensuring they’re neatly hidden or organized along walls.
Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities: In industrial environments, raceways are used to route heavy-duty electrical cables through production areas, ensuring that cables are protected from machinery and heavy traffic.
Data Centers: Raceways like cable trays are critical in data centers for organizing the large numbers of data cables that run between servers, routers, and other equipment.
Power Plants: For large-scale operations such as power plants, cable raceways provide a safe and organized way to route extensive electrical cables across expansive facilities.
Retail and Hospitality: In retail and hotel spaces, raceways help organize and protect the wiring for lighting, point-of-sale systems, and security systems, ensuring cables are kept neat and accessible for future maintenance.
3. What is an Electrical Conduit?

3.1 Definition and Basic Function
An electrical conduit is a type of pipe specifically designed to protect electrical cables and wires from external damage while providing a secure and organized route for wiring. The primary function of a conduit is to house electrical cables, safeguarding them against physical harm, moisture, corrosion, and other environmental factors that could potentially disrupt the safe operation of the electrical system. Conduits also ensure that electrical wiring remains properly organized and easily accessible for maintenance, upgrades, or future repairs.
3.2 How Electrical Conduit Works
Electrical conduits function as protective channels for electrical wiring. These conduits can be rigid or flexible, depending on the installation needs and the environmental conditions of the area. The conduit provides a secure and stable housing that keeps electrical cables from being damaged by impact, environmental elements (like water and chemicals), or accidental interference.
In typical applications, wiring is threaded through the conduit either during or after construction. The conduit itself may run along a building’s walls, floors, or ceilings, or it can be buried underground to provide long-term protection against the elements. Conduits also facilitate the ease of wire installation and maintenance, as they can be easily accessed, and the cables can be replaced or upgraded without having to remove significant portions of the building structure.
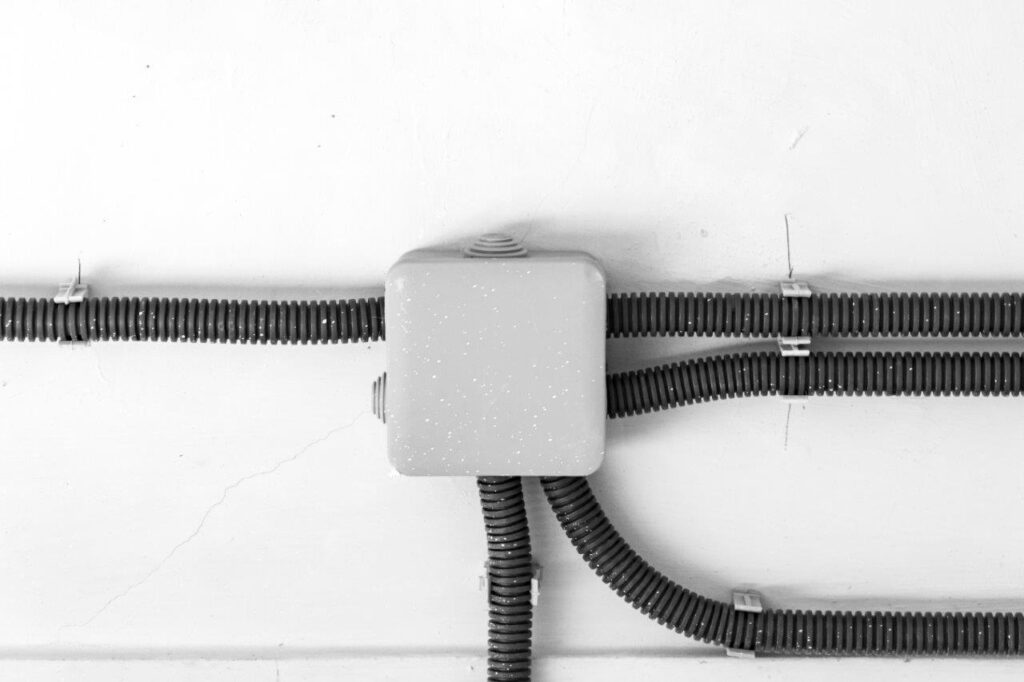

3.3 Why Use Electrical Conduit?
There are several important reasons why conduits are used in electrical installations:
Protection Against Physical Damage: Electrical conduits offer strong protection to electrical cables from external physical damage. Whether the cables are running along a busy street or in a high-traffic commercial area, conduits prevent them from being crushed, pierced, or cut. Without a protective conduit, cables are vulnerable to damage from equipment, tools, or even accidental impact. For example, an exposed wire running through a factory floor could easily be damaged by machinery, leading to potential electrical hazards. Conduits eliminate this risk by providing a solid barrier around the wiring.
Prevention of Environmental Damage: In harsh environments—such as outdoor areas exposed to moisture, extreme temperatures, or corrosive substances—electrical wiring is at risk of being compromised. Conduits provide a protective barrier that shields cables from elements like rain, snow, chemicals, or humidity, ensuring the integrity and longevity of the electrical system. For example, PVC conduits are commonly used in underground applications where moisture resistance is crucial, while steel conduits may be used in industrial areas with high temperatures or corrosive chemicals.
Organization of Electrical Wiring: One of the core functions of electrical conduits is to organize electrical wiring. Instead of having wires run loosely or exposed in a disorderly fashion, conduits help keep them contained and properly arranged. This not only helps to avoid clutter but also simplifies the process of installation, maintenance, and upgrades. In large buildings with numerous wires, such as office buildings, schools, or factories, having a conduit system helps reduce confusion, prevents wiring tangling, and allows technicians to work more efficiently.
Improved Safety: Electrical safety is paramount, and one of the key reasons for using conduits is to prevent electrical accidents. By encasing wiring in a conduit, you reduce the risk of accidental contact with live wires, thus minimizing the potential for electrical shock, fires, or short circuits. In areas where people may come into contact with the wiring—like commercial or residential spaces—conduits provide an extra layer of insulation, shielding the wiring from being exposed or damaged.
Code Compliance: Electrical codes and regulations, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States, often mandate the use of conduits in specific environments or for particular types of electrical installations. For instance, underground wiring is often required to be run inside conduit to prevent moisture damage. Additionally, certain areas with increased fire risk (such as commercial kitchens or industrial facilities) may require conduits for added protection. Compliance with these codes ensures that the electrical system is safe, meets all necessary standards, and avoids penalties or complications in case of inspections.
Ease of Maintenance and Upgrades: One of the benefits of conduit systems is the ease with which electrical wiring can be maintained or upgraded. Wiring within a conduit is generally easier to access than in a traditional installation where wires are hidden behind walls or ceilings. If you need to replace old wiring or add new cables, the conduit system allows you to do so with minimal disruption. In contrast, rewiring a system without conduits often requires tearing out walls or ceilings, making the process more costly and time-consuming.
3.4 Types of Electrical Conduit Materials
Electrical conduits can be made from various materials, with each offering specific advantages depending on the environment, application, and installation requirements.
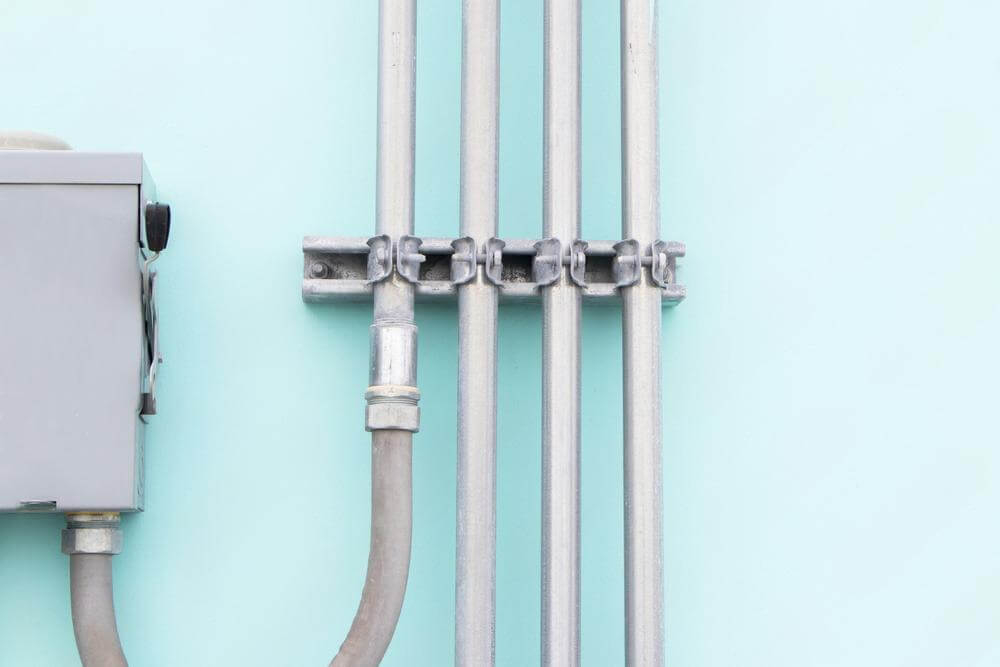

3.4.1 Metallic Conduits
Galvanized Rigid Steel (GRS): This is a heavy-duty conduit often used in industrial applications where protection from physical damage is critical. It is strong and durable, offering excellent protection against mechanical impact and environmental conditions.
Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT): EMT is a lightweight, thin-walled conduit made of galvanized steel. It is often used in commercial and residential installations where protection from physical damage is still important but where flexibility and ease of installation are also priorities.
Aluminum Conduit: This is a lighter alternative to steel conduit, offering corrosion resistance while still providing strong physical protection. Aluminum conduits are often used in outdoor environments or where weight is a concern.
Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC): This type of conduit is made from a spiral-wound metal strip, offering flexibility for applications where the conduit needs to bend around obstacles or where rigid conduit might be difficult to install. It is often used in settings that require movement or frequent changes, such as machinery or power equipment.
3.4.2 Non-Metallic Conduits:
PVC Conduit: Made from polyvinyl chloride, PVC is one of the most common types of non-metallic conduit. It is highly resistant to corrosion, moisture, and environmental damage, making it ideal for use in underground, wet, or corrosive environments. PVC conduit is lightweight, easy to install, and relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for residential and commercial installations.
Typically have two types, rigid plain conduit and flexible conduit, flexible conduit so called corrugated conduit or ENT,we make a brief introduction alone in the following.
Non-Metallic Flexible Conduit /Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing(ENT):
Made from a flexible plastic material, this conduit is often used in environments where flexibility is required but a non-metallic option is preferred. It is lightweight, easy to install, and resistant to moisture and chemicals.
Fiberglass Conduit:玻璃纤维是一种耐腐蚀材料,在金属导管可能不适合的恶劣环境中提供出色的保护。玻璃纤维导管通常用于暴露于化学品、潮湿或极端温度的区域,而其他类型的导管可能会随着时间的推移而变质。
HDPE 导管: 高密度聚乙烯 (HDPE) 导管是一种由耐用的热塑性材料制成的非金属导管。它以柔韧性、耐腐蚀性和耐受各种环境条件的能力而闻名。HDPE 导管广泛用于电气、电信和公用设施安装,尤其是在地下和室外应用中。
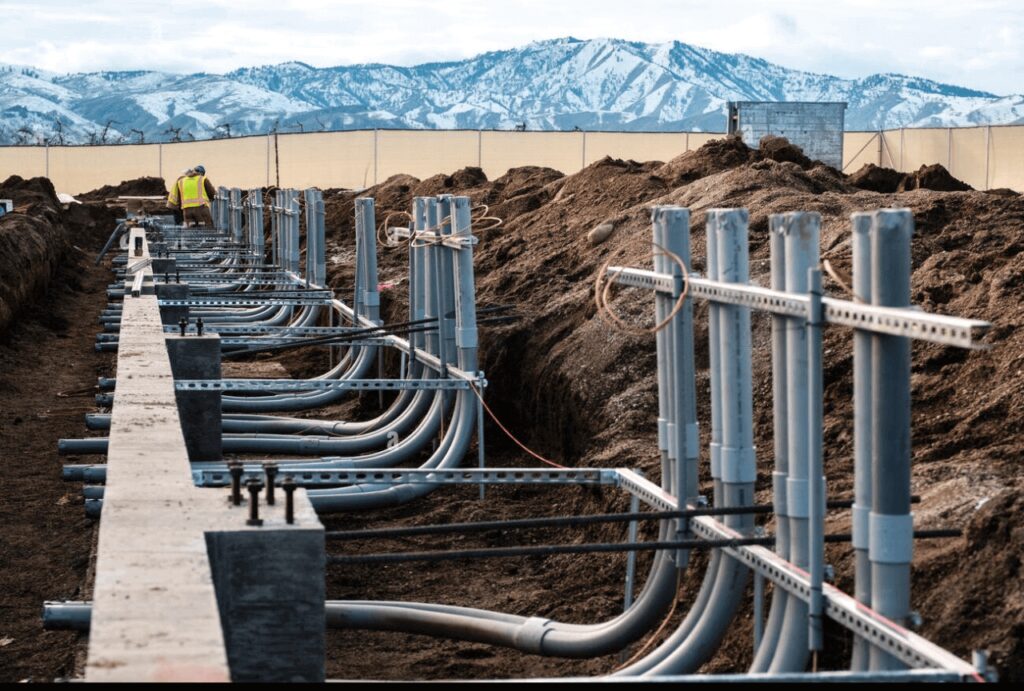

3.5 Applications of Electrical Conduit
电气导管广泛应用于不同领域,从住宅建筑到大型工业设施。一些最常见的应用包括:
住宅布线:住宅中经常使用导管来布线插座、开关和灯具。PVC 导管通常用于住宅中室外或地下布线。
商业建筑:在办公室、购物中心和医院等商业空间中,导管用于确保布线安全有序。EMT 或 GRS 导管经常用于商业环境中的裸露布线。
工业设施:在工厂或车间,电线导管对于保护电线免受机械损坏、化学品或极端环境条件的影响至关重要。在这些环境中,通常使用 GRS 或玻璃纤维等重型导管。
地下设施:导管为地下安装的电线提供关键保护,因为地下电线容易受潮和物理损坏。PVC 导管是地下应用最常见的选择。
4. Key Differences Between Electrical Raceway and Electrical Conduit
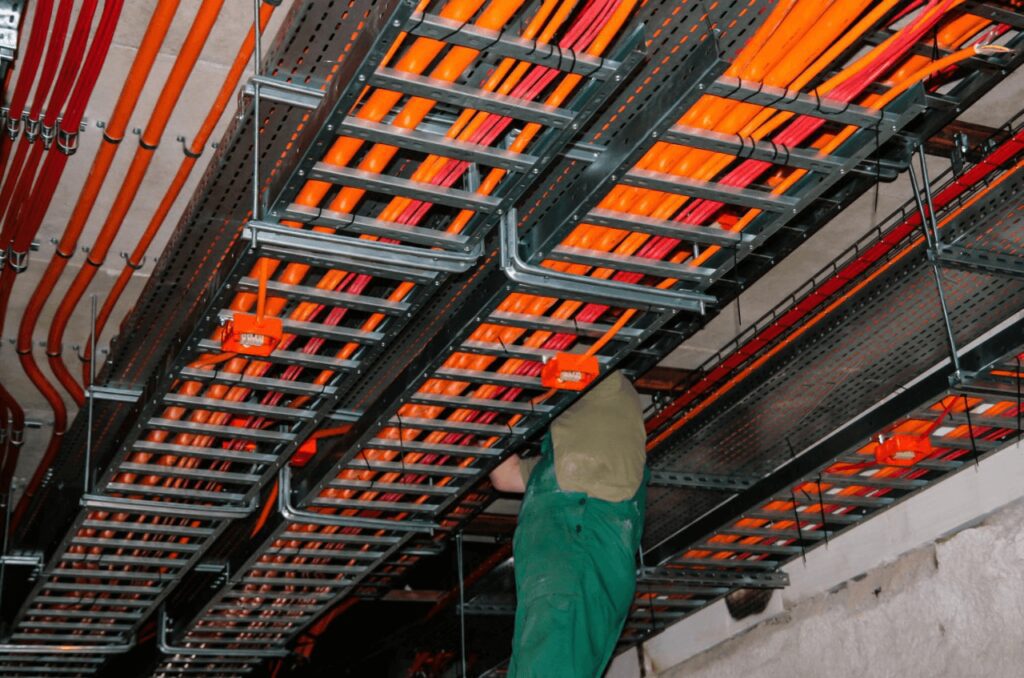

4.1 Shape and Design
电气走线:
形状:滚道通常 矩形的 或者 槽状 形状,尽管其形式可能因类型而异。一般设计特点 开放或部分封闭的系统,允许以有序的方式布线多条电缆。
扁平或低调:许多滚道都是扁平的、表面安装的系统(例如 线模),设计用于与墙壁、天花板或地板齐平。这些导轨具有 低调的矩形形状,使其易于沿现有结构安装。
模块化、可扩展:许多跑道,例如 电线管道,是模块化的,这意味着它们可以扩展和调整长度或布局,以适应安装的特定需求。它们的设计允许 轻松添加或修改 随着系统的增长或变化,进行布线。
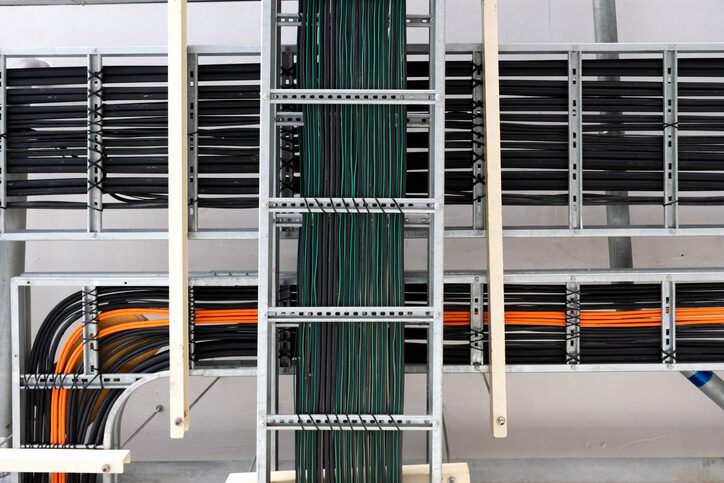

电气导管:
形状:导管是 圆柱形 形状,并且通常 死板的 或者 灵活的 管。圆柱形结构具有结构强度和耐用性,尤其适用于保护电线免受外部损坏。
刚性导管:这些是实心管,通常由 PVC, 钢, 或者 铝,并采用 圆形或环形横截面.这种圆柱形设计使其具有抗压缩性,是恶劣环境下保护电缆的理想选择。
柔性导管:这些通常 瓦楞,使它们能够轻松弯曲以适应角落或狭窄的空间。 柔性金属导管 (FMC) 和 液密柔性导管 (LFMC) 是常见类型,通常用于需要的应用程序 弯曲或灵活布线.
| 特征 | 电气走线 | 电气导管 |
| 形状 | 矩形、扁平或槽状;可模块化 | 圆柱形(刚性或柔性管) |
| 设计
类型 |
开放或部分封闭(例如,电缆托架、电线槽) | 全封闭(实心管或波纹管) |
| 安装简介 | 扁平、低调,适合表面安装或嵌入式安装 | 圆形,适用于刚性或柔性管道 |
| 容量 | 大型开放空间,设计用于容纳多条电缆 | 内部容量有限,适合单个或较小的电缆束 |
| 保护 | 提供有限的保护;主要用于组织和可访问性 | 提供出色的保护,防止外部损坏、潮湿和环境因素 |
| 灵活性 | 轻松扩展并适应新配置 | 灵活或刚性,但安装后适应性较差 |
4.2 Installation Methods and Adaptability
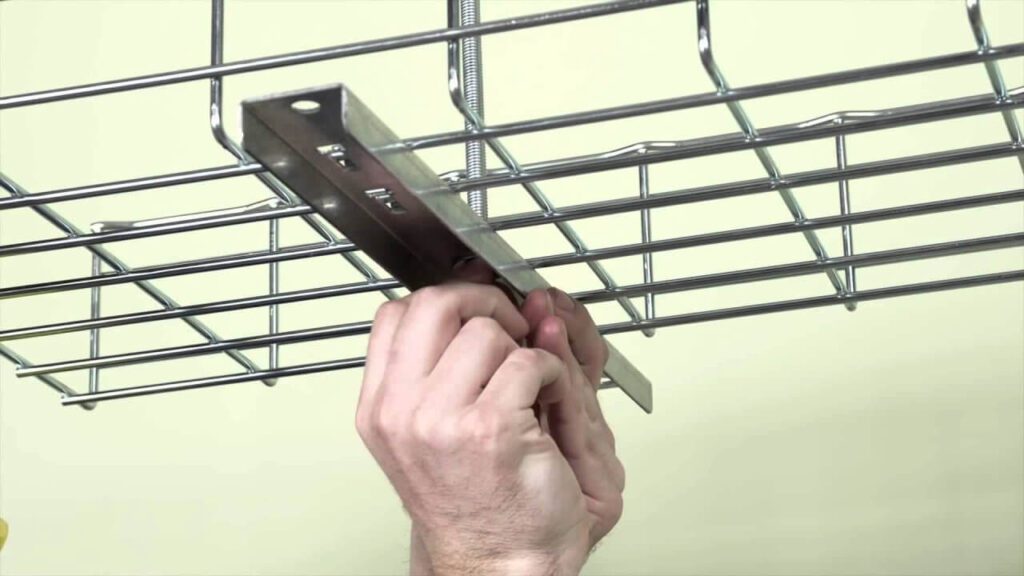

滚道
表面贴装:许多赛道,尤其是 表面贴装品种,设计用于使用螺钉或粘合剂固定在墙壁、天花板或地板上。这些类型通常 矩形的 或者 槽形 以确保电缆稳固固定。
凹进式:滚道也可以 凹陷 墙壁,使其看起来更加美观。 矩形或平面设计 整齐地安装在干式墙中,为电缆提供了一条隐藏但可触及的路径。
灵活的布局: 和 模块化设计,管道可适应直线、曲线或复杂路径,并且可以在将来轻松修改而不会中断系统。
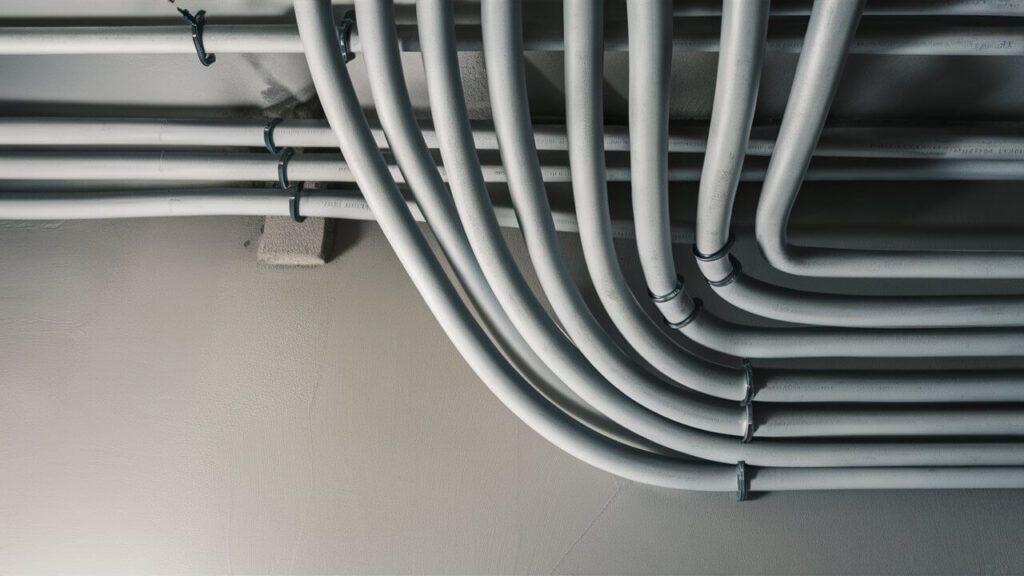

导管
固定路径:导管,尤其是 刚性导管 (PVC、钢材)通常沿固定路线安装,需要切割、穿线并使用夹具或接头固定。
弯曲和弯折:可以使用专用工具(例如,导管弯管机)弯曲刚性导管,但该过程比柔性导管更加耗费劳动力。
有限修改:安装后,如果不进行重大更改或切割,则很难改变导管路径。然而,柔性导管可以布设到狭窄或不规则的空间中。
4.3 Physical Protection: Enclosed vs. Open Designs
滚道
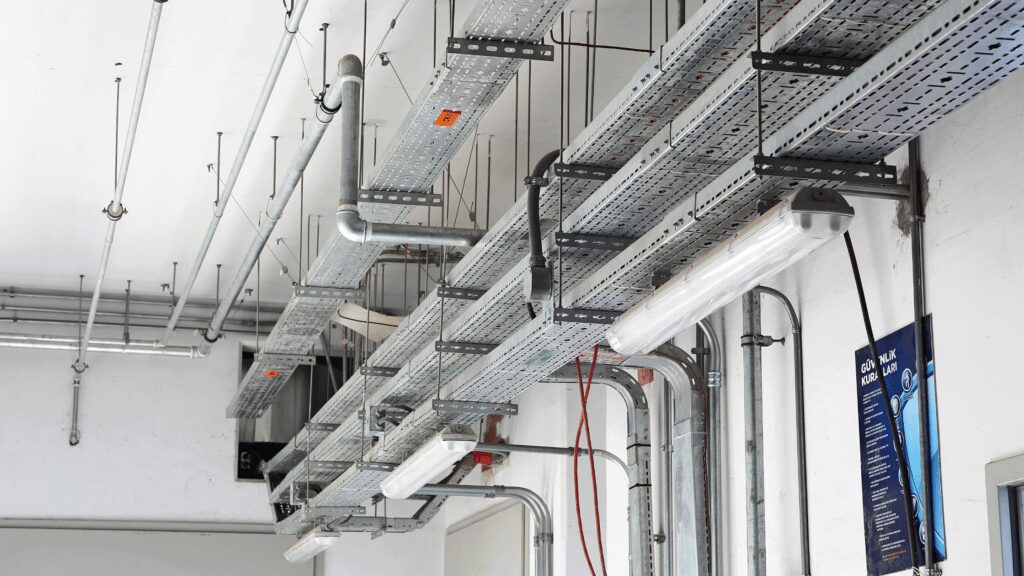

部分封闭: 赛道 电缆托盘 和 表面安装线槽 仅部分封闭,底部敞开或盖子可拆卸。这些设计使电缆接入和修改更加容易,但对外部冲击或环境因素的保护有限。
维护通道:由于滚道通常有 可拆卸盖板,它们是维护的理想选择,因为技术人员可以在不中断系统的情况下快速访问电缆。

导管
全封闭式:管道设计为全封闭系统,具有 密封圆柱形 保护电线免受物理损坏、潮湿和其他环境危害。
持久保护:圆柱形状提供 卓越的物理保护,尤其是在极端条件下的区域(例如工业环境或户外环境)。
4.4 Size and Capacity
滚道
更大容量,适合多根电缆:由于其 更广泛、更开放的设计。 例如, 电缆托盘 或者 电线管道 可以支持 多根电缆 使其成为大规模安装的理想选择。
更多通风空间: Open raceways like 电缆托盘 allow for better ventilation and cooling of cables, reducing the risk of overheating when carrying high-voltage or high-ampacity wiring.

导管
Tighter Capacity: Conduits, being cylindrical, generally have less space for wire management and are more focused on protecting individual conductors.
Amperage Capacity Limits: The interior cross-sectional area of conduits is limited, so proper sizing is essential to prevent overheating or excessive wear on cables. The NEC limits conduit fill to 40% of the internal area to maintain safe operation.
5. Key Considerations for Choosing Between Raceway and Conduit
When designing an electrical system, choosing between raceway and conduit is a crucial decision that impacts both the safety and efficiency of the installation. Both systems are used to protect and route electrical wiring, but they each have distinct features, benefits, and limitations.
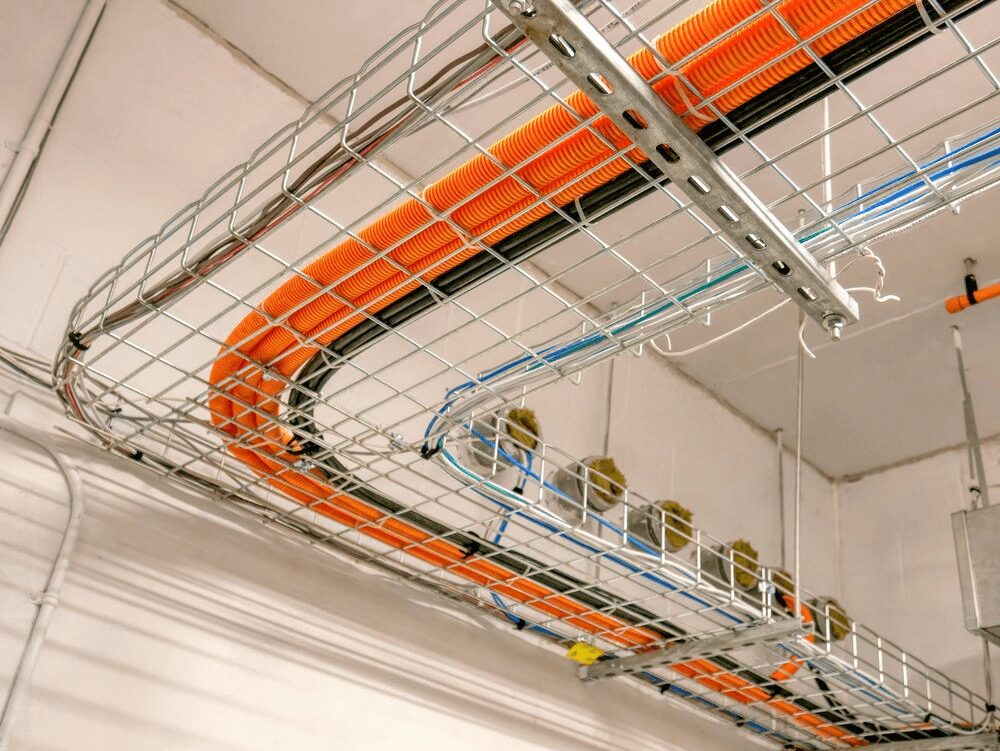

5.1 Type of Installation (Surface vs. Embedded)
One of the primary considerations when choosing between raceway and conduit is whether the installation will be surface-mounted 或者 embedded within a structure. This choice significantly affects both the system’s installation process and its long-term functionality.
滚道: Typically, raceways are used for surface-mounted installations where cables and wires are exposed or organized in a visible manner. Surface raceways, like 线模, are ideal for areas where aesthetics or future accessibility is a priority. They are easy to install, modify, and expand, making them a good option for retrofits 或者 low-voltage systems (e.g., data cabling, telecommunication lines).
Example: In office buildings, 表面安装线槽 are often used to route low-voltage data cables along walls, keeping them organized and easy to access for upgrades or maintenance.
Conduit: Conduits are often used in embedded 或者 in-wall installations, especially when the cables need to be protected from physical damage. Rigid conduits (e.g., RMC 或者 EMT) are ideal for applications where the wiring needs to be safely protected from external forces or environmental conditions.
Example: Electrical conduits are typically used for heavy-duty wiring in industrial applications, where wires are embedded in walls or underground to prevent damage and ensure compliance with safety codes.

5.2 Safety and Compliance with Standards
Safety is a critical consideration when choosing between raceway and conduit. Both systems serve to protect the electrical wires inside, but they provide different levels of protection based on the materials used and their installation environment. It’s also important to ensure compliance with relevant building codes 和 safety standards.
滚道: Raceways offer varying levels of protection depending on the type. For example, 电缆托盘 provide a high level of physical protection for multiple cables but do not fully enclose them, which can expose the cables to dust, moisture, and physical damage. However, raceways like 电线管道 或者 busways are fully enclosed and provide enhanced protection.
Regulations: When using raceways, it is important to check the National Electrical Code (NEC) 和 local regulations to ensure that the wiring system meets safety standards, especially regarding filling capacities and heat dissipation.
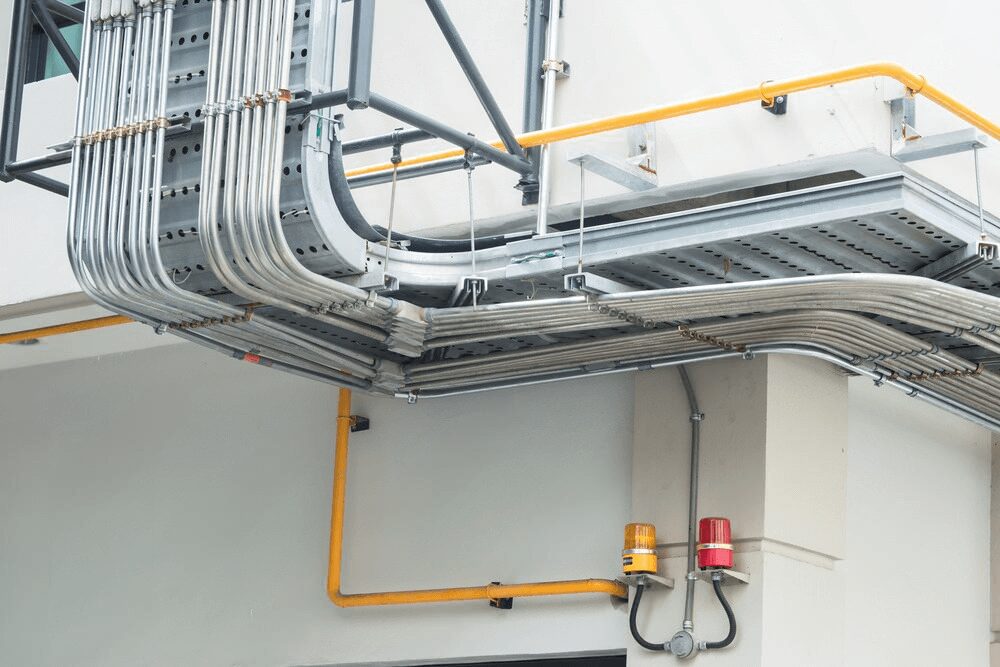

Conduit: Conduits, particularly metallic 和 死板的 varieties, offer superior protection from physical damage, chemical exposure, and environmental hazards. PVC conduit, while less durable than metallic conduit, is still widely used for applications requiring resistance to corrosion 和 moisture protection.
Safety Compliance: Conduit systems, especially for underground 或者 outdoor installations, must comply with NEC regulations, including proper grounding and bonding, to reduce the risk of electrical shock or fire hazards.
5.3 Environmental Conditions (Temperature, Moisture, and Exposure)
The environmental conditions where the wiring system will be installed play a significant role in determining whether a raceway or conduit is the best choice. Factors like temperature, moisture, and chemical exposure will dictate which material and system design is more suitable.
滚道: Raceways are more commonly used in dry 和 indoor environments, where minimal exposure to harsh conditions is expected. For instance, 表面安装线槽 work well in office buildings, residential areas, or areas with low risk of moisture or physical damage. However, in industrial or outdoor environments, raceways may not offer sufficient protection against elements like rain, dust, 或者 extreme temperatures.
Conduit: Conduits are specifically designed for more rugged environments. For example, PVC conduit can be used outdoors or underground, while metallic conduit can handle extreme temperatures, abrasion, 或者 chemical exposure in industrial settings.
Example: In outdoor installations, PVC 或者 HDPE conduit is preferred for applications where moisture resistance 和 durability are crucial, such as underground wiring or installations in wet environments.
5.4 Installation Complexity and Cost
The installation process and associated costs can be significant factors when choosing between raceways and conduits. These factors can depend on the system type, ease of installation, and the overall project budget.
滚道: Raceways, especially surface-mounted types, tend to be easier and faster to install than conduits. For instance, wiremold systems require minimal cutting and are often used for retrofit installations where cables are routed along existing walls. Raceways are typically less expensive and easier to work with, making them suitable for low-budget projects or areas where future modifications are expected.
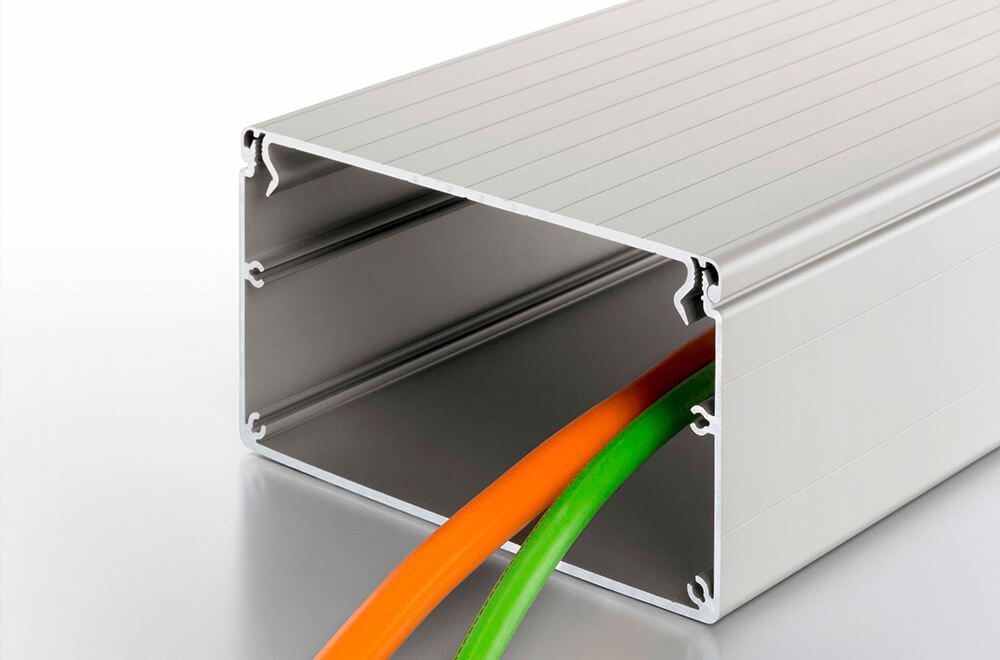

Cost: The initial cost of raceways can be lower than conduit systems, but long-term costs may increase if they need to be modified or if they offer less protection in certain conditions.
Conduit: The installation of 刚性导管 systems can be more labor-intensive 和 time-consuming 与线槽相比。金属导管需要切割、弯曲和穿线,这会增加安装时间和成本。然而,对于 高风险环境 或需要物理保护的地点, 刚性导管 尽管前期成本较高,但仍往往是首选。
劳动力成本:安装 刚性导管 系统,特别是 钢或铝由于装配、穿线和安装的复杂性,可能会显著增加劳动力成本。然而,对于 长期安装,增加的耐用性和保护性可能会证明更高的安装成本是合理的。
5.5 Future Flexibility and Maintenance
确保电气系统的未来发展,以便轻松升级或修改是另一个重要考虑因素。有些系统比其他系统更容易修改或维护,这取决于它们的设计。
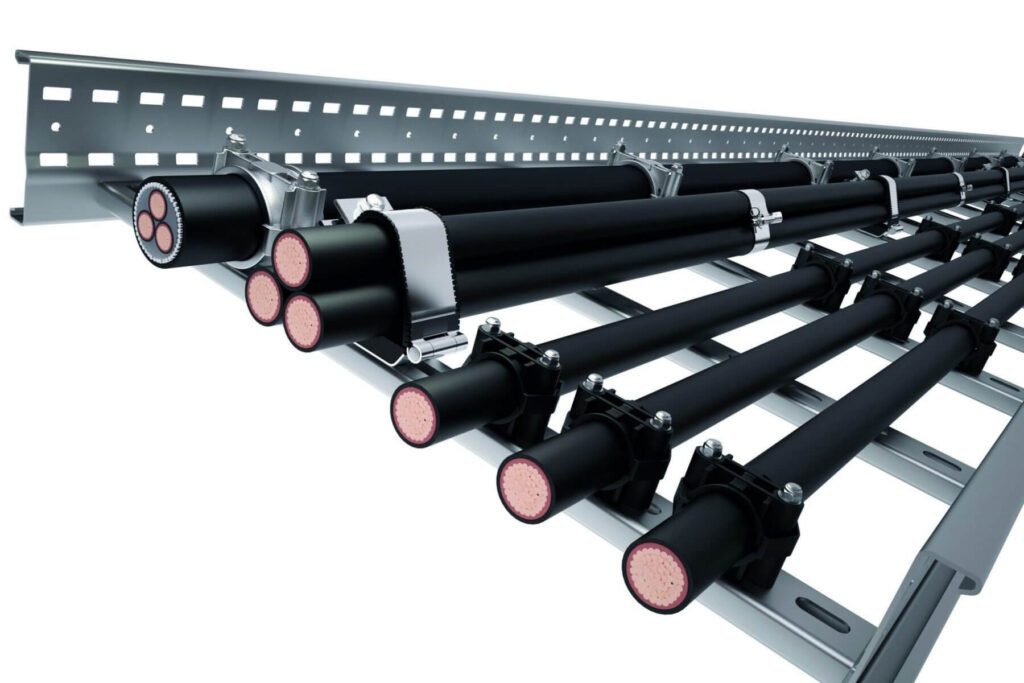

滚道: 跑道的最大优点之一是 灵活性。大多数电缆管道都可以轻松修改、扩展或升级,使其成为未来需要更改或添加的区域的绝佳选择。电缆管道的开放式结构允许快速接入线路,使维护更加轻松快捷。
Example:在办公楼或商业空间中,管道 表面安装线模 可以轻松修改布线路线,而无需对建筑结构进行重大更改。
Conduit:虽然管道系统更 永恒的一旦安装,修改起来就很困难,尤其是对于 刚性类型。 然而, 柔性导管 (例如, 固定模数转换)能够轻松调整布线路径,从而提供更大的灵活性 临时设施 或预计会频繁发生变化的环境。
5.6 Aesthetic and Visibility
在选择管道和导管时,美学因素可能会起到一定作用,尤其是在 商业的 和 住宅 布线系统的外观很重要的空间。
滚道:表面安装的线槽是可见的,通常可以集成到房间的设计中,以尽量减少其外观。许多线槽有各种 颜色 和 完成,让它们融入环境或与装饰相匹配。
Conduit:导管通常不太美观,尤其是在 表面贴装应用。但是,它们为线路提供了卓越的保护,这使得它们成为工业、户外或高风险环境中的首选。
6. 结论
选择电缆槽和导管是一个复杂的决定,取决于一系列因素,包括安装类型、环境条件、安全要求、预算和维护需求。电缆槽通常更容易安装且更具成本效益,通常用于表面安装、低风险应用。另一方面,导管为恶劣环境中的布线提供卓越的保护,通常是地下或墙内安装所必需的。
通过考虑您的电力项目的具体要求(无论是安全性、成本、未来灵活性还是环境因素),您可以在电缆管道和导管之间做出明智的决定,以确保最佳的系统性能和使用寿命。
我们明白,选择正确的电气导管和管道系统对于任何电气安装的成功都至关重要。作为一家位于中国的专业 PVC 导管制造商,Ctube 专注于提供高品质 PVC conduit,以及专为住宅和工业应用而设计的各种配件。

我们的产品在设计时充分考虑了耐用性、灵活性和安装方便性,可提供卓越的保护,防止环境损害、化学物质暴露和温度波动。无论您需要 硬质 PVC 导管, 柔性导管或定制解决方案,Ctube 提供可靠且经济高效的解决方案,以满足您的特定项目需求。
如果您正在寻找最好的电气管道系统以确保安全、高效和合规的安装,Ctube 是您值得信赖的高性能解决方案合作伙伴。
感谢您的阅读,祝您的项目顺利进行。
FAQs
1. 电气管道与导线管有何区别?
电线槽和导管之间的主要区别在于它们的结构和保护级别。电线槽通常是开放式系统,用于组织和布线电缆,而导管则是封闭的管道或管子,可完全保护电缆免受外部损坏。电线槽通常用于表面安装,便于接触电缆,而导管通常埋入或隐藏在墙内以提供额外的保护。
2.电气线槽如何保护电缆?
虽然线槽不像导管那样完全封闭电缆,但它们仍能提供一定的保护,防止电缆受到物理损坏、环境因素(如灰尘和湿气)和意外磨损。例如,电缆托盘或管道可防止电缆缠结,而表面安装的线槽则有助于防止电缆受到周围物体的撞击或磨损。
3.如何安装电气导管?
安装过程可能因导管类型而异,但通常涉及以下步骤:
- 规划路线:绘制管道走向图并测量所需的长度。
- 切割导管:使用钢锯、管道切割机或专用工具将导管切割至所需长度。
- 配件和连接:使用连接器、弯头和接头连接导管各部分。对于刚性导管,配件必须是螺纹的,而柔性导管则需要夹具或连接器。
- 固定导管:使用导管带、夹子或支架将导管固定到墙壁、天花板或地板上。
- 拉电线:安装好导管后,使用鱼带或其他拉线工具小心地将电线拉过导管。




