Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
Air quality in educational and healthcare facilities directly impacts survival rates during fires. Vulnerable populations (children, patients, and the elderly) face heightened risks due to underdeveloped or compromised respiratory systems.
Fire-related smog is a major threat to human health, often causing more harm than burns. In the UK, over 180,000 fires were recorded in England by September 2022, leading to 276 deaths. While burns are visible injuries, smoke inhalation silently affects the entire body, accounting for 50% to 80% of fire-related fatalities. Toxic gases like carbon monoxide and hydrogen cyanide make smog especially dangerous, leading to suffocation, organ failure, and long-term respiratory diseases. Experts estimate that 73% of fire survivors suffer from chronic conditions such as COPD, emphysema, and asthma. The devastating effects of smog highlight the urgent need for awareness and protection.
Enter LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits: a revolutionary solution designed to mitigate risks during fires. Unlike traditional materials, LSZH conduits minimize toxic emissions, ensuring safer evacuation routes and cleaner air. This makes them indispensable for schools and hospitals, where compliance with fire safety and air quality regulations is non-negotiable.
2. Background on LSZH Technology
LSZH, which stands for Low Smoke Zero Halogen, is an innovative conduit technology specifically developed to enhance safety in environments where air quality and occupant health are of paramount concern. This chapter delves into the core characteristics of LSZH, its historical evolution, the scientific principles behind its performance, and how it compares to traditional conduit materials.
2.1 Definition and Core Characteristics
LSZH conduits are engineered to emit minimal smoke and no halogenated compounds when exposed to high temperatures, such as during a fire. The term “low smoke” refers to the conduit’s ability to produce substantially less smoke compared to conventional materials, while “zero halogen” indicates that the material is free from halogen elements like chlorine, fluorine, bromine, or iodine. This is crucial because, when ignited, halogenated compounds can produce highly corrosive and toxic gases, posing severe risks to both health and property.
The material composition of LSZH conduits typically involves specialized polymers that have been modified with flame retardants and smoke suppressants. These polymers are carefully engineered to maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions while ensuring that, in the event of a fire, the emissions are non-toxic and non-corrosive. The design principles focus on achieving an optimal balance between durability, flexibility, and environmental safety. Manufacturers often incorporate additives that enhance the physical properties of the polymer, ensuring that the conduit performs reliably over its service life in demanding installations.
2.2 Historical Development and Evolution
The evolution of LSZH technology is marked by a series of milestones that reflect the growing need for safer building materials, particularly in sectors where human safety is critical. Initially developed during the late 20th century, LSZH conduits emerged from research into fire safety and material science aimed at addressing the shortcomings of traditional halogenated materials. Early versions of these conduits were primarily used in niche applications; however, as awareness of the health risks associated with toxic smoke increased, the adoption of LSZH expanded rapidly.
In the early 2000s, regulatory bodies began to implement stricter standards for fire safety and indoor air quality, particularly in public buildings such as schools and hospitals. This regulatory shift acted as a catalyst for innovation in the field, with manufacturers investing heavily in R&D to improve the performance and cost-effectiveness of LSZH materials. Over the years, key innovations in polymer chemistry and extrusion technologies have led to more robust and versatile LSZH conduits that now meet, and often exceed, the rigorous demands of modern safety codes.
2.3 Scientific Mechanisms and Material Science of LSZH Conduits
LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits are engineered to provide superior fire safety, minimal smoke production, and reduced toxicity, making them an ideal choice for schools, hospitals, and enclosed public spaces. To fully understand their benefits, it’s essential to examine the scientific mechanisms behind their fire resistance and the material composition that makes them different from traditional PVC or metal conduits.
2.3.1 The Chemistry Behind LSZH Conduits
The defining feature of LSZH conduits is their halogen-free polymer composition. Unlike traditional PVC, which contains chlorine, LSZH conduits are made from specialized thermoplastic compounds that do not produce toxic halogenated gases when burned.
LSZH materials replace halogen-based additives with halogen-free flame retardants, such as magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) and aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)₃).
These additives absorb heat and release water vapor when exposed to high temperatures, acting as a cooling and fire-suppressing mechanism.
This process delays combustion, reduces heat release, and prevents flame spread.
2.3.2 Smoke Suppression and Low Toxicity Mechanisms
Another key benefit of LSZH conduits is their low smoke emission, which is crucial in ensuring clear evacuation routes during fires.
Reduced Carbon Content: LSZH materials contain fewer carbon-rich compounds, resulting in less smoke production during combustion.
Charring Effect: Instead of producing dense black smoke like PVC, LSZH conduits form a char layer that insulates the material underneath, further preventing heat penetration.
Non-Corrosive Combustion Byproducts: Unlike PVC, which releases acidic gases (HCl), LSZH conduits generate only small amounts of water vapor and non-toxic carbon-based residues, making them safer for both people and electronic equipment.
Scientific Advantage: Studies show that in an enclosed space, smoke inhalation accounts for over 80% of fire-related fatalities. LSZH conduits significantly reduce this risk by limiting smoke and toxic gas production.
2.3.3 Material Properties: Strength, Flexibility, and Durability
LSZH conduits are formulated to balance mechanical strength, flexibility, and longevity, making them suitable for diverse applications in sensitive environments.
Mechanical Strength and Impact Resistance
LSZH conduits are engineered with high tensile strength, preventing cracks and fractures under mechanical stress.
They maintain impact resistance even in cold temperatures, unlike traditional PVC, which becomes brittle over time.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
The polymer composition allows LSZH conduits to be bendable without breaking, simplifying installation in complex wiring systems.
Unlike metal conduits, which require specialized bending tools, LSZH conduits can be shaped manually or with basic tools.
Thermal Stability and UV Resistance
LSZH conduits maintain their integrity in extreme temperatures, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
Many LSZH formulations include UV stabilizers, preventing degradation from prolonged sun exposure, a major issue with untreated PVC.
2.4 Comparison with Traditional Conduits: PVC vs. Metal vs. LSZH
Traditional conduit materials, such as PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and metal conduits (steel or aluminum), have been widely used in electrical installations for decades. While these materials provide durability and protection for electrical wiring, they have significant drawbacks when it comes to fire safety, air quality, and environmental impact. LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) conduits address these concerns by offering a safer, more sustainable alternative.
2.4.1 LSZH vs. PVC Conduit
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) is one of the most commonly used conduit materials due to its affordability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation. However, it has significant safety drawbacks when exposed to fire:
High Smoke and Toxicity Risks: When burned, PVC emits large amounts of black smoke and releases toxic halogen gases, particularly chlorine gas. This gas reacts with moisture in the air to form hydrochloric acid, which can cause severe respiratory problems and corrode nearby equipment.
Flammability Issues: PVC conduits can sustain combustion, meaning that once ignited, they continue to burn and contribute to fire spread.
Brittle Over Time: Prolonged exposure to UV radiation or extreme temperatures can cause PVC to degrade and become brittle, increasing the likelihood of cracking.
2.4.2 LSZH vs. Metal Conduit
Metal conduits, including steel and aluminum, are widely used in commercial and industrial applications due to their strength and durability. However, they also have several disadvantages compared to LSZH conduits:
Heavy and Difficult to Install: Metal conduits are significantly heavier than LSZH, requiring additional labor and specialized tools for installation.
High Conductivity of Heat: Metal conduits can become extremely hot in case of a fire, potentially igniting surrounding materials or increasing the risk of burns during emergency situations.
Corrosion Issues: Although galvanized steel and aluminum are resistant to corrosion, they are not entirely immune. In humid or chemically aggressive environments (e.g., hospitals with sterilization chemicals), metal conduits can degrade over time.
Cost: The material and labor costs for installing metal conduits are higher compared to LSZH or PVC alternatives.
2.5 Application in Schools and Hospitals
2.5.1 Safeguarding Classroom Environments
Schools are dynamic environments where safety risks multiply due to high occupancy, diverse activities, and aging infrastructure. LSZH conduits address these challenges by integrating seamlessly into critical zones.
Science Labs and Workshops: Flammable chemicals, Bunsen burners, and electrical equipment create fire hazards. LSZH conduits prevent toxic smoke from spreading during incidents, protecting students and staff.
Libraries and Data Centers: Paper-rich libraries and server rooms are prone to electrical fires. LSZH’s flame-retardant properties prevent fire escalation, while low smoke emission preserves irreplaceable books and tech infrastructure.
High-Occupancy Areas (Auditoriums, Cafeterias): Crowded spaces require rapid evacuation. LSZH’s minimal smoke output ensures visibility, while halogen-free materials eliminate choking hazards from toxic fumes.
2.5.2 Enhancing Safety in Hospital Facilities
Hospitals require the highest level of fire safety and air quality control due to the vulnerability of patients, the presence of life-supporting equipment, and strict health regulations. LSZH conduits play a crucial role in ensuring a safe and compliant healthcare environment.
Critical Care Units and Patient Rooms: In intensive care units (ICUs), neonatal care, and patient recovery areas, maintaining clean air is paramount. Traditional conduits can release toxic fumes if exposed to high heat, compromising patient health. LSZH conduits mitigate this risk by preventing hazardous emissions, ensuring a safer atmosphere for patients, healthcare workers, and visitors.
Emergency Exits and Evacuation Routes: In the event of a fire, emergency exits and hallways must remain clear and safe for evacuation. Traditional conduits can contribute to smoke accumulation, reducing visibility and increasing panic. LSZH conduits significantly lower smoke production, ensuring that escape routes remain navigable and safe for patients and hospital personnel.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Labs: Hospitals house advanced imaging equipment, including MRI and CT scanners, which require intricate electrical and data cabling. LSZH conduits provide superior cable protection while preventing interference and maintaining fire-resistant properties, ensuring operational continuity in diagnostic departments.
3. Selecting the Appropriate LSZH Conduit Type
As we mentioned above, selecting the appropriate Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH) conduit is crucial in schools and hospitals, where fire safety, air quality, and long-term durability must be prioritized. LSZH conduits significantly reduce the emission of toxic gases and smoke in the event of a fire, making them essential for enclosed public spaces.
These conduits are available in various configurations, incorporating fire-resistant additives, liquid-tight coatings, and metal reinforcements to enhance their mechanical, thermal, and environmental performance, and we will make a brief introduce in the following.
3.1 Standard LSZH Conduits (General-Purpose Use)
Standard LSZH conduits serve as the foundation for electrical installations in buildings where fire safety and air quality control are primary concerns. They are manufactured from thermoplastic compounds engineered to resist ignition and limit smoke release in case of fire. Within this category, conduits are further divided into rigid LSZH conduits and flexible LSZH conduits, each suited to specific installation requirements.
3.1.1 Rigid LSZH Conduit
Rigid LSZH conduits are designed for permanent installations that require strong mechanical protection and stable conduit routing. They are constructed from high-strength halogen-free polymer materials that provide excellent resistance to impact, compression, and mechanical stress. These conduits are ideal for embedded wall installations, ceiling-mounted electrical infrastructure, and underground applications where durability is a key concern.
The primary advantage of rigid LSZH conduits is their ability to protect electrical wiring from external forces while maintaining a fixed pathway for cables. This ensures long-term reliability and minimizes the risk of conduit displacement or damage due to environmental factors.
3.1.2 Flexible LSZH Conduit
Flexible LSZH conduits are designed to accommodate electrical systems that require adaptability and ease of installation. Unlike rigid conduits, flexible variants allow for movement and bending without compromising their fire-retardant and low-smoke properties. They are typically manufactured from specialized halogen-free polymer composites that provide a balance between flexibility and durability.
These conduits are particularly useful in dynamic environments where electrical installations must navigate confined spaces, machinery, or modular structures. Their ability to bend and conform to complex layouts makes them suitable for use in medical equipment wiring, temporary installations, and retrofit applications in older buildings.
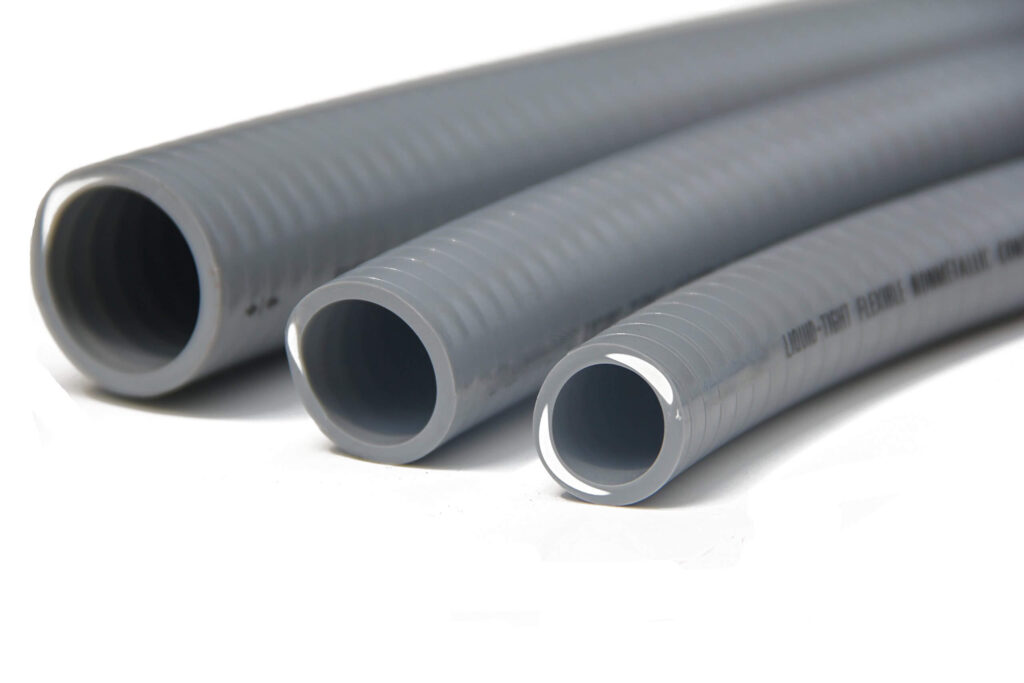
3.2 Liquid-Tight and Corrosion-Resistant LSZH Flexible Conduits
Liquid-tight and corrosion-resistant LSZH flexible conduits are designed to provide superior protection against moisture, chemical exposure, and environmental contaminants. These conduits feature a sealed, liquid-tight outer sheath that prevents water and chemical ingress, making them highly resistant to humidity, cleaning agents, and other corrosive substances. Unlike standard LSZH conduits, this variant incorporates a reinforced polymer structure that enhances its flexibility while maintaining its protective barrier against external elements.
These conduits do not typically contain a metal core, ensuring high flexibility for installations in confined or irregular spaces. The LSZH composition ensures compliance with fire safety regulations by limiting smoke and toxic gas emissions in case of combustion, making them suitable for sensitive environments such as hospitals and educational facilities.
These conduits are ideal for environments where moisture and chemical exposure are significant concerns. In hospitals, they are commonly used in sterilization rooms, laboratories, and operating theaters, where frequent cleaning and disinfection take place. In schools, they are suitable for outdoor installations, underground wiring, and kitchens, where exposure to humidity, cleaning agents, and temperature fluctuations can affect conventional conduit materials. Their flexibility allows for easy installation in confined spaces while maintaining a high level of fire safety compliance.
3.3 LSZH Metal-Reinforced Conduits
LSZH metal-reinforced conduits combine the fire-resistant and low-toxicity benefits of LSZH polymer coatings with the added mechanical strength of an internal galvanized steel or aluminum core. This construction provides significantly enhanced impact resistance while maintaining compliance with strict air quality standards.
Unlike purely flexible liquid-tight LSZH conduits, metal-reinforced conduits are designed for installations requiring additional structural support. The galvanized steel core offers superior durability and rigidity, making it suitable for high-traffic areas or environments with potential physical impact. In contrast, aluminum-core variants provide a lightweight alternative while maintaining excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for overhead or suspended conduit installations.
Designed for environments requiring enhanced structural protection, LSZH metal-reinforced conduits are widely used in hospital emergency departments, ICU units, and MRI rooms, where shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is essential. In schools, they are beneficial in high-traffic areas, gymnasiums, and industrial training facilities, where mechanical impact resistance is necessary. Their reinforced structure ensures durability, while the LSZH coating provides fire safety and compliance with strict air quality regulations.
4. Ensuring Safety and Compliance with LSZH Conduits in Schools and Hospitals
4.1 Compliance with National and International Standards
For LSZH conduits to be deemed suitable for installation in schools and hospitals, they must meet a variety of national and international safety standards. These standards focus on fire resistance, smoke emission, material toxicity, and overall system durability, ensuring that the conduits do not compromise the safety of the environment in the event of a fire or other hazardous situations.
NEC (National Electrical Code): In the United States, the NEC provides guidelines for the installation of electrical systems, including the use of LSZH conduits. The code emphasizes fire safety and dictates that conduits must be non-combustible or low-smoke-producing to minimize risks during an emergency.
IEC Standards: The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) provides global standards for electrical installations. LSZH conduits must comply with IEC 61034 (for smoke density) and IEC 60754 (for halogen gas emissions), which ensure that these materials will not emit harmful gases or smoke when exposed to heat.
UL (Underwriters Laboratories): UL certification is a critical indicator that the LSZH conduit has passed rigorous testing for flame resistance, mechanical strength, and overall electrical safety. LSZH products often carry UL 94 certification to indicate their flame-retardant properties.
4.2 Fire Safety and Smoke Emission Standards
One of the primary advantages of LSZH conduits is their ability to limit smoke and toxic gas emissions in the event of a fire. This feature is crucial in the safety of schools and hospitals, where large numbers of people may need to evacuate quickly in the event of an emergency.
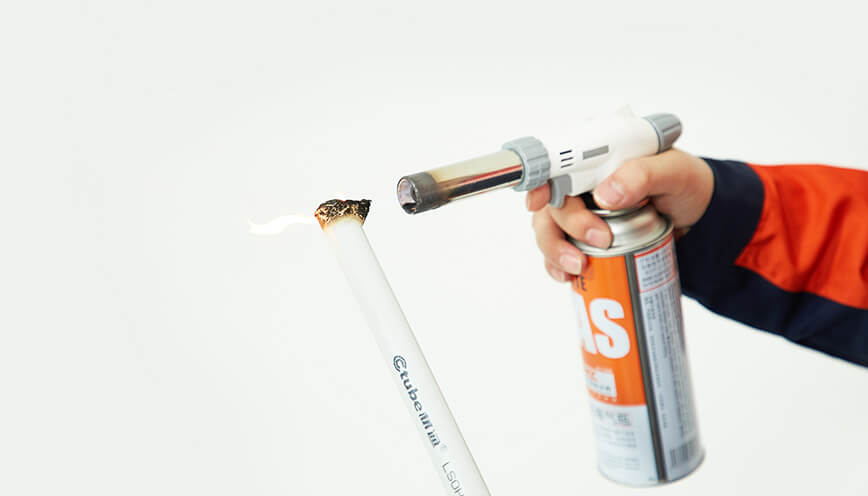
Fire Resistance and Smoke Density: LSZH conduits are specifically designed to minimize the production of smoke when exposed to fire. The materials used in LSZH conduits do not produce harmful gases like hydrogen chloride (HCl) or chlorine, which are common in standard PVC products. This makes LSZH conduits highly suitable for environments where human health is at risk, such as schools and hospitals.
Temperature Rating and Fire Resistance: LSZH conduits typically have a high-temperature resistance, often rated up to 90°C (194°F). These conduits are resistant to combustion and can withstand the high heat generated in fires, allowing electrical systems to continue functioning until evacuation is complete.
4.3 Environmental and Health Regulations
In addition to fire safety, LSZH conduits are often selected for their compliance with environmental and health standards, ensuring that installations do not contribute to harmful pollution or long-term health hazards.
RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances): LSZH conduits typically comply with the European Union’s RoHS directive, which limits the use of hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in electrical equipment. This standard ensures that LSZH conduits contribute to a safer, more sustainable environment.
Low Toxicity and Halogen-Free Composition: The halogen-free composition of LSZH conduits ensures that, in the event of combustion, no toxic halogenated compounds are released into the environment. This reduces the risk of harmful fumes that can affect both first responders and building occupants.
5. Installation Best Practices for LSZH Conduits in Schools and Hospitals
5.1 Planning and Design Considerations for LSZH Conduit Systems
The planning stage is crucial when designing an LSZH conduit system. It ensures that the system meets the specific electrical and safety needs of the facility, while also complying with local codes and regulations.
Conducting a Site Assessment: Before installation begins, it is essential to perform a thorough site assessment. This involves evaluating the building’s layout, identifying areas that require electrical conduit, and assessing environmental factors such as moisture levels and temperature extremes. For schools and hospitals, special attention must be paid to areas like classrooms, operating rooms, laboratories, and patient care areas, which have specific electrical system requirements.
Choosing the Right LSZH Conduit Type: Based on the site assessment, the appropriate type of LSZH conduit must be selected. For example, flexible LSZH conduits are often more suitable for installations in tight spaces, while rigid LSZH conduits may be ideal for areas where more robust protection is required. Additionally, environmental factors such as exposure to chemicals, moisture, or high-impact areas may dictate the use of more specialized conduits like liquid-tight or metal-reinforced LSZH conduits.
Routing and Layout Design: The routing of LSZH conduits should be designed to minimize interference with other systems such as HVAC, plumbing, and fire suppression systems. In hospitals, where space is limited and functionality is critical, careful planning ensures that the conduit system does not obstruct pathways, create potential hazards, or limit access for maintenance and upgrades.
5.2 Installation Process for LSZH Conduits
Once the planning phase is complete, the installation of LSZH conduits can proceed. Installers should follow these best practices to ensure the conduit system is installed correctly and efficiently:
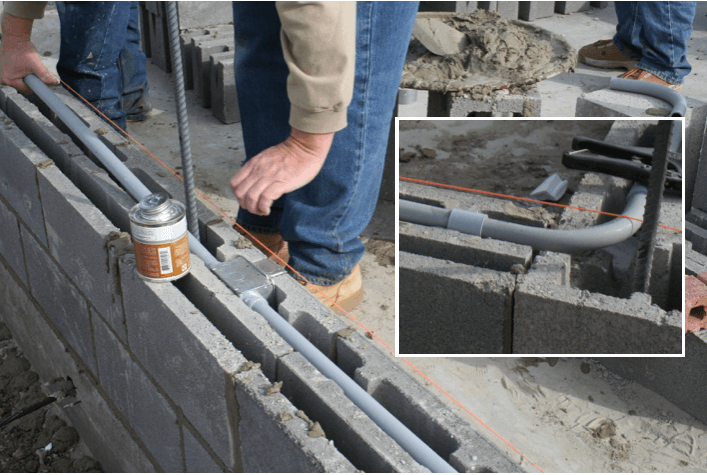
Cutting and Preparing LSZH Conduits: LSZH conduits are relatively easy to cut using standard PVC cutters or hacksaws for rigid conduits, while flexible conduits can be cut with specialized tools. Installers should ensure that the ends of the conduits are smooth and free of burrs to facilitate proper fittings and prevent potential damage to the cables inside.
Connecting LSZH Conduits: Proper connections are essential for a secure and reliable conduit system. Use compatible fittings such as elbows, couplings, and adapters to join segments of conduit. In flexible LSZH conduit installations, connectors should be securely tightened to prevent water or chemical ingress. For rigid conduit systems, solvent cement or mechanical couplings are often used to create tight, permanent connections. Care must be taken to ensure that the connections are aligned correctly to prevent strain on the conduit and cables.
Sealing and Weatherproofing: In areas exposed to external conditions, such as outdoor installations or areas prone to water exposure, sealing the conduits is essential. Seals or gaskets may be required at connection points to ensure water-tightness and prevent moisture from entering the conduit system. This is particularly important for applications in environments like hospital outdoor areas, where protection from water damage is crucial.
5.3 Testing and Quality Assurance
After the LSZH conduit system is installed, it is essential to perform thorough testing to ensure that the installation meets all relevant safety and performance standards.
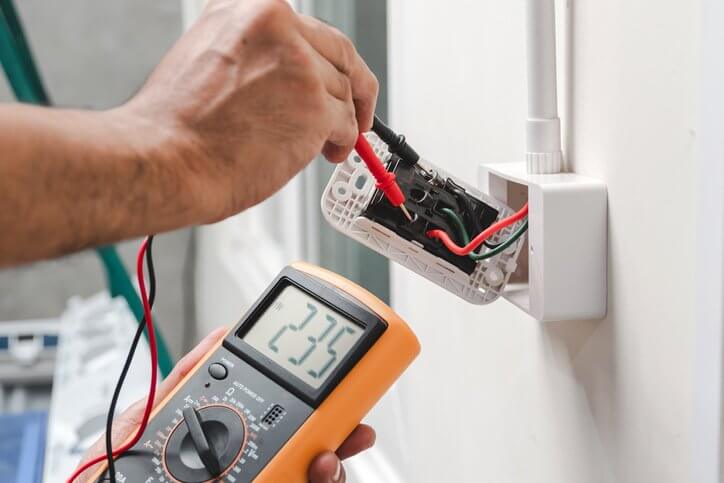
Visual Inspection: A visual inspection should be conducted to verify that the conduit is installed correctly, with no signs of physical damage or improper connections. This inspection should also check for compliance with safety codes, such as proper grounding and clearances from other building systems.
Electrical Continuity Testing: Electrical continuity testing should be performed to ensure that the conduit is properly grounded and does not interfere with the electrical system. Any discontinuities should be addressed immediately to prevent electrical hazards.
Leak Testing: For installations involving flexible or liquid-tight LSZH conduits, leak testing is important to ensure that the conduit system is adequately sealed against moisture and other contaminants. This is particularly important in sensitive environments like hospital sterilization rooms or pharmaceutical production areas.
6. Conclusion
The use of LSZH conduits in schools and hospitals is critical for maintaining strict air quality standards and ensuring fire safety in environments where occupant health is a priority. Unlike traditional PVC conduits, LSZH alternatives significantly reduce toxic emissions during fires, minimizing risks associated with smoke inhalation and halogenated gas exposure. This makes them an essential component in modern educational and healthcare infrastructure, where stringent safety and environmental regulations must be met.
The selection of an appropriate LSZH conduit type must be evaluated based on various factors, including mechanical strength, flexibility, liquid-tight properties, and resistance to environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and temperature variations. Rigid LSZH conduits offer superior structural integrity, making them ideal for fixed installations, while flexible LSZH conduits provide adaptability in complex wiring layouts. Additionally, liquid-tight and metal-reinforced variants enhance durability in harsh conditions, ensuring long-term performance and compliance with safety regulations.
Ctube offer high-quality LSZH standard conduits that have passed all relevant tests and certifications. Our products are rigorously tested to meet stringent safety and environmental standards, providing a reliable solution for schools, hospitals, and other sensitive environments. By choosing our certified LSZH conduits, facilities can enhance safety, achieve compliance, and contribute to a healthier and more sustainable environment.
Thank you for your reading, hope this post helpful. If you have project requirement, please contact us. Good luck with your projects.
FAQs
1. Are LSZH conduits more expensive than traditional PVC conduits?
Yes, LSZH conduits generally cost more due to their specialized formulation and safety benefits, but they provide long-term advantages in fire safety and regulatory compliance.
2. Do LSZH conduits require special installation techniques?
No, LSZH conduits are installed similarly to traditional conduits, but proper handling and compliance with regulations ensure optimal performance.
3. Can LSZH conduits be used in outdoor installations?
Yes, some LSZH conduits, especially liquid-tight, metal-reinforced variants and UV resistance, are designed for outdoor use and can withstand exposure to moisture, UV rays, and temperature changes.