Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
Electrical conduit fittings are integral to protecting wiring from physical damage, environmental exposure, and other hazards. They not only maintain the integrity of the electrical system but also comply with safety standards across industrial, commercial, and residential applications. PVC conduits, in particular, are favored for their durability, resistance to corrosion, and cost-effectiveness.
Despite serving similar roles in electrical installations, the contrasting design and performance aspects of their conduits fittings can significantly impact their suitability for different applications.
2. Design and Functionality Comparison Between PVC Flexible & Rigid Conduit
2.1 Structural and Material Differences
Both rigid conduit and flexible conduit (ENT) are made from nonmetallic materials derived from polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This ensures a baseline of chemical resistance and durability in moist or corrosive environments.
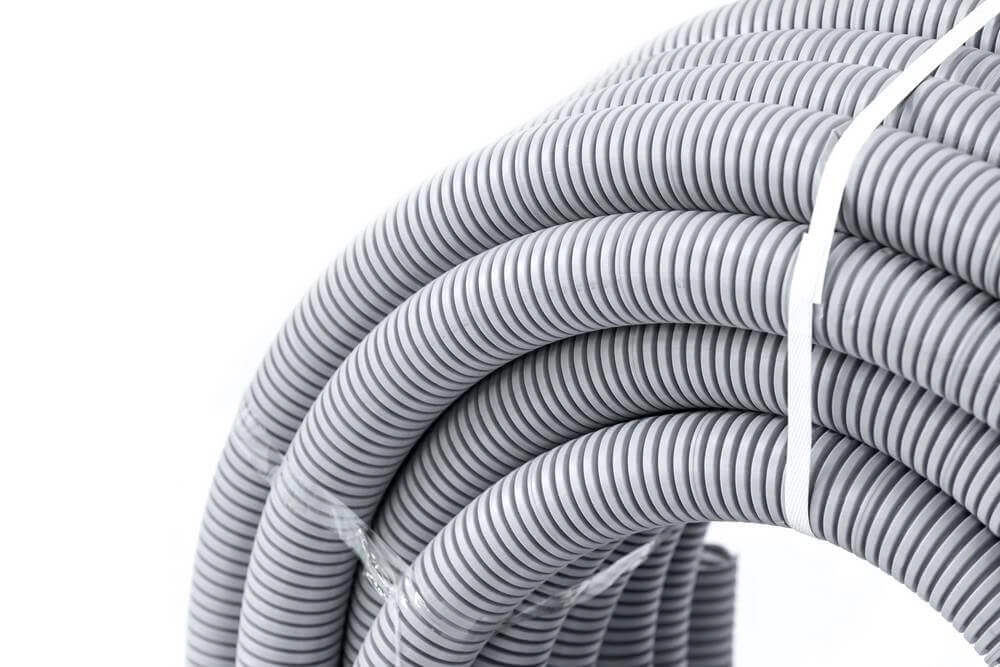
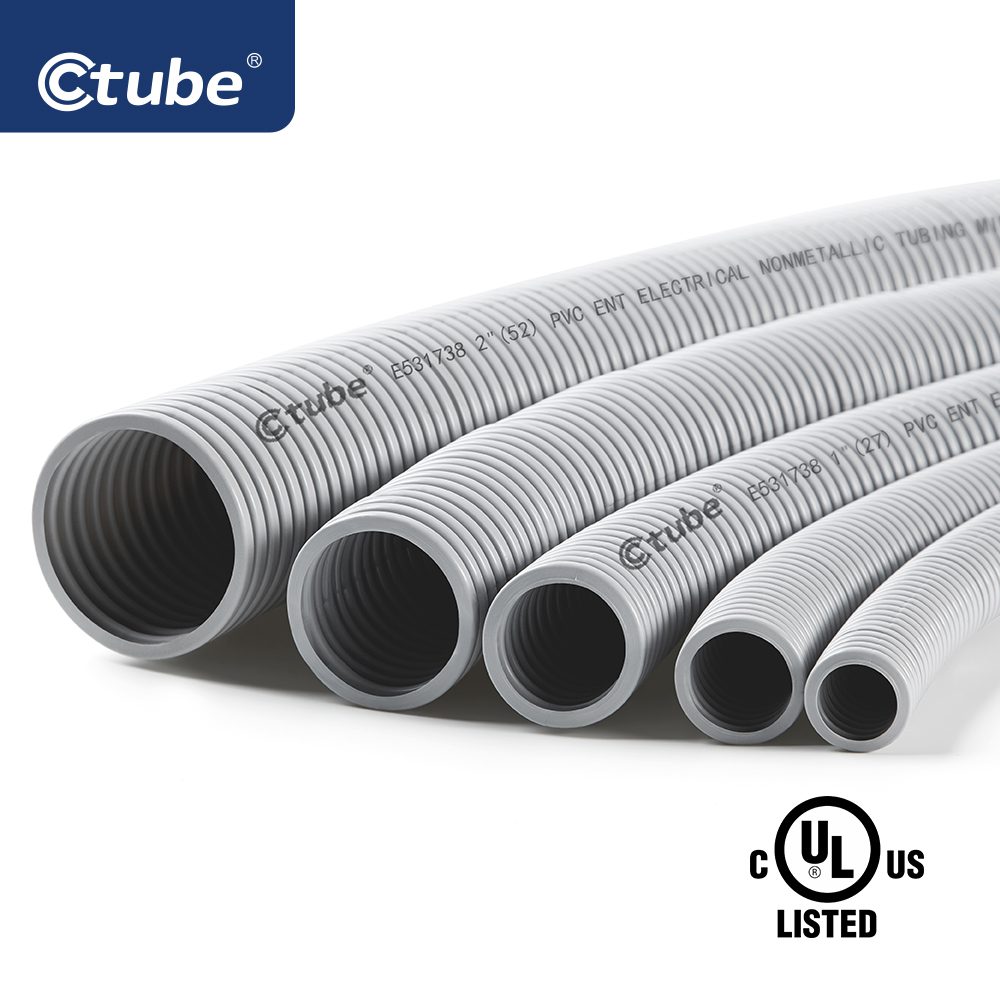
PVC flexible conduit, often referred to as PVC corrugated conduit and recognized in the NEC as Electrical Nonmetallic Tubing (ENT), is defined as a nonmetallic, pliable, corrugated raceway of circular cross section. This flexibility means that the conduit can be bent by hand with reasonable force without the need for additional tools, making it ideal for installations requiring curved or irregular pathways.
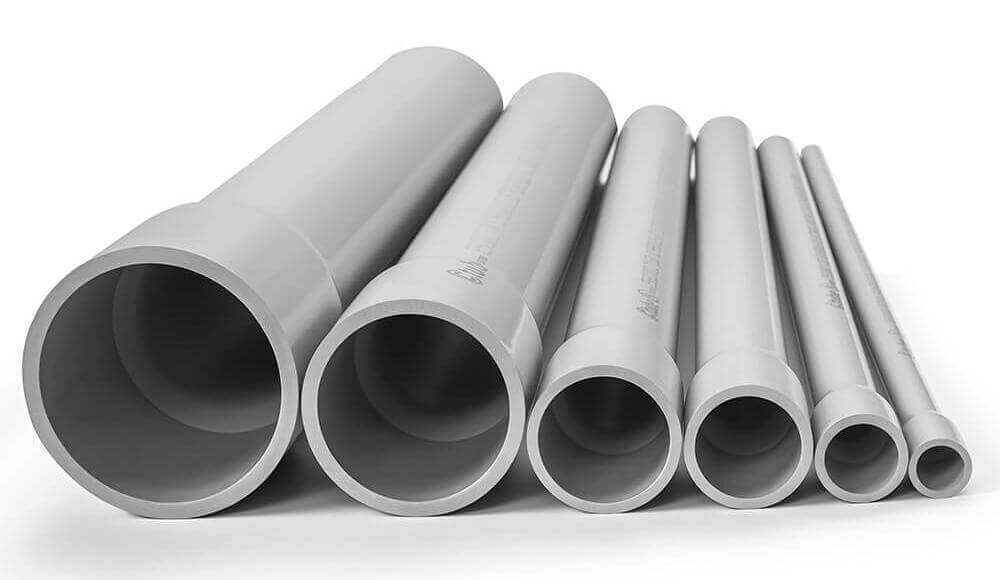
In contrast, PVC rigid conduit is characterized as a rigid nonmetallic raceway of circular cross section, maintaining a firm, unyielding structure that does not allow for easy bending.
This fundamental difference in appearance and mechanical behavior directly influences the design of their respective accessories. For PVC flexible conduit, the accessories must be engineered to accommodate its inherent flexibility and the undulating, corrugated surface. Connectors, couplings, and fittings designed for ENT systems typically incorporate adjustable features, flexible seals, or slip-on designs that can adapt to minor variations in the conduit’s diameter and shape.
Conversely, accessories for PVC rigid conduit are designed with a focus on precision and durability. Because the rigid conduit maintains a uniform, fixed shape, its accessories can utilize standardized, fixed couplings that lock securely in place. The emphasis here is on achieving a robust, permanent connection that can reliably withstand mechanical stresses, vibrations, and impacts without the need for flexibility.
2.2 Performance and Durability
Both PVC conduit systems are engineered for long-term durability under various environmental conditions. For aboveground applications, rigid PVC conduits are designed to withstand extreme conditions by being flame retardant and resistant to impacts, crushing, heat-induced distortion, low temperatures, and sunlight exposure. Flexible conduit (ENT), while meeting the same baseline standards for flame retardancy and chemical resistance, emphasizes ease of installation with its corrugated design.
Rigid PVC Conduit is engineered to withstand continuous loading and can be used for direct burial (without concrete encasement) provided it meets the necessary strength requirements.
According to the National Electrical Code (NEC), ENT is not permitted to be buried directly in the ground. This limitation reflects its design as a flexible, corrugated raceway optimized for aboveground or concealed applications where direct exposure to soil loading is not anticipated.
2.3 PVC Conduit Fittings Requirements
Since fittings are used in conjunction with electrical conduit, they must adhere to the same standards and performance requirements to ensure a secure, code-compliant electrical system. The integrity of an entire conduit system depends not only on the conduit itself but also on the fittings that connect and support it. Improperly designed or mismatched fittings can compromise the performance of the conduit, leading to issues such as reduced mechanical strength, moisture ingress, or poor electrical continuity in grounded systems. Therefore, fittings must be made from materials that match or exceed the durability, corrosion resistance, and environmental protection characteristics of the conduit they accompany.
For example, rigid PVC conduit, which is designed for direct burial, exposure to sunlight, or high-impact resistance, requires fittings that can withstand similar stresses. These fittings must provide secure, watertight, and mechanically strong connections that prevent separation due to thermal expansion, mechanical forces, or underground pressure. Likewise, electrical nonmetallic tubing (ENT) fittings must be compatible with the flexible nature of the conduit, allowing easy installation while maintaining sufficient mechanical retention and protection against contaminants. In both cases, compliance with industry standards such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), UL listings, and ASTM specifications ensures that the entire system functions reliably over its intended lifespan.
Additionally, performance requirements for conduit fittings extend to considerations such as fire resistance, chemical resistance, and ease of installation. Some applications may require specialized fittings, such as expansion joints for accommodating thermal movement in outdoor installations or liquid-tight connectors for areas prone to moisture exposure. By ensuring that conduit fittings meet the same performance criteria as the conduit itself, installers can create a safe, efficient, and durable electrical system that complies with regulatory requirements and withstands the challenges of its operating environment.
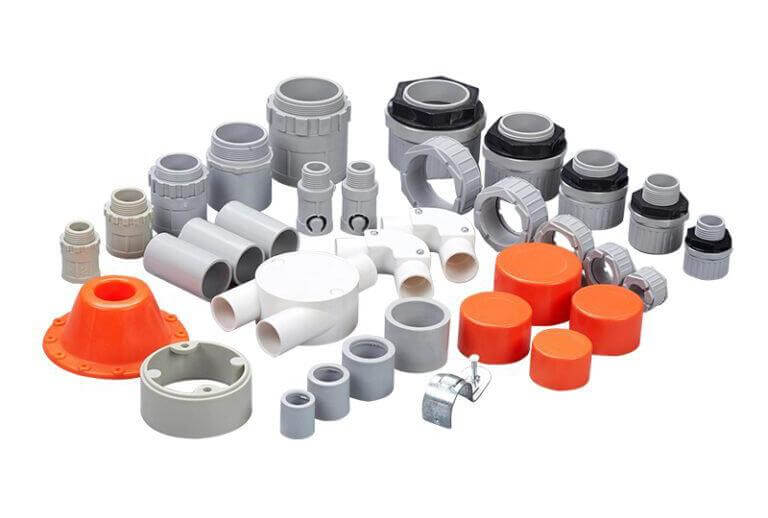
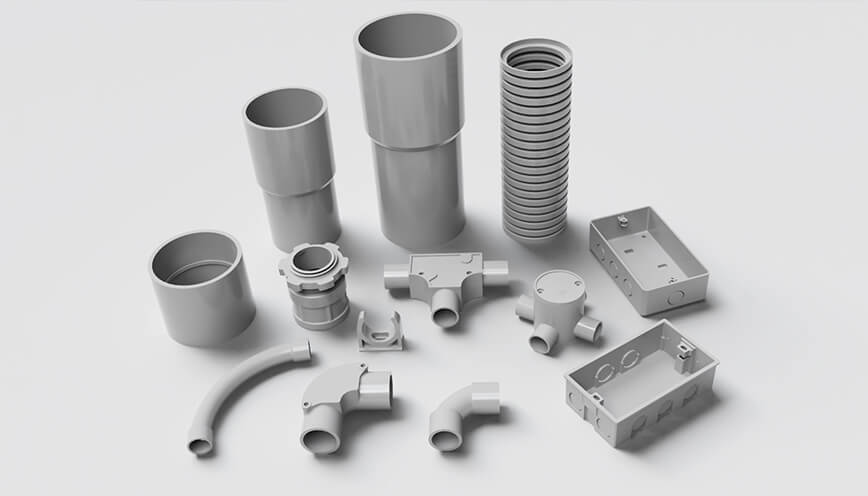
3. Accessories for PVC Rigid Conduit and Flexible Conduit
Both PVC rigid conduit and electrical nonmetallic tubing (ENT) require accessories to complete an electrical raceway system. However, due to their structural differences, the types and quantity of fittings used vary. Rigid conduit, which cannot be bent by hand, relies more on specialized fittings to achieve directional changes, transitions, and secure connections. In contrast, flexible conduit, being naturally pliable, requires fewer bending accessories but still needs appropriate connectors to maintain a secure system. Despite these differences, both types of conduit share some common accessories, although the design and connection mechanisms differ.
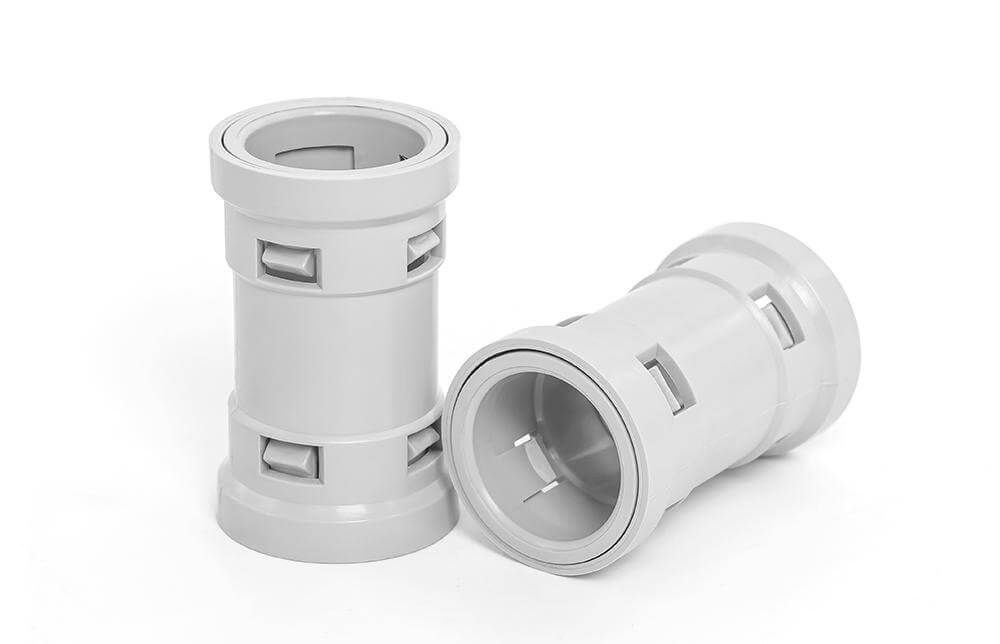
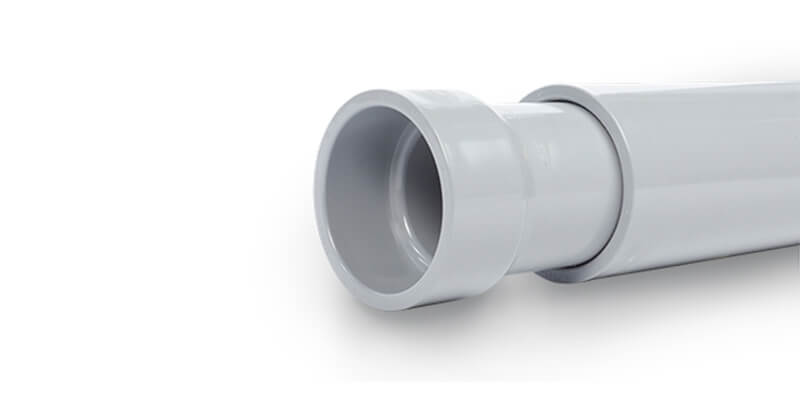
3.1 Couplings (Joining Two Conduit Sections)
3.1.1 Appearance of Couplings for Rigid PVC Conduit
Shape & Structure:
Cylindrical and symmetrical – The coupling has a straight, even shape with smooth outer walls.
Uniform diameter – The interior and exterior maintain a consistent diameter throughout the coupling.
Deep socket design – The inner walls are designed to allow conduit ends to slide in deeply for a secure bond, often with a small internal ridge or stop to prevent over-insertion.
Surface Texture & Finish:
Smooth exterior – The surface is usually clean and free of complex ridges, allowing for easy cement bonding.
Glossy or matte finish – Depending on the manufacturer, the surface may have a slight gloss from the PVC material or a more matte, industrial look.
3.1.2 Appearance of Couplings for Flexible PVC Conduit
Shape & Structure:
More complex, segmented design – Unlike the uniform shape of rigid couplings, flexible conduit couplings may have multiple sections with ridges, slots, or interlocking parts.
Slightly tapered ends – Some couplings have tapered openings to make insertion easier.
Locking tabs or compression rings – Many flexible conduit couplings feature small protruding clips or built-in rings that help secure the conduit in place.
Surface Texture & Finish:
Ribbed or grooved exterior – Instead of a smooth surface, flexible conduit couplings often have indentations, ridges, or locking mechanisms that help with grip and securing the conduit.
Matte or semi-gloss finish – While typically less glossy than rigid PVC couplings, the finish may have a slight shine depending on the material used.
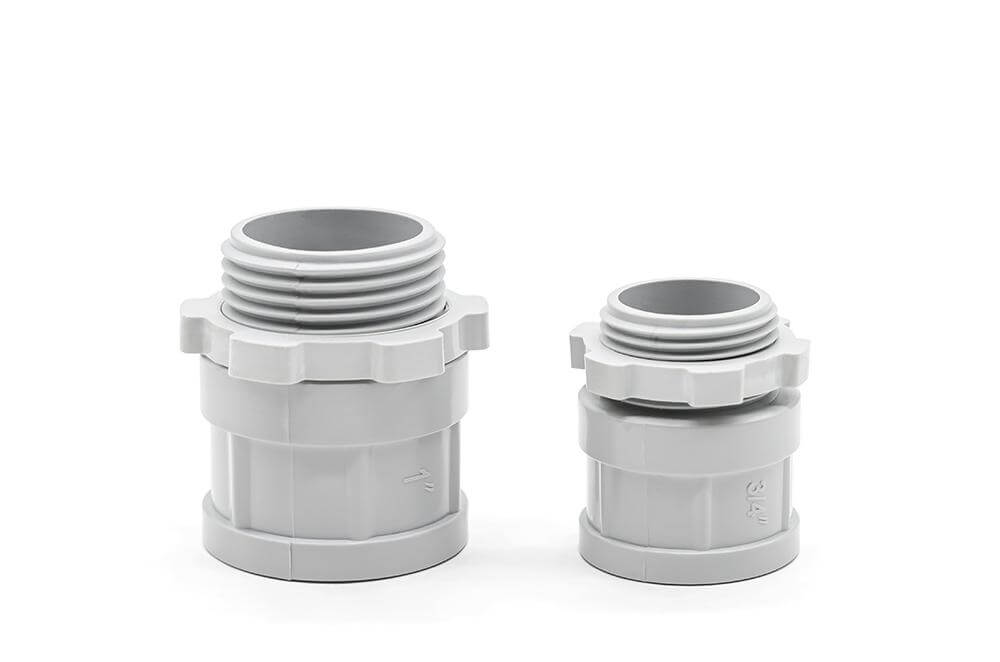
3.2 Male Adapter (Joining Conduit and Electrical Box )
3.2.1 Rigid Conduit Male Adapter
Threaded Section: The threads are shorter, flatter, and uniform, designed to create a precise, tight seal with rigid conduit fittings. The threading pattern ensures secure engagement with metal boxes, couplings, or other conduit components, reducing the risk of loosening over time.
Grip & Locking Ring: The grip area features evenly spaced, low-profile ridges, allowing for a firm hold during installation while keeping the adapter’s profile compact. The locking ring is integrated smoothly into the body without any external flanges, emphasizing a streamlined design for easy insertion into rigid conduit fittings.
Body Design & Reinforcement: The cylindrical body is solid and compact, lacking additional reinforcement ribs or flexible features. Since rigid conduits do not bend or flex, the adapter does not need extra support against movement. This design ensures long-term durability and a strong mechanical connection in permanent installations.
Base Section & Connection Mechanism: The base is flat and smooth, allowing for a direct-fit connection without the need for additional securing elements. This structure is ideal for rigid conduit systems, which rely on their own structural integrity for support.
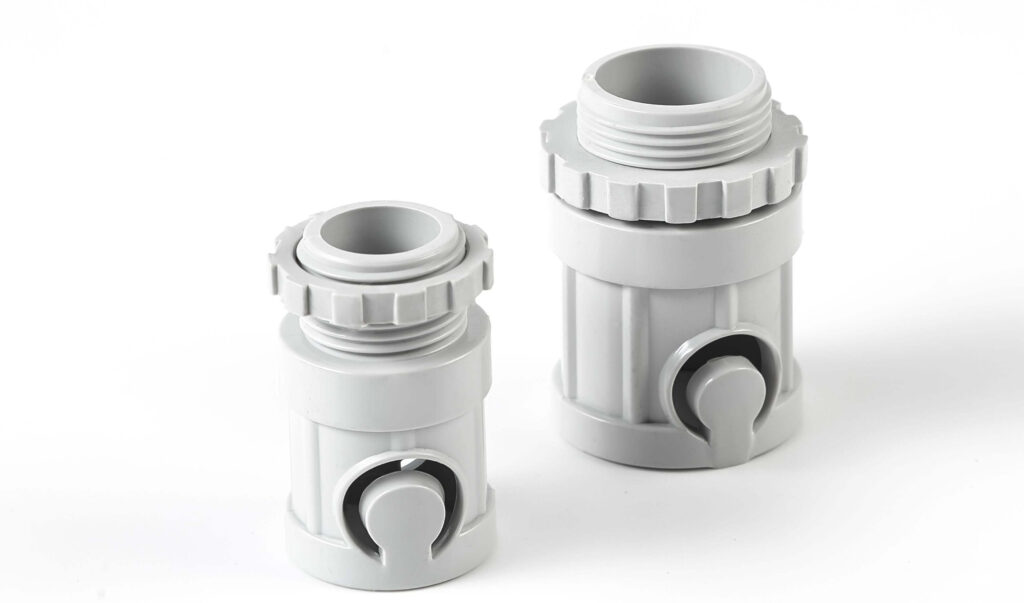
3.2.2 Flexible Conduit Male Adapter
Threaded Section: The threads are taller, more pronounced, and slightly tapered, allowing for a tighter grip on flexible conduit systems. This design helps compensate for small variances in conduit diameter and provides better retention when subjected to movement or vibration.
Grip & Locking Ring: The grip area has deeper, more defined ridges, improving manual tightening and preventing slippage during installation.
Body Design & Reinforcement: The adapter features vertical ribs along its body, enhancing structural strength while maintaining flexibility. These ribs help resist compression while allowing slight movement, making the adapter more adaptable to dynamic installations.
Base Section & Connection Mechanism: The base is curved and contoured, allowing for a flexible yet firm connection with non-metallic flexible conduits. This ensures that the adapter can accommodate subtle conduit movements without becoming loose.
Clamp or Fastening Mechanism: Unlike rigid conduit adapters, the flexible conduit male adapter includes a locking or clamping mechanism, often with a rotating or snap-fit component. This ensures that the flexible conduit remains securely attached even under movement or vibration.
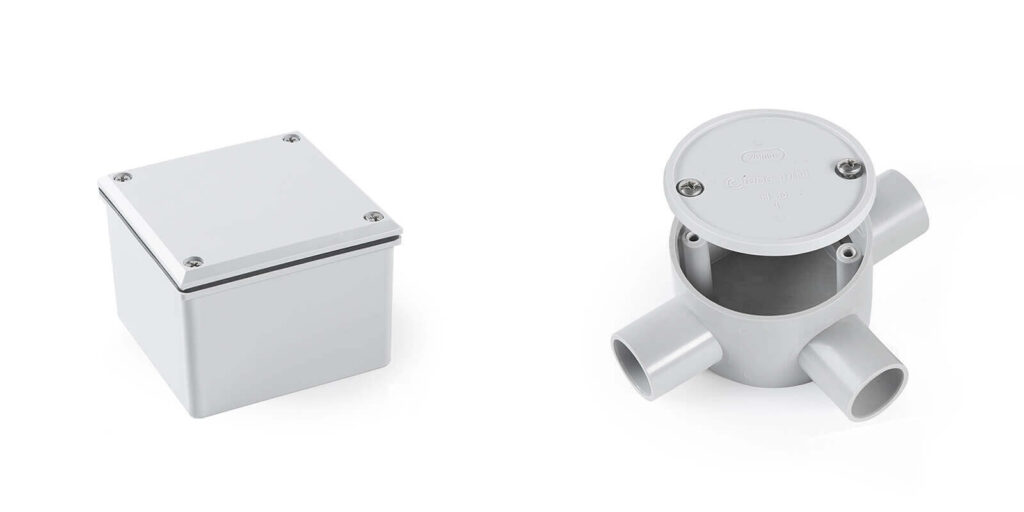
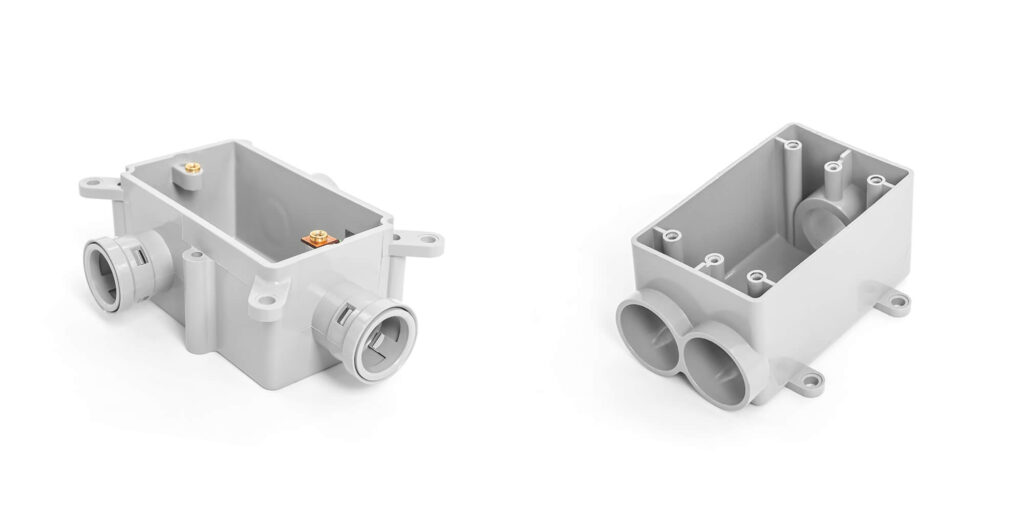
3.3 Electrical Box
These boxes are available in square, rectangular, or round configurations, offering versatility to suit diverse installation requirements. Some disiged to make the circuit. And some designed to accommodate standard electrical sockets or switches, their form factor ensures seamless integration with wall plates or surface-mounted systems. Some electrical boxes are available for both types of conduit,but the different connectors that need to be selected to make the connection.
But some boxes are designed for the specific conduit. A key advantage lies in their pre-molded, fixed entrances, which eliminate the need for additional male adapters. This streamlined design reduces installation time, lowers material costs, and minimizes potential leak points.
Typically paired with square or rectangular boxes, rigid conduits are anchored to the short sides of rectangular models. This alignment ensures structural stability and maintains a clean, linear layout, critical for industrial or exposed installations where precision and durability are prioritized. The fixed entries are often threaded to securely grip metal conduits, preventing movement or dislodgment.
Round or square boxes designed for corrugated or flexible conduits allow entries to be positioned on any side, enabling dynamic routing around obstacles or through tight spaces. The smooth, non-threaded entries accommodate the bending nature of flexible tubing, while reinforced edges prevent abrasion or tearing during installation.
Users can freely select the number of entry/exit points based on project complexity—from simple single-conduit setups to multi-branch systems. For instance, a rectangular rigid conduit box might feature two primary entries on opposing short sides for a straight-through layout, while a round flexible box could include multiple ports around its perimeter for 360-degree routing flexibility.
3.4 Straps and Clamps
Straps and clamps are used to secure conduit to walls, ceilings, or other structural surfaces. They come in various shapes and sizes, but generally feature a curved metal or plastic band that wraps around the conduit.
When fastened with screws or bolts, these accessories keep the conduit neatly aligned and prevent it from sagging or shifting over time. By maintaining proper support at regular intervals, straps and clamps also help protect against vibration and mechanical damage, ensuring the conduit remains stable throughout its service life.
3.5 Plugs and Caps
Plugs and caps are used to seal off unused conduit openings or temporarily close the end of a conduit run. Plugs typically thread into the interior of a conduit or conduit body, while caps fit over the outside. They are invaluable when planning future expansions, as they protect the wiring system from contaminants and physical damage until additional conduit or fittings are installed.
By keeping out water, dust, and debris, plugs and caps help maintain the safety and reliability of the overall electrical setup.
4. Fittings Used for PVC Rigid Conduit
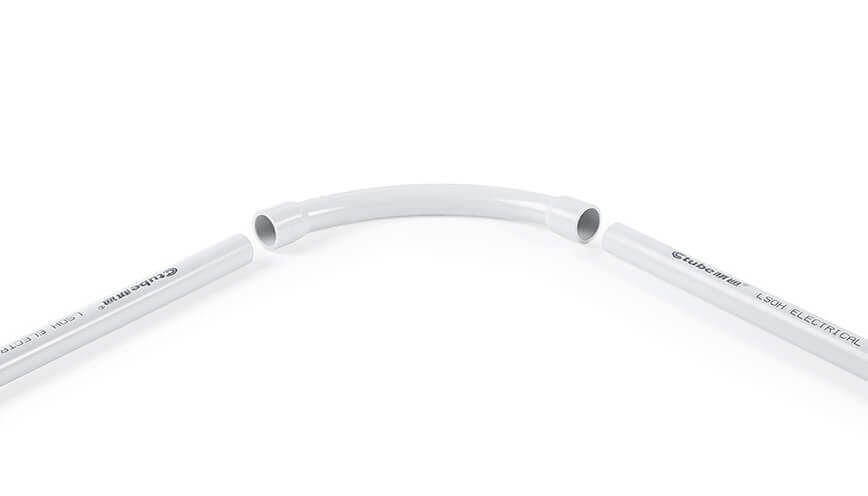
4.1 Elbow
An elbow is a curved fitting designed to change the direction of a rigid conduit run. Common angles include 45°, 90°, and occasionally 22.5°or other angles to accommodate various installation needs.
Elbows help navigate around corners, structural obstacles, or transitions between horizontal and vertical runs. They are typically bell on both ends so they can connect seamlessly with straight sections of rigid conduit, creating a continuous, enclosed path for electrical wiring.
4.2 Sweep Bend
A sweep bend is a type of elbow distinguished by its extended arc, resulting in a gentler curvature than a standard elbow. This elongated radius is especially beneficial in applications where cable pulling is a concern, as the gradual bend reduces friction and the risk of damaging conductors.
Sweep bends are often used in long conduit runs or in situations where frequent wire maintenance or future upgrades are anticipated. The smoother interior surface and wider turn radius can also help prevent cable insulation from chafing, making sweep bends a popular choice in both commercial and industrial settings that require minimal wear on wiring.
4.3 Conduit Body
A conduit body is a compact, enclosed fitting that provides an accessible junction or pull point within a rigid conduit system. It typically features a removable cover, allowing electricians to feed, inspect, and manage wires without having to dismantle significant portions of the conduit run. Conduit bodies come in various shapes—such as LB, LL, LR, T, and C—indicating the direction and number of conduit openings.
Their interior cavity offers enough space to make wire splices or changes in direction, making them invaluable for installations where cables need to navigate tight spaces or complex layouts. By providing a convenient entry point for troubleshooting, conduit bodies help reduce installation time and long-term maintenance costs.
4.4 Expansion Couplings
Expansion couplings are specialized fittings designed to accommodate the natural expansion and contraction of conduit runs caused by temperature changes or building movement. They typically consist of two telescoping sections that slide within each other, allowing the conduit system to lengthen or shorten without placing undue stress on joints or bending the conduit itself.
Expansion couplings are particularly important in outdoor or industrial environments where significant temperature swings can occur, as they prevent cracks or splits that could compromise both structural integrity and electrical safety.
5. Comparison of Standards for PVC Rigid and Flexible Conduit Fittings
The distinction between PVC rigid conduit and flexible corrugated conduit (ENT) is further codified in industry-specific standards, which govern their design, testing, and application to ensure safety and performance.
For instance, UL 651 outlines requirements for rigid PVC conduit and its fittings, emphasizing criteria such as crush resistance, flame retardancy, and suitability for direct burial or outdoor exposure. In contrast, UL 1653 applies specifically to electrical nonmetallic tubing (ENT) and its fittings, focusing on flexibility, bend radius, and resistance to deformation under stress, while explicitly prohibiting direct burial due to insufficient load-bearing capacity.
Similarly, regional standards like AS/NZS 2053.2 (rigid PVC conduit) and AS/NZS 2053.5 (corrugated conduit) reinforce these differences: AS/NZS 2053.2 mandates rigorous mechanical strength and UV stability for rigid systems, whereas AS/NZS 2053.5 prioritizes pliability, moisture resistance, and compatibility with dynamic installations.
These standards ensure that fittings are engineered and tested to address the unique challenges of their respective conduit types.
Choosing fittings aligned with the correct standard mitigates risks such as conduit separation, moisture ingress, or mechanical failure, as mismatched components may lack the structural or environmental resilience required for their intended use. Adherence to these standards not only aligns with regulatory mandates like the NEC but also guarantees that electrical systems meet safety benchmarks, reducing hazards and ensuring long-term reliability in diverse operating conditions.
6. Conclusion
Distinction between PVC flexible (corrugated) conduit fittings and PVC rigid conduit accessories lies in their structural design, application suitability, and performance requirements. While both conduit types are crafted from durable, corrosion-resistant PVC and serve to protect electrical wiring, their inherent physical characteristics dictate vastly different roles in electrical installations. These fundamental differences extend to their respective fittings, which are engineered to complement the unique demands of each conduit type.
Ultimately, the efficacy of an electrical raceway system depends on harmonizing conduit selection with application-specific challenges. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each conduit type—flexible for versatility and rigid for resilience—installers can optimize safety, compliance, and longevity. Whether navigating tight spaces with ENT or anchoring industrial layouts with rigid PVC, the interplay between conduit and fittings ensures reliable protection for electrical systems, balancing innovation with time-tested durability in modern infrastructure.
Ctube is a professional conduit supplier with over ten years of experience in the industry. We specialize in high-quality PVC conduit, solar UPVC conduit, and LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduit, ensuring durability and compliance with industry standards. We offer a full range of conduit fittings, and also provide customization for bulk orders to meet the specific needs of your project. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial applications, Ctube provides reliable solutions for safe and efficient electrical installations. If you have project requirements, feel free to contact us.
Thank you for your reading and good luck with your projects.