Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction to LSZH Conduits
In today’s world, the demand for safer, more sustainable construction materials is growing rapidly. One such innovation revolutionizing the electrical industry is LSZH conduits, which stands for Low Smoke Zero Halogen conduits. These conduits are designed to prioritize safety and environmental considerations without compromising performance.
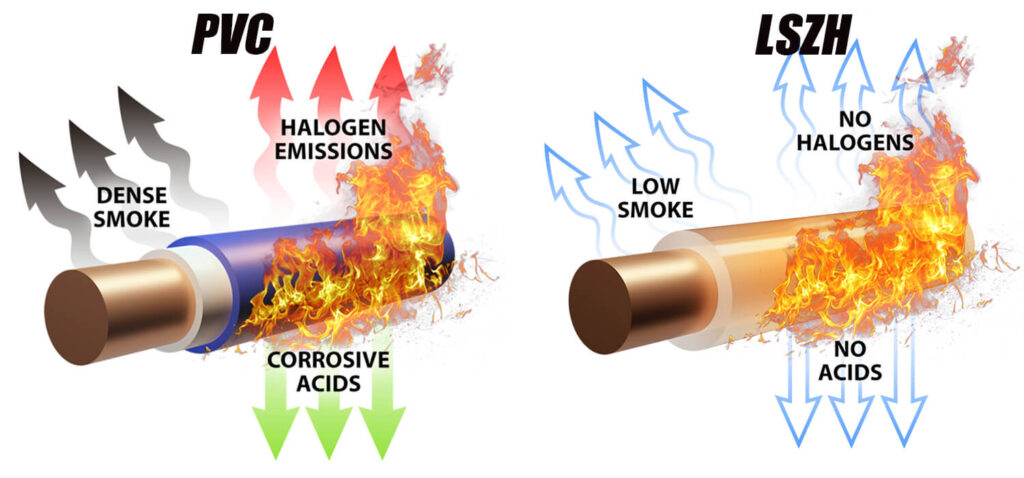
When traditional PVC conduits burn, they release harmful halogens and thick smoke, posing serious health risks and complicating evacuation during emergencies. In contrast, LSZH conduits are engineered to emit minimal smoke and no toxic halogen gases during combustion, making them a preferred choice for safety-critical applications.
1.1 The Importance of Material Innovation
Material innovation plays a crucial role in modern electrical conduit systems, especially as industries face stricter safety regulations and growing expectations for sustainability. LSZH conduits exemplify how advancements in material science can meet these challenges head-on. They provide solutions to long-standing problems associated with traditional materials, such as smoke toxicity and environmental impact.
This post aims to showcase why LSZH conduits are superior to traditional PVC conduits by exploring their unique characteristics and key benefits. From enhanced fire safety to eco-friendly properties, LSZH conduits are a forward-looking solution for industries that value safety, compliance, and sustainability. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding of how LSZH conduits can redefine safety standards in various applications.

2. What Are LSZH Conduits?
Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) conduits are a type of electrical conduit material specifically engineered to enhance fire safety in various environments. They are designed to offer superior performance compared to traditional PVC conduits, primarily by reducing harmful emissions during a fire and ensuring safer conditions for evacuation and firefighting operations. In this article, we will explore what LSZH conduits are, how they work, and why they are increasingly preferred in critical environments.
2.1 Definition and Composition of LSZH Materials
LSZH conduits are made from materials that produce minimal smoke and no halogen gases (such as chlorine, fluorine, and bromine) when exposed to fire. These materials are usually thermoplastics that contain inorganic fillers, most commonly aluminum trihydrate (ALTH), which helps in fire retardation. When exposed to high temperatures, ALTH undergoes an endothermic reaction that absorbs heat and releases water vapor (steam). This process helps to cool the surrounding area, disrupt combustion, and form a protective char layer that prevents the spread of flames.
This composition makes LSZH conduits not only fire-resistant but also significantly safer than traditional conduits. Unlike standard materials, LSZH conduits produce no toxic or corrosive gases, and their low smoke density helps maintain visibility and breathable air during a fire. These features make LSZH materials crucial in spaces where safety is paramount, such as public transportation systems, healthcare facilities, and offshore platforms.
2.2 Understanding LSZH, LSOH, and Other Names
LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) and LSOH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) are terms often used interchangeably, but they are closely related in terms of their properties. Both refer to materials used in electrical conduits and cables that produce minimal smoke and no halogen gases when burned, significantly enhancing safety during a fire.
LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen): This term refers to materials that emit a low amount of smoke and are free from halogenated compounds (such as chlorine, fluorine, bromine, and iodine). These materials are commonly used in environments where fire safety is critical, such as public transport systems, hospitals, and high-rise buildings. The absence of halogens ensures that toxic gases like hydrogen chloride or hydrogen fluoride are not produced during combustion, which can otherwise cause severe health risks.
LSOH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen): LSOH is essentially another way to refer to LSZH materials. In many cases, these terms are used interchangeably, especially in the context of cable and conduit products. LSOH materials offer the same benefits as LSZH, such as low smoke density and the prevention of halogen gas emissions during combustion. The terminology difference often comes from regional preferences or specific industry standards.
Other name for reference:
Zero Halogen (ZH): Refers to materials that are free from halogens, minimizing toxic gas emissions during fires.
Low Smoke Halogen-Free (LSHF): Highlights both low smoke emission and the absence of halogens, often used in public infrastructure.
Low Smoke Zero Halogen Free (LS0HF): Emphasizes low smoke and halogen-free properties, commonly used in critical environments like nuclear plants.
Halogen-Free (HF): Describes materials without halogens, often paired with other fire-safety features like low smoke or flame retardance.
Flame-Retardant Low Smoke (FRLS): Combines flame resistance and low smoke emission, used in high-risk applications like aerospace.
Fire-Resistant, Low Smoke (FRLS): Focuses on materials that resist fire and emit minimal smoke, ensuring continued operation during fires.
Non-Halogenated (NH): Refers to materials free of halogen compounds, often low-smoke, but requires verification of other fire-safety features.
Polymeric Low Smoke Zero Halogen (PLSZH): Materials made from polymers that are both low in smoke and free of halogens, offering flexibility and fire safety.
3. Key Characteristics of Low Smoke Halogen Free Conduits
3.1 How LSZH Conduits Emit Less Smoke During Combustion
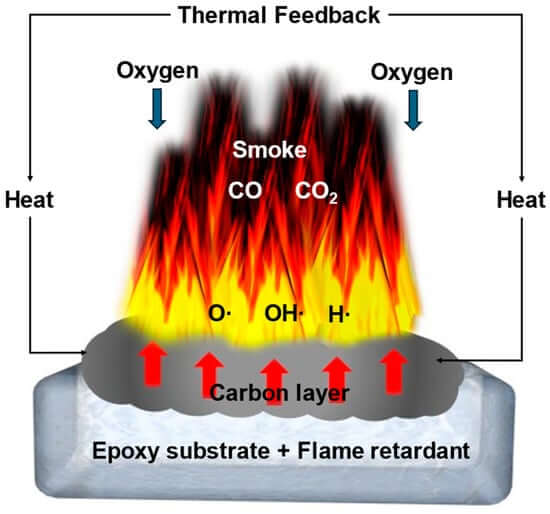
One of the standout features of Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) conduits is their ability to produce significantly less smoke during combustion compared to traditional materials like PVC. This characteristic is crucial for maintaining visibility and ensuring the safety of individuals during emergencies, especially in environments where evacuation or firefighting operations may be challenging.
When materials burn, they release smoke as a byproduct of the combustion process. The composition of the material, including its chemical makeup and the presence of various fillers, plays a significant role in determining how much smoke is produced. In the case of LSZH conduits, these materials are specially designed to emit minimal smoke when exposed to fire.
Aluminum Trihydrate (ALTH): A key component of LSZH materials is aluminum trihydrate (ALTH), an inorganic filler used to enhance fire resistance. When LSZH conduits catch fire, the ALTH undergoes an endothermic reaction, absorbing heat and releasing water vapor (steam). This steam disrupts the combustion process, preventing the material from burning as easily and reducing the smoke generated.
Zero Halogen Emission: Traditional materials like PVC release halogen gases when they burn, which contribute to the formation of dense, toxic smoke. LSZH materials are free from halogens, meaning they do not emit harmful gases like chlorine, bromine, or fluorine. This halogen-free nature prevents the generation of thick, opaque smoke that can make it difficult to see during a fire, which is a significant safety risk in confined spaces.
Char Formation: In addition to producing steam, the aluminum trihydrate in LSZH conduits also helps form a char layer on the surface of the material during combustion. This char layer acts as a protective barrier, reducing the spread of fire and further limiting smoke emissions. The char traps particulates and prevents the release of additional smoke and gases into the environment.
3.2 Why Halogen-Free Composition and Materials Matter for Safety
The composition of a material plays a significant role in determining its behavior during a fire. One of the standout features of Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) conduits is their halogen-free composition, which directly impacts their safety and performance in fire situations.
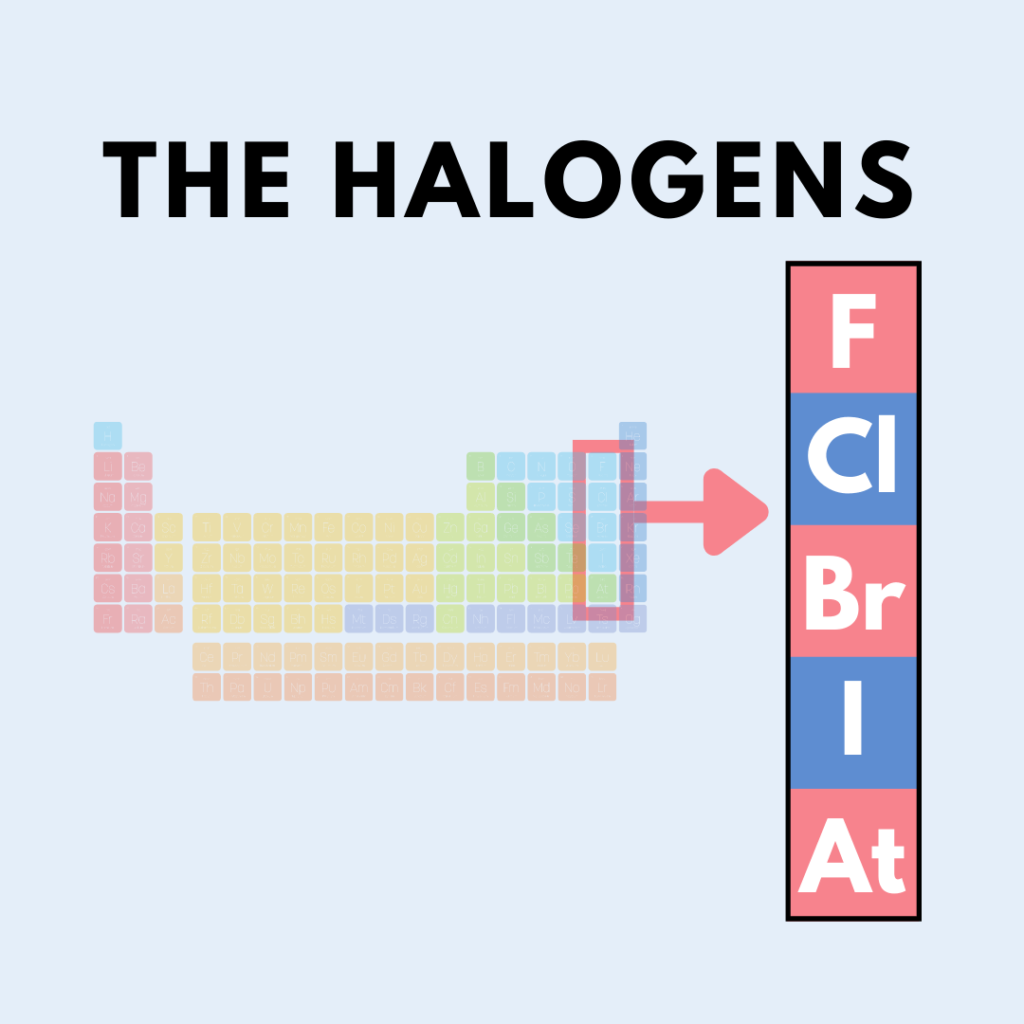
The term “halogen” refers to a group of chemical elements in the periodic table that includes fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. These elements are commonly used in manufacturing various products, including plastics, cables, and coatings, due to their ability to enhance certain properties like flame resistance. However, the presence of halogens in materials, especially when exposed to fire, poses significant safety hazards. In contrast, halogen-free materials, such as LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) materials, are designed to eliminate these dangers, offering a safer alternative in fire-prone environments.
Halogens are often added to materials as flame retardants to reduce the risk of ignition. When exposed to high temperatures, halogens can react with other compounds in the material, forming free radicals that inhibit the combustion process. This helps to delay the ignition of the material. However, the benefits of halogens in flame retardancy come at a significant cost during a fire:
Toxic Gas Emissions: When materials containing halogens, like PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), catch fire, they release harmful gases such as hydrogen chloride (HCl), hydrogen fluoride (HF), and hydrobromic acid (HBr). These gases can be toxic, corrosive, and extremely dangerous to human health and the environment. For example, hydrogen chloride, when mixed with moisture (such as in the respiratory system), forms hydrochloric acid, which can cause severe damage to the lungs and eyes.
Corrosive Effects: Halogenated gases are not only toxic but also corrosive, posing risks to both people and equipment. When released during a fire, these gases can corrode metal components, leading to long-term damage to electrical systems, machinery, and other sensitive infrastructure. In environments like data centers, aircraft, and nuclear plants, where sensitive electronics and equipment are crucial, this can be disastrous.
Obscured Visibility: Halogenated materials, especially when burning, produce thick, black smoke that significantly reduces visibility in an emergency. This makes it harder for occupants to escape and for firefighters to navigate the affected area. The dense smoke is not only visually impairing but also harmful to the respiratory system.
3.3 Flame-Retardant Properties of LSZH Conduits
One of the standout characteristics of Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) conduits is their enhanced fire safety performance, which is largely attributed to their flame-retardant properties. In fire-prone environments, particularly in enclosed or densely populated spaces, ensuring that cables and conduits do not contribute to the spread of fire is crucial. LSZH conduits, with their high level of flame resistance, play a vital role in protecting lives and property during a fire.
LSZH conduits are specifically designed to meet high fire safety standards, making them an ideal choice for installations in areas where fire resistance is a top priority. Unlike traditional PVC conduits, which can burn rapidly and contribute to the spread of fire, LSZH materials are treated to provide excellent flame resistance and slow down the progression of flames.
The flame-retardant properties of LSZH conduits are a result of their carefully engineered composition. LSZH materials typically include inorganic fillers such as aluminum trihydrate (ATH), which serves a dual purpose during a fire. ATH acts as a flame retardant by releasing water vapor and cooling the surrounding area when heated, effectively suppressing the flames and limiting their spread. Additionally, these materials are formulated to form a char layer upon combustion, which acts as a barrier to further flame penetration and helps protect the surrounding structures.
Low Flame Spread: LSZH conduits are designed to resist the spread of flames along their surface, ensuring that fire does not travel rapidly through electrical wiring or conduit systems.
Self-Extinguishing Behavior: Once the source of fire is removed, LSZH conduits tend to self-extinguish more rapidly than traditional PVC, which can continue to burn even after the external flame source has been eliminated.
Reduced Combustion Risk: The combination of inorganic fillers and non-halogenated materials significantly reduces the amount of fuel available for combustion, minimizing the overall fire load and risk of a fire spreading.
3.4 Eco-friendly Composition and Disposal Benefits
As the world increasingly turns toward sustainability, the environmental impact of building materials has become a critical consideration. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits stand out as a more eco-friendly option in the electrical conduit market, thanks to their environmentally conscious composition and their role in supporting sustainable building practices.
One of the defining features of LSZH conduits is their halogen-free composition. Unlike traditional PVC conduits, which contain halogens like chlorine and can release toxic gases when burned, LSZH materials are made using non-halogenated materials, significantly reducing the environmental and health hazards associated with their disposal and burning.
Halogen-Free Materials: The absence of halogens, such as chlorine, means that LSZH conduits do not produce toxic gases like hydrogen chloride when they are exposed to fire. In contrast, halogenated materials like PVC can emit poisonous gases such as dioxins and furans, which are harmful to both humans and the environment. By opting for LSZH materials, the potential for pollution from these dangerous substances is significantly reduced, making them a safer choice for both the environment and human health.
Non-Toxic Emissions: When burned, LSZH conduits release significantly fewer toxic fumes compared to traditional PVC. This not only reduces the health risks for individuals in proximity to a fire but also minimizes the environmental damage caused by the release of harmful chemicals into the atmosphere. This makes LSZH conduits a much more environmentally responsible option, especially in areas where air quality is a concern.
Recyclability: Many LSZH materials are designed to be more recyclable than their PVC counterparts. Although recycling infrastructure for LSZH is still evolving in some regions, the absence of halogens and other hazardous chemicals makes these conduits easier to recycle and reprocess. This contributes to the overall reduction of landfill waste and supports a circular economy in the construction and electrical industries.
3.5 Adherence to Global Safety Standards and Certifications
In today’s rapidly evolving construction and electrical industries, adhering to global safety standards and ensuring that infrastructure is future-ready are crucial elements for both safety and longevity. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits are increasingly recognized for their ability to meet and exceed these requirements, making them an excellent choice for modern electrical systems.
LSZH conduits are specifically designed to meet the stringent safety regulations that govern building materials and electrical systems worldwide. These regulations ensure that materials used in construction not only perform optimally but also pose minimal risk to human health and the environment. LSZH materials are compliant with various international safety standards and certifications, making them a reliable choice for a variety of industries.
Fire Safety Standards: One of the primary concerns when selecting materials for electrical installations is fire safety. LSZH conduits excel in this area by meeting or exceeding international standards for flame retardancy and smoke suppression. For example, LSZH materials adhere to safety standards like:
- IEC 61034: A standard for testing smoke density in cables and conduit materials.
- IEC 60332-1: Ensures that cables and their sheaths (including conduits) are resistant to flame propagation when exposed to fire.
- UL 94: A widely recognized standard for determining the flammability of plastic materials, ensuring that LSZH conduits do not ignite or burn easily under certain conditions.
Halogen-Free Certifications: As LSZH conduits are halogen-free, they comply with several important standards related to toxic gas emission reduction. The most notable of these certifications are:
- RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): An important European Union directive that restricts the use of certain hazardous materials, including halogens, in electrical and electronic products. LSZH conduits are designed to meet RoHS compliance requirements, ensuring they are free from harmful substances.
- CE Marking: This certification signifies that LSZH materials comply with European health, safety, and environmental protection regulations.
Environmental Standards: In addition to fire safety and halogen-free certifications, LSZH conduits meet various environmental standards, ensuring they are manufactured with minimal ecological impact. They comply with:
- ISO 14001: This international standard outlines the criteria for an effective environmental management system. Manufacturers of LSZH conduits often adhere to this standard, demonstrating their commitment to sustainability in their production processes.
Building Codes and Industry-Specific Regulations: In many sectors, including the nuclear, transportation, and military industries, stringent regulations govern the use of materials for safety-critical applications. LSZH conduits are frequently specified for use in high-risk environments where fire safety and reduced smoke emissions are paramount. The railway industry and submarine installations, for instance, require materials that comply with DEF STAN 02-711 (UK military standard) and ASTM E662 (for measuring smoke density), both of which LSZH conduits meet.
4. LSZH vs Traditional PVC Conduit, Challenges and Considerations for Conduit Choosing
To provide a quick reference for the key differences between LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) and Traditional PVC conduits, we have created a comparison table below. This table highlights the features, benefits, and drawbacks of each material to help professionals make informed decisions based on their project requirements.
| Feature | LSZH Conduit | Traditional PVC Conduit |
| Smoke Emission | Low smoke emission during combustion, improves visibility and safety in fires | High smoke emission, can obscure visibility during fires |
| Halogen Content | Zero halogen (no chlorine, bromine, or iodine) | Contains halogens (e.g., chlorine), which release toxic gases when burned |
| Toxicity of Gases | No toxic or corrosive gases released during combustion | Releases toxic gases, including hydrochloric acid and hydrogen chloride |
| Fire Resistance | Flame-retardant, helps prevent the spread of fire | Flame-retardant |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, less environmental harm due to halogen-free composition | Higher environmental impact due to halogen content and greater smoke output |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized materials and manufacturing process | Lower cost, more affordable for large-scale installations |
While LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits offer significant advantages in terms of safety, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance, there are some challenges and considerations that need to be addressed before they can be fully integrated into electrical projects.
Higher Cost One of the primary challenges associated with LSZH conduits is their higher cost compared to traditional PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduits. The production of LSZH materials involves the use of specialized compounds and additives, such as aluminum trihydrate for flame retardancy, which can make them more expensive. Additionally, the manufacturing processes required to ensure the material’s low smoke and halogen-free properties are more intricate, further driving up the price.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations LSZH conduits may not be as widely available as traditional PVC conduits, especially in certain regions or specific markets. While demand for fire-safe and environmentally friendly materials is growing, limited supply or reliance on specialized suppliers can sometimes result in delays or increased lead times.
5. Applications of Low Smoke Halogen Free Conduits
Healthcare Facilities: Hospitals and medical centers demand the highest safety standards to protect patients, staff, and critical equipment. LSZH conduits are a preferred choice for these facilities as they reduce toxic gas emissions and smoke during fires, ensuring safer evacuation. Additionally, their non-corrosive properties protect sensitive medical devices and wiring systems, making them indispensable in operating rooms, intensive care units, and emergency power systems.
Data Centers: Data centers house high-value servers and networking equipment, where fire-related damage can lead to catastrophic data loss and operational downtime. LSZH conduits provide superior fire resistance and prevent the spread of corrosive gases, protecting IT infrastructure and maintaining the integrity of data systems. Their adoption ensures compliance with strict fire safety regulations, offering peace of mind to businesses that depend on uninterrupted data access.
Transportation Systems: Modern transportation networks, including railways, subways, and airports, rely on LSZH conduits for their safety and durability. These conduits are used extensively in tunnels, control rooms, and signaling systems. In confined spaces, their low smoke emission and absence of toxic halogens significantly enhance passenger and worker safety, facilitating clear evacuation routes and protecting critical infrastructure.
Residential and Commercial Buildings: In high-density residential complexes and commercial buildings, LSZH conduits are increasingly replacing traditional PVC to meet stricter building codes. They are ideal for electrical and networking installations, as they reduce the risk of fire hazards and contribute to a healthier indoor environment. Architects and contractors prioritize LSZH conduits for green building certifications and future-proofing properties.
Airports: Airports are bustling hubs where fire safety is paramount. LSZH conduits are integral to electrical and communication systems in terminals, baggage handling zones, and control towers. Their low-smoke and halogen-free properties ensure safe evacuation and prevent damage to critical aviation systems, such as radar and navigation equipment, ensuring uninterrupted operations even in emergencies.
Schools and Educational Institutions: Safety in schools and universities is critical, particularly in protecting children and staff. LSZH conduits are widely used in these facilities to minimize risks during fires. They emit less smoke and avoid releasing harmful halogens, ensuring better air quality and visibility for safe evacuations. LSZH conduits also align with sustainability goals, promoting safer and eco-friendlier building practices in education.
Industrial and Manufacturing Plants: Factories and manufacturing facilities often house flammable materials and high-energy equipment, necessitating robust fire safety measures. LSZH conduits are employed to safeguard electrical wiring in hazardous zones. Their flame-retardant properties reduce the risk of fire spread, while their resistance to corrosive gases ensures the longevity of industrial control systems, even in harsh environments.
6. Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving world, ensuring safety and sustainability in infrastructure is more important than ever. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits stand out as a critical solution for reducing fire-related risks, protecting human lives, and minimizing environmental impact. Their low smoke emission, halogen-free composition, and enhanced fire safety performance make them an essential choice for industries prioritizing health, safety, and eco-conscious practices.
Ctube is a trusted manufacturer specializing in high-quality PVC conduits and fittings designed to meet the needs of various industries. From PVC conduit like Schedule 40 and 80 conduits to Low-Smoke Halogen-Free (LSZH) conduits for enhanced fire safety, Ctube delivers innovative and sustainable solutions. Our product range includes durable and UV-resistant solar conduits, flexible conduits, and a variety of fittings such as elbows, couplings, and electrical boxes—all rigorously tested for reliability and compliance with international standards like UL, CSA, ASTM, AS/NZS 2053.
Thanks for your reading, and good luck with your projects.
FAQs
1. Can Ctube’s conduits be customized for specific projects?
Absolutely. Ctube offers customization options for sizes, colors, and designs, ensuring that our conduits and fittings are tailored to meet the specific requirements of your project. Whether you’re working on a residential, commercial, or industrial installation, we can provide a solution that fits your needs.
2. Are Ctube’s products certified for safety and quality?
Yes, all Ctube products are rigorously tested and comply with international safety and quality standards, including UL, ASTM, and AS/NZS 2053. We ensure that our products meet the highest performance standards, offering reliable solutions for all your electrical conduit needs.
3. How do I order Ctube products for my project?
You can easily order Ctube products by visiting our website or contacting our sales team directly. We offer competitive pricing and timely delivery for both small and large-scale projects, with full support throughout the ordering process.