Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
Electrical conduit systems serve as essential protective pathways for electrical wiring, helping to safeguard cables from mechanical damage, physical stress, and environmental factors like moisture. However, water infiltration can pose a significant threat to these systems. Whether it’s exposure to heavy rainfall, underground installations, or condensation buildup, water can lead to serious electrical hazards, including corrosion, short circuits, and even electrical fires. This makes sealing electrical conduits from water not only important but critical for maintaining the safety, durability, and longevity of electrical systems.
In this post, we’ll explore why it’s crucial to prevent water from entering electrical conduits, identify the common causes of water ingress, and offer practical solutions to ensure your conduit system remains protected from moisture. Proper sealing can help you avoid costly repairs, maintain the integrity of electrical installations, and, most importantly, ensure the safety of your electrical infrastructure.
1.1 Why Water Sealing is Critical for Electrical Conduit
1.1.1 Preventing Electrical Hazards
Water is a powerful conductor of electricity, and when it comes into contact with electrical wiring inside a conduit, it can cause shorts and increase the risk of electrical shock or fire. In wet conditions, electrical components become more susceptible to failure, leading to potential hazards that could endanger lives.
1.1.2 Ensuring System Longevity
Water damage can drastically reduce the lifespan of electrical systems. Moisture can degrade the insulation on wiring, cause rust to form inside metal conduits, or lead to the development of mold and mildew, which can further damage the system. By sealing conduits properly, you not only prevent these issues but also help extend the overall service life of the system.
1.1.3 Compliance with Safety Regulations
Electrical systems must comply with national safety standards, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local building codes. These regulations often require that electrical conduit installations be sealed in areas where water exposure is likely. Failing to seal the conduit could result in non-compliance, leading to potential fines or the need to redo the work.
1.2 Common Causes of Water Entry into Electrical Conduits
1.2.1 Outdoor Exposure
Electrical conduits exposed to the elements, such as those installed along the exterior of buildings or in outdoor environments, are highly susceptible to water ingress. Rain, snow, and even humidity can find their way into conduits, especially if the system is not adequately sealed at joints, fittings, or entry points. In these scenarios, water can accumulate in the conduit and eventually make its way inside, potentially causing short circuits or corrosion of electrical components.
1.2.2 Underground Installations
Conduits installed underground face even more significant risks of water entry. In addition to surface water from rainfall or irrigation, underground conduits are exposed to groundwater, which can seep into the conduit over time. Water from flooding, poor drainage, or leaks in nearby plumbing systems can also affect underground conduits, especially if they’re not properly sealed at every junction or entry point.
1.2.3 Condensation
Condensation can occur inside electrical conduits when the temperature inside the conduit is significantly different from the surrounding environment. For instance, if the conduit carries wires in a warm interior space but passes through a cooler exterior wall, moisture can condense inside the conduit, leading to water accumulation. Over time, this moisture can damage electrical wiring and contribute to corrosion, particularly in metal conduits.
2. Types of Electrical Conduit and Their Vulnerability to Water
Choosing the correct type of electrical conduit is vital for protecting wiring systems against water damage, corrosion, and other environmental hazards. Electrical conduits are designed to shield cables from physical damage and environmental factors, including moisture. However, not all conduit materials offer the same level of protection against water.
Understanding the various materials used for electrical conduits—such as PVC, metal, and fiberglass—can help ensure that the installation is secure and that the wiring remains protected in environments where water or moisture is a concern. In this section, we’ll examine each type of conduit material, highlighting its vulnerability to water, its advantages and limitations, and the best practices for sealing each conduit type to prevent water infiltration.
2.1 PVC Conduit: Durability and Limitations
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) conduit is one of the most widely used materials for electrical installations, especially in wet and outdoor environments. It is lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to a variety of environmental factors, including moisture. While PVC conduit offers excellent water resistance, there are some limitations, particularly in extreme weather conditions, impacts, and long-term exposure to UV rays.
2.1.1 Durability of PVC Conduit
- Water Resistance: PVC conduit excels in wet environments, making it ideal for underground installations and areas with high moisture. Unlike metal conduits, PVC does not corrode or rust, ensuring long-term protection of electrical wiring even in the most humid or submerged conditions.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC is highly resistant to a range of chemicals, making it suitable for industrial settings where water may be contaminated with pollutants or chemicals. This feature is particularly beneficial in environments such as sewage treatment plants, agricultural settings, or other industries where chemical exposure is common.
- Impact Resistance: PVC is durable and can withstand physical stress without cracking or breaking easily. This makes it a reliable choice for both residential and industrial applications, where protection from external forces is essential.
2.1.2 Sealing PVC Conduit to Prevent Water Infiltration
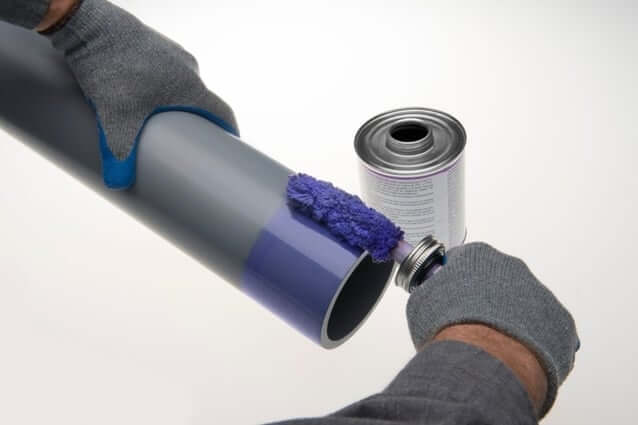
- Proper Joint Sealing: To ensure that water does not enter the conduit system, it is crucial to seal all joints and fittings with solvent cement. This creates a permanent bond that prevents water leakage, ensuring that the conduit system remains intact over time.
- Rubber Soft PVC Gaskets and O-Rings: Adding rubber or soft PVC gaskets and O-rings at entry points (such as where conduit connects to electrical panels or junction boxes) can further enhance water resistance. These seals form a barrier that prevents moisture from entering while maintaining the conduit’s structural integrity.
2.2 Metal Conduit (EMT, Rigid, and IMC) and Water Sealing Needs
Metal conduits, such as Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT), Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC), and Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), are known for providing excellent mechanical protection. While they offer robust defense against physical damage, they also present certain vulnerabilities when exposed to moisture, requiring specific sealing methods to prevent water ingress.
2.2.1 Vulnerability of Metal Conduit to Water
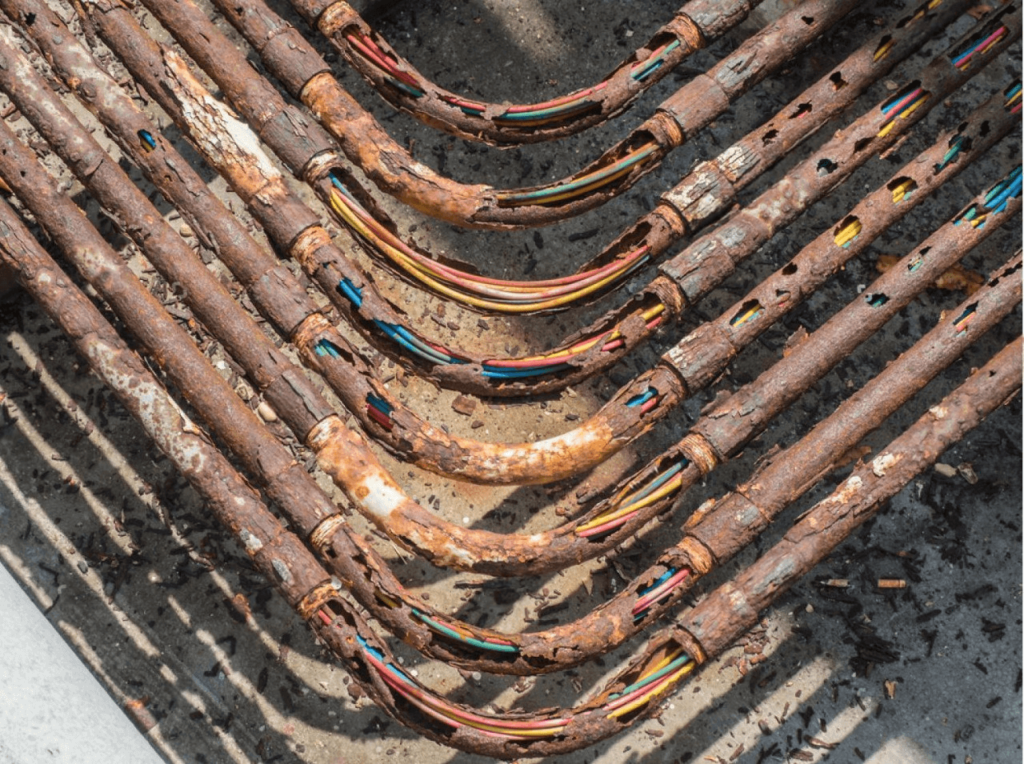
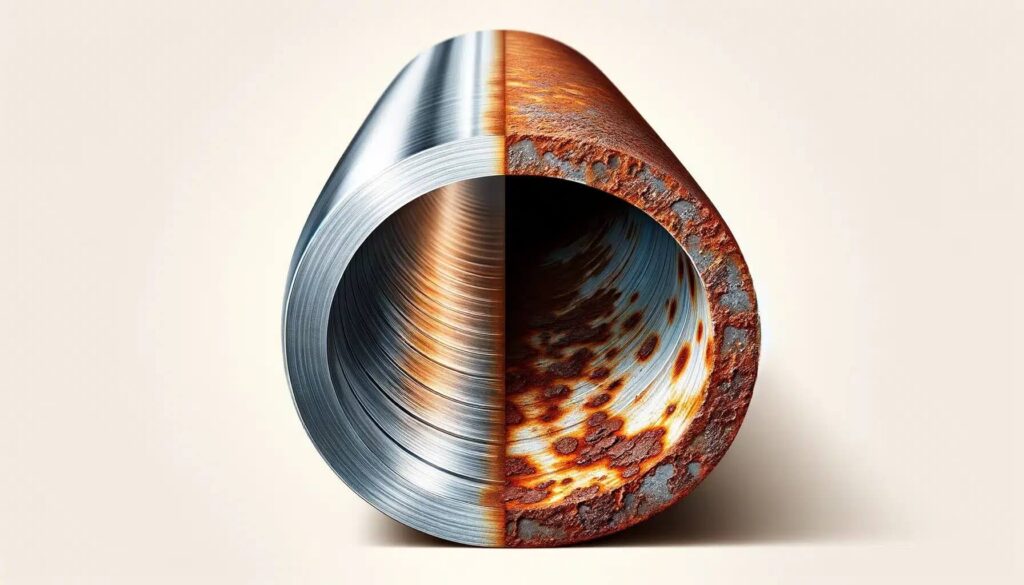
- Corrosion: Metal conduits are prone to rust and corrosion when exposed to water, especially in humid environments. EMT, being made of thin-walled steel, is particularly susceptible to corrosion, though RMC and IMC, despite being thicker, can also degrade over time if not properly sealed.
- Water Accumulation: If the joints and fittings of metal conduit systems are not sealed effectively, water can accumulate inside. This pooling can lead to short circuits or rusting of the wiring within the conduit, causing potential system failures or electrical hazards.
- Condensation: In areas with significant temperature fluctuations, condensation can form inside metal conduits. As the air cools, moisture in the atmosphere condenses inside the conduit, creating an opportunity for water to accumulate and cause damage to both the conduit and its contents.
2.2.2 Water Sealing for Metal Conduit
- Watertight Connectors and Fittings: To prevent water from entering the system, it’s essential to use watertight connectors, gaskets, and seals. These specially designed components ensure that all joints and connection points are fully sealed, protecting the electrical system from water ingress.
- Thread Sealant for Threaded Connections: For RMC and IMC, which feature threaded connections, applying thread sealant or tape is crucial to create a waterproof seal. Using a high-quality thread sealant designed for wet environments helps prevent leaks and maintains a secure, water-tight connection.
- Corrosion-Resistant Coatings: In areas with high moisture exposure, galvanized or stainless steel conduit should be used to resist corrosion. The addition of corrosion-resistant coatings enhances the longevity of the conduit and ensures that it remains durable even in challenging environments.
- PVC-Coated Metal Conduit: For applications in highly corrosive environments (such as coastal areas or underground installations), metal conduits can be coated with PVC. This provides the structural protection of metal, while the PVC coating offers additional water resistance.
2.2.3 Considerations for Different Types of Metal Conduit
- EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing): EMT is lightweight and easy to install but has thin walls, making it more vulnerable to corrosion in wet environments. It’s important to use watertight fittings and consider additional protective coatings or galvanized EMT for outdoor applications.
- RMC (Rigid Metal Conduit): RMC offers more protection due to its thicker walls. However, it still requires watertight sealing at all joints and the use of corrosion-resistant coatings to maintain its integrity in moist conditions.
- IMC (Intermediate Metal Conduit): IMC is stronger than EMT and more corrosion-resistant, but it still needs to be properly sealed at all connection points to prevent water infiltration.
2.3 Fiberglass Conduit and Its Vulnerability to Moisture
Fiberglass conduit is increasingly being used in environments where moisture resistance and durability are crucial. Known for its strength and resistance to corrosion, fiberglass conduit offers superior protection against water compared to both PVC and metal options. However, like any material, fiberglass is not entirely immune to moisture-related issues and requires proper sealing techniques to ensure its effectiveness.
2.3.1 Advantages of Fiberglass Conduit
- Corrosion Resistance: One of the main benefits of fiberglass conduit is its resistance to corrosion. Unlike metal conduits, which can rust when exposed to water, fiberglass remains unaffected by moisture, making it an ideal choice for installations in chemically aggressive environments, coastal areas, or other wet conditions.
- Waterproof: Fiberglass does not absorb water, ensuring that the conduit remains structurally intact even when exposed to prolonged moisture. Its high water resistance makes it an excellent option for environments where other materials might fail due to constant exposure to water or humidity.
- Durability: Fiberglass is both lightweight and strong, offering durability without the heavy weight of metal. It can withstand physical impacts and is resistant to cracking, making it a reliable choice for environments where conduit systems are subjected to harsh conditions or physical stress.
2.3.2 Water Sealing for Fiberglass Conduit
- Gasket Seals: To prevent water from entering at junctions and entry points, it is crucial to use proper gasket seals. Rubber or silicone gaskets are commonly employed to create a watertight barrier that ensures moisture does not infiltrate the conduit system.
- Threaded Fittings: For fiberglass conduit systems that use threaded connections, it’s essential to apply a thread sealant to prevent water from seeping through the threads. A high-quality sealant will help maintain a waterproof seal at the connection points, preventing moisture ingress.
3. Choosing the Right Waterproofing Method Based on Conduit Location
The location and exposure of electrical conduit systems play a significant role in determining the most effective waterproofing solution. Whether the conduit is outdoors, underground, or indoors, each environment presents unique challenges for sealing and protecting electrical systems from water. This section outlines the most appropriate waterproofing methods tailored to specific conduit locations and the requirements of each scenario.
3.1 Outdoor Installations: Ensuring Long-Term Protection
Outdoor electrical conduit systems face exposure to various environmental factors, including rain, snow, UV rays, and fluctuating temperatures. Selecting the right waterproofing method ensures that the conduit remains intact, functional, and protected from water infiltration over time.
3.1.1 Challenges of Outdoor Installations
- Exposure to Rain and Moisture: Rain, snow, and humidity can infiltrate conduit systems if seals are not strong enough to withstand constant exposure to moisture.
- UV Degradation: Ultraviolet (UV) rays can degrade certain materials, particularly plastics like PVC. This degradation can lead to brittleness and cracks, allowing water to enter.
- Temperature Extremes: Outdoor environments experience temperature fluctuations that cause materials to expand and contract. Seals must be flexible and durable enough to handle these changes.
3.1.2 Recommended Waterproofing Methods
- Solvent Cement or other adhesive (PVC/ Fibergalss Conduit): Solvent cement is highly effective in creating waterproof joints for PVC conduit used outdoors. For added protection, choose a solvent cement rated for outdoor use with UV-resistant properties. A UV-resistant primer can further enhance the durability of PVC joints against sun damage.
- Rubber Gaskets and O-Rings (Metal Conduit): In metal conduit systems, rubber gaskets and O-rings provide reliable, flexible seals that remain intact even in extreme temperatures, ensuring protection against water ingress.
- Watertight Connectors: For junctions between conduit and electrical boxes, watertight connectors should be used. These connectors have built-in seals to prevent water from entering through the interface, ensuring the safety and functionality of the system.
3.2 Underground Conduit Systems: Preventing Water Ingress
Underground conduit systems face the challenge of managing water infiltration from both groundwater and surrounding soil. Water is often present in varying amounts due to fluctuating water tables or soil moisture. For the continued reliability of electrical wiring, especially in high-moisture or flood-prone areas, effective waterproofing is essential.
3.2.1 Challenges of Underground Installations
- Conduit Depth and Soil Pressure: The deeper the conduit is buried, the more pressure the surrounding soil exerts on it. This increased pressure can stress the seals, potentially compromising their effectiveness. For installations in deeper depths or areas with high soil pressure, it is advisable to use thicker-walled conduits, such as Schedule 80 PVC, which offer higher resistance to both pressure and potential damage. Ensure that seals and fittings are rated to handle the additional stress from surrounding earth.
- Soil Conditions and Moisture Containment: The type of soil plays a crucial role in determining the waterproofing methods needed for underground conduit. In highly porous or water-retentive soil, additional protective coatings or wraps may be necessary to prevent water infiltration. Moisture containment is essential in these conditions to ensure that water does not enter the conduit, especially in areas prone to flooding or with high groundwater levels.
- Groundwater Exposure and Monitoring: In areas with fluctuating water tables or frequent flooding, it is vital to monitor moisture levels around the conduit. Long-term exposure to groundwater can increase the risk of water infiltration. Using sealing techniques designed to withstand constant moisture exposure, such as specialized gaskets and coatings, will help protect the integrity of the conduit system over time.
3.2.2 Recommended Waterproofing Methods
- Solvent Cement with Reinforced Seals (PVC Conduit): For underground PVC conduit, solvent cement is the primary method of sealing. To ensure maximum protection, reinforced PVC fittings and sealing compounds like butyl rubber can be applied around joints to prevent any water ingress from surrounding soil or groundwater.
- Rubber Gaskets (Metal Conduit): For metal conduit systems, rubber gaskets are essential for sealing threaded joints. For rigid metal conduit (RMC) or intermediate metal conduit (IMC), use heavy-duty rubber gaskets or sealing washers designed specifically for underground use to provide extra protection against moisture.
- Flexible Water-Resistant Tape: Waterproof adhesive tape can be applied over coupling points or other areas where additional sealing is needed. This method acts as a supplementary solution to enhance other sealing methods, particularly for temporary use or additional reinforcement.
- Watertight Seals for Junction Boxes: Use watertight connectors and junction boxes rated for underground use. These provide secure, moisture-resistant seals to keep electrical connections dry and intact.
3.3 Indoor Applications: Preventing Condensation and Moisture
Although indoor conduit systems are less exposed to external weather conditions, they still face the risk of water infiltration from condensation, plumbing leaks, or high humidity. Preventing water from entering conduit joints is crucial for safeguarding electrical wiring and ensuring system reliability.
3.3.1 Challenges of Indoor Installations
- Condensation: Temperature fluctuations in areas such as basements, crawl spaces, or attics can cause condensation to form on the interior surfaces of the conduit. Over time, this can lead to moisture buildup within the conduit.
- Plumbing Leaks: In buildings with plumbing systems running close to electrical conduits, plumbing leaks can result in water seeping into the conduit. This poses a significant risk of short circuits or corrosion.
- High Humidity: Areas with consistently high humidity, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or industrial settings, can allow moisture to accumulate inside the conduit, potentially causing electrical issues.
3.3.2 Recommended Waterproofing Methods
- Condensation Barriers (PVC and Metal Conduit): Installing condensation barriers along the conduit system can help prevent water buildup. This is particularly effective in areas where the temperature inside and outside the conduit differ, leading to condensation.
- Watertight Connectors (for Indoor Boxes): Watertight connectors with rubber gaskets or O-rings should be used where the conduit enters junction boxes or enclosures. These connectors help ensure that no moisture seeps in through small gaps, especially from plumbing leaks or condensation.
- Sealant for Joints and Fittings: Flexible sealants, such as silicone or rubber gaskets, can be applied around conduit joints and fittings to prevent moisture infiltration. Silicone sealant is especially useful for indoor applications as it remains durable and flexible, even with minor shifts in the conduit due to temperature changes.
- Insulating Coatings: For areas prone to condensation, applying insulating coatings or wraps around the conduit can help regulate the temperature of the system. This prevents the cooling of moist air inside the conduit, which can lead to condensation.
4. Step-by-Step Guide for Sealing Electrical Conduit from Water
Sealing electrical conduit from water is essential to ensure the safety and longevity of electrical systems, especially in outdoor, underground, or high-moisture environments. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of effectively sealing conduits, preventing water ingress, and protecting electrical systems from water damage.
Step 1: Choose the Right Waterproofing Method
Before starting the sealing process, assess the type of conduit, its location, and the environmental conditions. Choose a waterproofing method that matches the conduit material and the specific water exposure risks. For example, PVC Conduit use solvent cement or silicone sealant for joints and fittings.
Step 2: Prepare the Area and Gather Necessary Materials
Preparation is key to ensuring a successful sealing process. Before sealing your conduit, gather all the materials and tools you’ll need for the job. You should also make sure the installation area is clean and dry to ensure proper adhesion.
Materials You Will Need:
Waterproofing products: Solvent cement, silicone sealant, rubber gaskets, waterproof tape, or butyl rubber sealant (depending on your chosen method).
- Cleaning supplies: Rags, isopropyl alcohol (for cleaning surfaces), and a wire brush (for metal conduits).
- Sealing tools: Caulk gun (for silicone sealant), brush (for solvent cement), and gloves.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Safety gloves, safety glasses, and work boots.
Preparation:
- Clean the Conduit: Ensure the surfaces to be sealed are clean and free from dirt, oil, or moisture. Use isopropyl alcohol and a clean rag for PVC and fiberglass conduits. For metal conduits, use a wire brush to remove rust and debris.
- Check for Cracks or Damages: Inspect the conduit for any visible cracks or damages that may need repair before sealing. Cracks should be patched using appropriate methods like epoxy or specialized adhesive.
Step 3: Apply Waterproofing Material
The next step is to apply the appropriate waterproofing product. The application method will vary depending on the type of material used for the conduit and the selected waterproofing product. For example,
For PVC Conduit:
- Apply Solvent Cement: Use a brush or applicator to apply a thin layer of solvent cement to both the inside of the fitting and the outside of the conduit. Ensure even coverage.
- Join the Conduit and Fitting: Quickly join the conduit to the fitting and twist slightly to ensure an even distribution of the cement. Hold for a few seconds to ensure proper adhesion.
- Clean Excess Cement: Wipe off any excess cement with a clean rag to avoid residue that could interfere with the seal.
For Metal Conduit (EMT, Rigid, IMC):
- Use Rubber Gaskets or O-Rings: Place rubber gaskets or O-rings into the connector or coupling before joining conduit pieces.
- Apply Butyl Rubber Sealant: For high-pressure environments, apply a layer of butyl rubber sealant around the fitting or connector before joining.
- Tighten the Connection: Securely tighten the connection, ensuring the rubber gasket or sealant compresses to form a tight seal.
For Fiberglass Conduit:
- Apply Silicone Sealant: Apply a bead of silicone sealant around the edges of the conduit fittings and joints. Use a caulk gun for precise application.
- Press and Hold the Fittings: Press the fittings firmly into place, ensuring the silicone sealant makes an even bond.
- Smooth the Sealant: Use a wet finger or tool to smooth the silicone sealant and ensure a uniform, watertight finish.
Step 4: Install Watertight Connectors or Boxes
For junction boxes or other critical points where conduit meets electrical boxes, watertight connectors are essential. These connectors feature pre-installed gaskets that create a water-resistant seal between the conduit and the box.
- Place Watertight Connectors: Attach the watertight connector to the box or junction point. Ensure the connector’s gasket lines up properly to form a tight seal.
- Tighten Securely: Use a wrench to tighten the connector without overtightening, which could damage the gasket.
- Test the Seal: After installation, inspect the connection to ensure the seal is tight and properly aligned.
Step 5: Allow Proper Curing Time
Once the waterproofing materials are applied, it’s important to allow adequate curing or drying time before exposing the conduit to water or moisture. The curing time will depend on the type of waterproofing material used.
- Solvent Cement: Typically cures in about 15 minutes to 1 hour, but complete strength is achieved after 24 hours.
- Silicone Sealant: Typically takes 24 hours to fully cure. However, it may become waterproof within a few hours.
- Rubber Gaskets: No curing time is needed, but allow time for pressure to compress the gasket properly.
- Butyl Rubber Sealant: Cures in approximately 24 hours.
Step 6: Test the Waterproof Seal
After the sealant has fully cured, it’s important to test the integrity of the seal. This step ensures that the sealing process was successful and that no water will ingress into the conduit system.
- Visual Inspection: Inspect the sealed joints and fittings to ensure the sealant or gaskets are properly in place. Look for any gaps, cracks, or uneven coverage.
- Water Test: Conduct a water test by spraying or applying water to the sealed areas. Observe for any signs of leakage. If water leaks, reapply the sealant or check for improper installation of gaskets.
- Pressure Test (for underground applications): In underground applications, consider using a pressure test to simulate the conditions the conduit will face. If there’s any leakage under pressure, the seal needs to be reapplied or reinforced.
Step 7: Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Periodically check the sealed conduit systems, especially in areas with frequent exposure to moisture, such as basements, outdoor installations, or underground.
Over time, sealant and gaskets may degrade due to wear and exposure to elements. Reapply sealant or replace gaskets if necessary. Replace damaged sections of conduit promptly.
5. Conclusion
Sealing electrical conduit from water is an essential aspect of ensuring the safety, functionality, and longevity of electrical systems. By using the right materials, sealants, and techniques tailored to specific conduit types and environmental conditions, you can effectively protect your electrical infrastructure from water damage. Whether you’re working with PVC, metal, or fiberglass conduits, proper preparation, application, and ongoing maintenance are key to creating a reliable, long-lasting waterproof barrier.
From selecting appropriate sealants to adhering to industry standards and performing regular inspections, these best practices will help prevent costly repairs, enhance safety, and extend the lifespan of your electrical systems. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll ensure your conduit systems remain free from water ingress, even in the harshest conditions. Water sealing is not just about preventing leaks—it’s about protecting your investment, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining the integrity of your electrical installations for years to come.
6. High quality PVC Conduit and Fittings with Excellent Waterproof
Ctube is a trusted manufacturer and supplier of high-quality PVC conduits and fittings, offering solutions designed to protect electrical systems from water exposure. PVC conduits are naturally resistant to corrosion and moisture, making them ideal for underground installations and environments prone to wet conditions.
Ctube provide extensive range of products, including Schedule 40, Schedule 80, and DB Series PVC conduits, is perfect for both residential and commercial applications, providing a reliable, cost-effective solution for preventing water ingress. We also provide conduit fittings like waterproof adaptable box and junction box with special design.
If you have projects requirements, please contact us.
Thanks for your reading, and good luck with your projects.

FAQs
1. Can PVC conduit be used in wet environments?
Yes, PVC conduit is naturally resistant to moisture and corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor and underground installations. However, it’s important to properly seal connections with solvent cement or silicone to ensure a watertight system.
2. What is the difference between PVC and fiberglass conduit for water resistance?
While both PVC and fiberglass conduits are water-resistant, fiberglass offers superior protection against high-pressure water, harsh chemicals, and UV exposure. PVC is more cost-effective and sufficient for most residential and commercial applications, but fiberglass is preferred in extreme conditions.
3. Is it necessary to seal all conduit fittings?
Yes, it’s essential to seal all conduit fittings, including elbows, couplings, and junction boxes, especially in outdoor or underground installations. Any gap or unsealed connection can allow water to seep into the conduit.