Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
Flexible conduit connectors are specialized fittings designed to securely join sections of flexible conduit—a type of tubing that protects and routes electrical wires or cables. Unlike rigid conduits, these connectors accommodate bends, vibrations, and movement while maintaining a sealed, durable pathway.
Understanding their purpose and types will help in selecting the right connector for specific projects, ensuring safe and efficient electrical installations.
The following post will introduce the flexible conduit connector, which is available in different materials, types and designs.
2. Common Electrical Conduit Fittings and Their Definitions
When installing electrical conduit systems, various types of fittings are required to securely join, terminate, or transition conduits. These fittings are essential to ensure proper protection, grounding, and mechanical strength of the conduit installation. The selection of fittings often depends on whether the conduit is Rigid or Flexible, as each system has specific requirements.
According to the UL 514B Standard — which covers Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings — there are many types of fittings designed for use with rigid metal conduit (RMC), intermediate metal conduit (IMC), electrical metallic tubing (EMT), and flexible conduit systems. Some fittings are used exclusively for rigid conduit, others are designed specifically for flexible conduit, while certain fittings are common and compatible with both systems.
Bushing: Installed at conduit ends to protect wires from abrasion as they exit or enter the raceway.
Conduit Body: Provides access to the conduit interior at junctions or endpoints and includes a removable cover.
Reducing Coupling: Joins two raceways of different diameters.
Elbow: Changes the direction of conduit, typically at 45° or 90° angles.
Expansion Fitting: Accommodates thermal expansion and contraction in rigid metal conduit systems.
Connector: Used to terminate conduit to an electrical box or enclosure. Available for both rigid and flexible conduit.
Sealing Fitting: Prevents the passage of gases, vapors, or flames through conduit systems. Common to both rigid and flexible conduits.
Sealing Ring: Ensures a water-tight seal in both rigid and flexible conduit systems.
Hub: Connects rigid conduit to enclosures while maintaining watertight integrity.
Transition Coupling: Connects flexible metal conduit to non-flexible metallic raceways.
Support Clamp: Supports and maintain the conduits.
Above we mentioned are some common types for rigid and flexible conduit, and in the following, we will emphasize on the fittings used in flexible conduit such as bushing, connector to box and conduit, coupling for conduit, elbow and more.
3. Designs Introduce: Detailed Types of Flexible Conduit Connectors
3.1 Bushing
Description: Bushings are cylindrical or bell-shaped components used primarily to insulate the sharp edges of conduit ends, preventing damage to wires passing through.
They are typically made from materials like thermoplastic (e.g., PVC), rubber, or silicone and are designed to fit snugly over the conduit end. The shape can vary from a simple cylindrical sleeve to more complex designs with flared ends for easier wire insertion.
Materials and Designs:
Thermoplastic Bushings: These are common for PVC flexible conduits and provide excellent insulation against sharp edges. They are often injection-molded for precise dimensions and durability.
Rubber Bushings: Often used in applications requiring high flexibility and resistance to abrasion. Rubber bushings can be molded with different hardness levels to suit specific requirements.
Threaded vs. Non-Threaded: Bushings can be either threaded for screw-in applications or non-threaded for slip-on designs. Threaded bushings provide a secure mechanical lock, while non-threaded ones offer ease of installation.
Sealed Bushings: Some bushings include seals or gaskets to prevent moisture ingress, ensuring that the electrical system remains protected in damp environments.
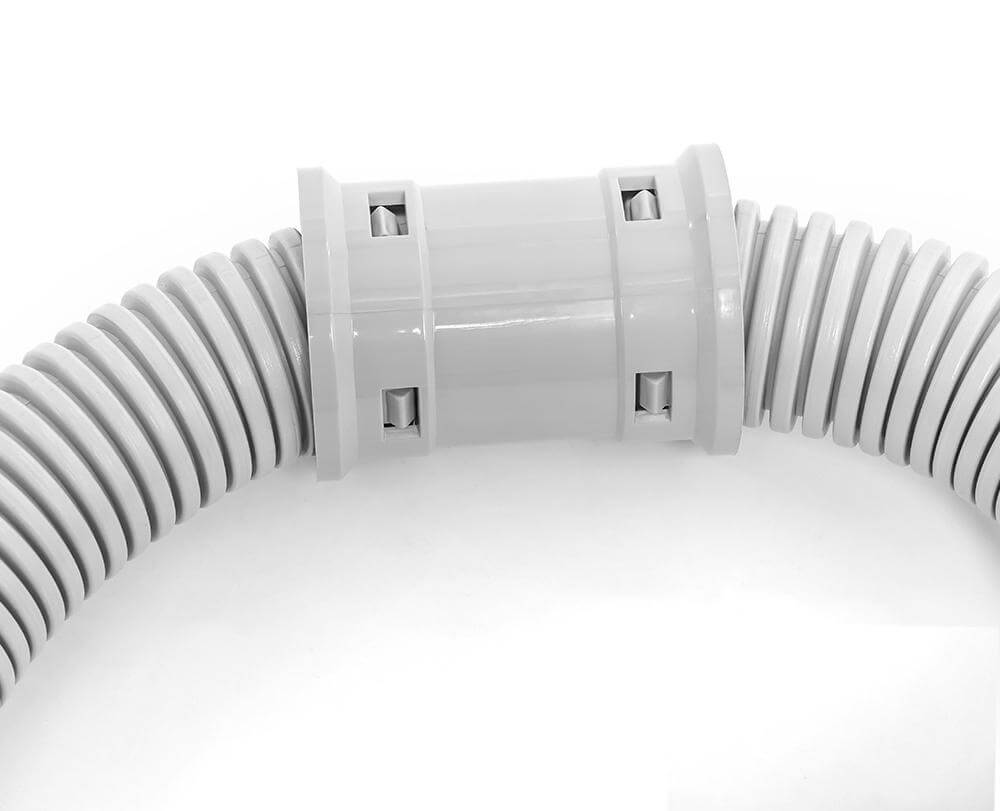
3.2 Straight Coupling
Description: Straight couplings are tubular connectors designed to join two lengths of flexible conduit in a straight line, providing a continuous pathway for electrical wiring.
They are typically made from PVC or other thermoplastics and feature a smooth interior to minimize friction on wires. The design often includes a slight taper at each end to facilitate easy insertion of the conduit.
Materials and Designs:
PVC Straight Couplings: Commonly used for PVC flexible conduits, these couplings are durable and resistant to corrosion. They are often color-coded to match specific conduit sizes.
Threaded vs. Non-Threaded: Available in both threaded and slip-on designs, depending on the application requirements. Threaded couplings offer a secure mechanical connection, while slip-on designs are quicker to install.
Sealed vs. Unsealed: Some couplings may include seals or gaskets to prevent moisture ingress, ensuring that the electrical system remains protected in damp environments.
Reinforced Couplings: Some designs include internal reinforcement, such as metal or fiberglass, to enhance strength and durability.
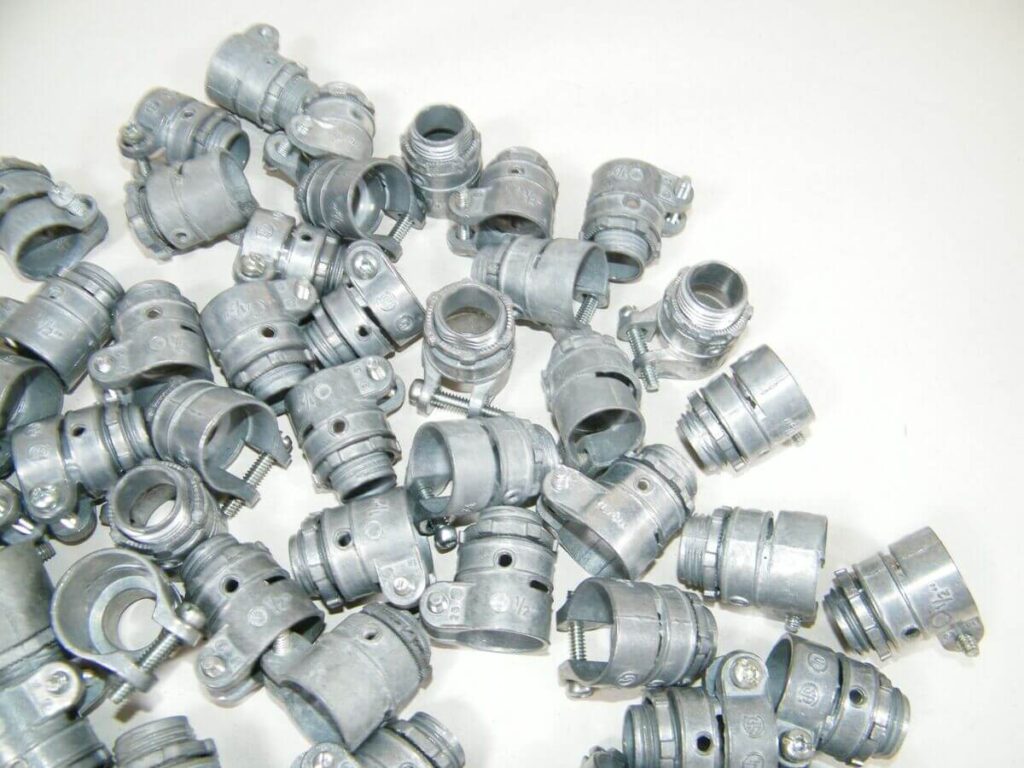
3.3 Conduit to Box Connector
Description: Conduit to box connectors, also known as male adapters, are used to link flexible conduit to electrical boxes or enclosures. These connectors typically feature a threaded design with a locknut ring to secure the conduit in place. They are often referred to as male adapters because they have a male thread that screws into the box.
Materials and Designs:
Metal Connectors: Often used for flexible metal conduits, these connectors provide strong mechanical connections. They are typically made from galvanized steel or aluminum.
Plastic Connectors: Suitable for PVC flexible conduits, offering corrosion resistance and ease of installation. Plastic connectors are often injection-molded for precision.
Threaded vs. Non-Threaded: Available in both designs to accommodate different box types. Threaded connectors provide a secure lock, while non-threaded ones are quicker to install.
Locknuts and Gaskets: Some connectors include locknuts and gaskets to ensure a watertight seal when attached to the box.
3.4 Elbow Connector
Description: Elbow connectors are curved or angled connectors used to change the direction of flexible conduit, typically by 90 degrees, 45 degrees, or other angles.
They are essential for routing conduit around obstacles or altering the direction of the conduit path. The design often includes a smooth, curved interior to minimize friction on wires and prevent damage.
Materials and Designs:
PVC Elbow Connectors: Common for PVC flexible conduits, these connectors are flexible and resistant to corrosion. They are often molded with a slight flexibility to accommodate minor adjustments.
Threaded vs. Non-Threaded: Available in both designs to suit different installation needs. Threaded elbows offer a secure mechanical connection, while non-threaded ones are quicker to install.
Sweeps: Specialized elbows designed for smooth bends, minimizing friction and stress on wiring. Sweeps are typically longer than standard elbows to reduce the bend radius.
Role: Elbow connectors provide flexibility in installations, allowing conduit to navigate around corners or redirect the path of wiring. They are essential for creating efficient and space-saving electrical layouts.
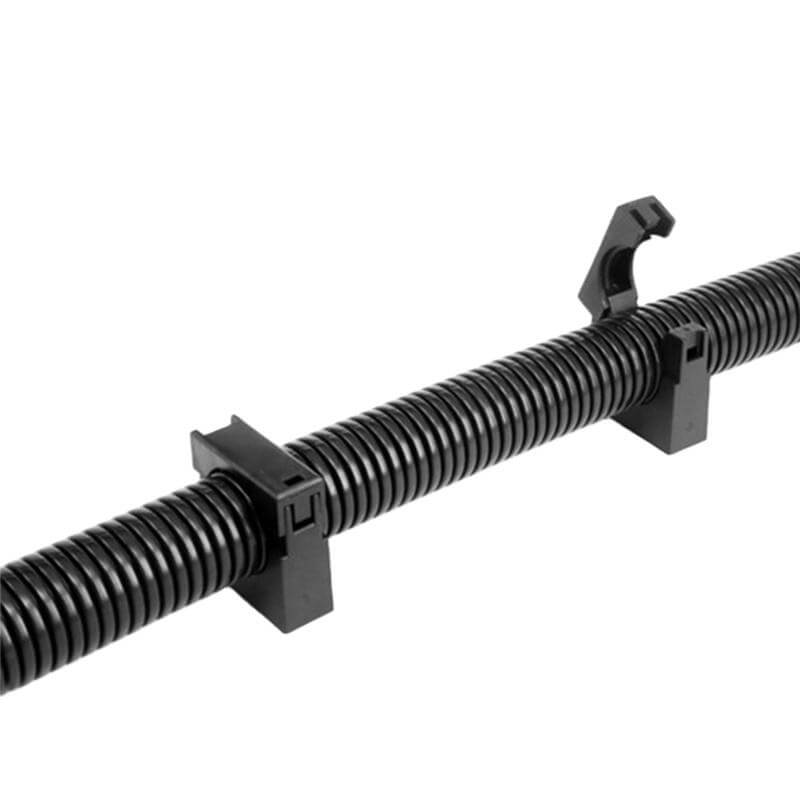
3.5 Conduit Clamp
Description: Conduit clamps are used to secure flexible conduit in place, preventing movement or vibration that could compromise the electrical system. They are available in various designs to accommodate different conduit sizes and types. The clamps typically feature a spring-loaded or adjustable design to grip the conduit securely.
Materials and Designs:
Spring Steel Clamps: Common for heavy-duty applications, offering strong holding power. These clamps are often used in industrial settings.
Adjustable Clamps: Suitable for flexible conduits, these clamps can accommodate varying diameters. They are typically made from durable plastics or metals.
Quick-Install Clamps: Designed for fast mounting without tools, ideal for flexible metal or non-metallic conduits. These clamps often feature snap-fit designs.
Cable Ties and Straps: Some installations use cable ties or straps as an alternative to traditional clamps, providing a quick and easy way to secure conduit.
Types of Conduit Clamps:
One-Hole Clamps: Simple and cost-effective, these clamps secure conduit with a single attachment point.
Two-Hole Clamps: Provide additional stability by using two attachment points, often used for heavier or longer conduit runs.
Saddle Clamps: These are used to secure conduit to a surface without drilling holes. They are often U-shaped and can be adjusted to fit different conduit sizes.
3.6 Explosion-Proof Connectors
Description: Explosion-proof connectors are designed to protect electrical systems in hazardous environments where flammable gases or vapors are present. These connectors are engineered to prevent electrical arcs or sparks from igniting explosive atmospheres. They are typically made from materials like stainless steel, cast iron, or aluminum alloy, which provide strength and corrosion resistance.
Materials and Designs:
Flame & Explosion-Proof Thread: These connectors feature flame-proof threads to prevent explosions from spreading outside the connector body. They are machined to precise tolerances to ensure safety in hazardous locations.
Stainless Steel Bodies: Often used for flexible explosion-proof conduits, stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance and strength.
Threaded Connections: Available in various thread types, including metric (e.g., M20x1.5-M63x1.5) and NPT (e.g., NPT1/2″ to NPT2″), allowing for flexibility in connecting different conduit sizes and types.
Sealed Designs: Include integrated sealing gaskets to prevent flammable gases or vapors from entering the connector body, ensuring safety in Class 1 Division 1 and Class 2 Division 1 hazardous locations.
4. Material Introduce: Detailed Types of Flexible Conduit Connectors
Each type of flexible conduit—whether nonmetallic or metallic—requires specific fittings made from materials that suit their physical properties and installation requirements. In this section, we will explore in detail the different types of materials used for flexible conduit connectors, categorized by the conduit type. Understanding the characteristics of each fitting material will help ensure reliable, safe, and compliant electrical installations.
4.1 Fittings for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Flexible Conduit
Fittings for Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Flexible Conduit are essential components used to ensure safe, secure, and reliable connections within flexible non-metallic conduit systems. These fittings are specifically designed to maintain the flexibility of the conduit while providing mechanical protection and electrical continuity.
According to NEC® Section 300.15, “Fittings and connectors shall be used only with the specific wiring methods for which they are designed and listed.” Therefore, fittings for PVC flexible conduit must be used only with non-metallic conduit systems and must comply with the appropriate product standards.
PVC flexible conduit fittings are typically made from non-metallic materials, such as:
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Nylon
- Other thermoplastic compounds
These materials provide excellent resistance to corrosion, moisture, and environmental factors, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
The key functions of PVC flexible conduit fittings include:
- Securing the conduit to boxes, enclosures, and panels
- Maintaining the integrity of the conduit system
- Providing strain relief to prevent damage to the conductors
- Protecting against water ingress when used with liquidtight flexible conduit
There are several common types of PVC flexible conduit fittings:
- Straight Connectors – Used to terminate the conduit to an electrical box or enclosure in a straight run.
- 90° and 45° Elbow Connectors – Used to make smooth directional changes without bending the conduit excessively.
- Couplings – Used to join two sections of flexible conduit together.
- Adapters (Male and Female) – Used to transition between conduit and threaded openings or other conduit types.
- Strain Relief Connectors – Provide additional protection to prevent conductor damage caused by pulling or movement.
For wet locations or outdoor installations, liquidtight PVC flexible conduit fittings are available. These fittings include gaskets or sealing rings to prevent moisture from entering the conduit system.
The performance and safety requirements for these fittings are covered under standards such as:
- UL 514B – Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings
- NEMA FB-1 – Fittings, Cast Metal Boxes, and Conduit Bodies for Conduit and Cable Assemblies
- CSA C22.2 No. 18.3 – Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings (for Canadian installations)
Proper selection and installation of fittings are critical to maintaining system integrity. It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and ensure that fittings are listed and marked for use with PVC flexible conduit systems to comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC®) and other applicable standards.
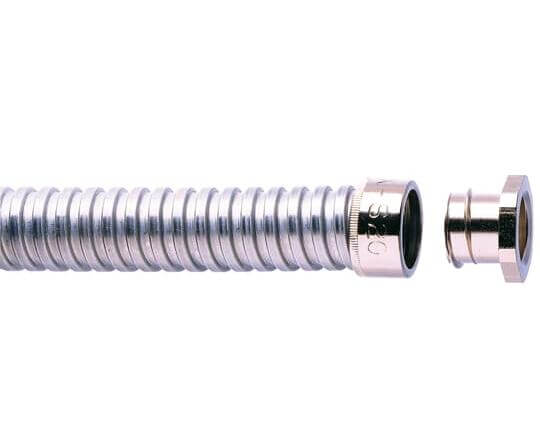
4.2 Fittings for Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC)
Section 300.15 of the NEC® requires, for Flexible Metal Conduit (FMC), fittings must be selected carefully to meet these requirements and ensure a safe, compliant electrical installation.
FMC fittings are designed to provide a secure mechanical and electrical connection while protecting conductors from external damage. These fittings are typically listed for use with FMC and may also be listed for use with Armored Cable (Type AC) and Metal-Clad Cable (Type MC). It is essential to consult the manufacturer’s instructions, product labels, and literature to confirm the specific wiring methods and conduit types for which the fitting is listed.
Flexible Metal Conduit fittings are identified by the nominal trade size of the conduit they are designed for, commonly ranging from 1/2 inch (16 mm) through 4 inches (103 mm). In recent years, metric designators corresponding to traditional trade sizes have also been introduced to help standardize product selection.
FMC fittings are available in a variety of materials, including:
- Fabricated steel
- Cast malleable iron
- Cast aluminum
- Cast zinc
The material type is typically chosen based on design requirements or installer preference, as all listed FMC fittings meet the same minimum performance criteria. The applicable standards for FMC fittings include:
- ANSI/UL 514B – Conduit, Tubing, and Cable Fittings
- ANSI/NEMA FB 1
There are three general categories of FMC fitting connection types:
- Clamp-Type Connectors – Secure to the outside of the conduit.
- Direct-Bearing Screw-Type Connectors – Screw directly into the inside of the conduit.
- Screw-In Connectors and Couplings – Thread inside the conduit for mechanical and electrical bonding.
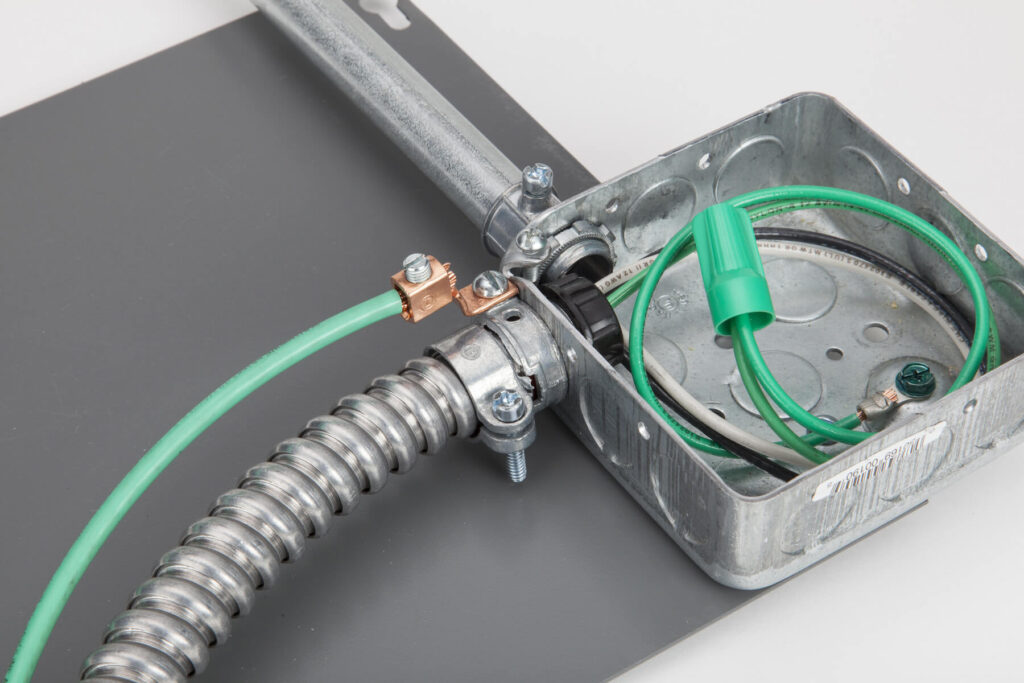
All FMC connectors use either a locknut or an integrated feature to ensure a secure connection and electrical continuity with enclosures. Some outlet and switch boxes may also come with integral clamps for use with FMC. Additionally, transition couplings are available to connect FMC to Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC) or Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT).
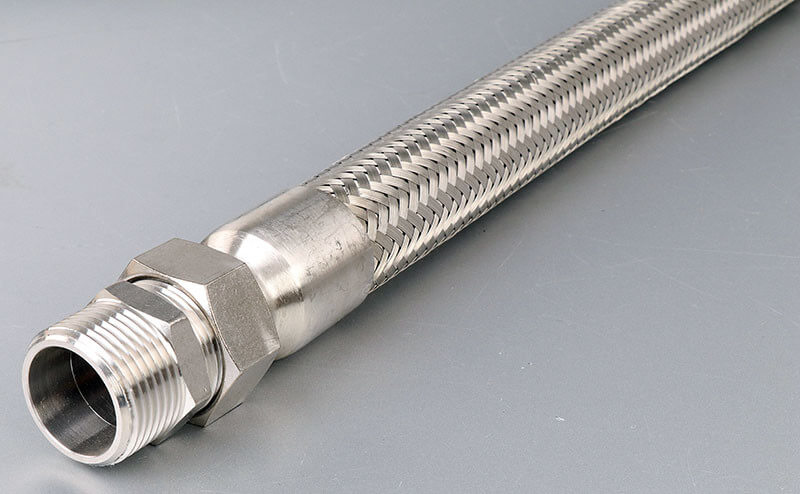
4.3 Fittings for Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC)
Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduit (LFMC) is used in electrical systems that require both flexibility and protection of conductors from moisture, vapors, and solids. It is suitable for use in exposed or concealed locations, outdoors, in concrete or masonry, and for direct burial when specifically listed and marked “For Direct Burial.” For detailed permitted and prohibited uses, refer to NEC Article 350. Additionally, NEC Article 250 permits LFMC to serve as an equipment grounding conductor when properly installed.
4.3.1 Fitting Requirements and Selection
Fittings used with LFMC must comply with the provisions in Section 300.15, 350.6, and 350.42 of the National Electrical Code (NEC):
Fittings and connectors must be used only with the specific wiring method they are designed and listed for.
LFMC must only be used with listed and approved terminal fittings.
Angle connectors (45° and 90°) are not permitted for concealed raceway installations.
In many cases, fittings listed for LFMC may also be listed for Type LFNC-B Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit. Such fittings will be clearly marked “LFNC-B” or with an equivalent marking. Always consult the manufacturer’s labels, instructions, and literature to confirm the fitting’s intended and listed use.
The performance and listing requirements for LFMC fittings are covered under UL 360 – Liquidtight Flexible Steel Conduit.
4.3.2 Design and Application Considerations
LFMC fittings are generally of the compression gland type, designed to:
- Prevent the ingress of moisture and liquids into the conduit system.
- Ensure continuous electrical continuity.
- Provide mechanical protection to conductors entering enclosures.
Common fitting types include:
- Straight connectors
- Angle connectors (45° and 90°)
- Fittings with or without locknuts
When fittings are supplied with locknuts and sealing rings, they are used to provide a liquidtight seal at an enclosure knockout or fitting joint. In threaded entries, these fittings may create a liquidtight joint without using locknuts or sealing rings.
Some fittings may come with an optional insulated throat to protect conductors from abrasion, especially recommended when using 4 AWG or larger conductors. Though not mandatory, many installers prefer insulated throats for enhanced conductor protection.
LFMC fittings may also be suitable for adverse environments when used with enclosures rated for such conditions. These applications are covered by:
- ANSI/NEMA 250 – Enclosures for Electrical Equipment (1000 Volts Maximum)
- ANSI/UL 50 – Enclosures for Electrical Equipment
Fittings for LFMC are typically identified by trade sizes ranging from 3/8 inch to 4 inches. Recent updates include metric designators corresponding to these sizes for consistency and ease of selection.
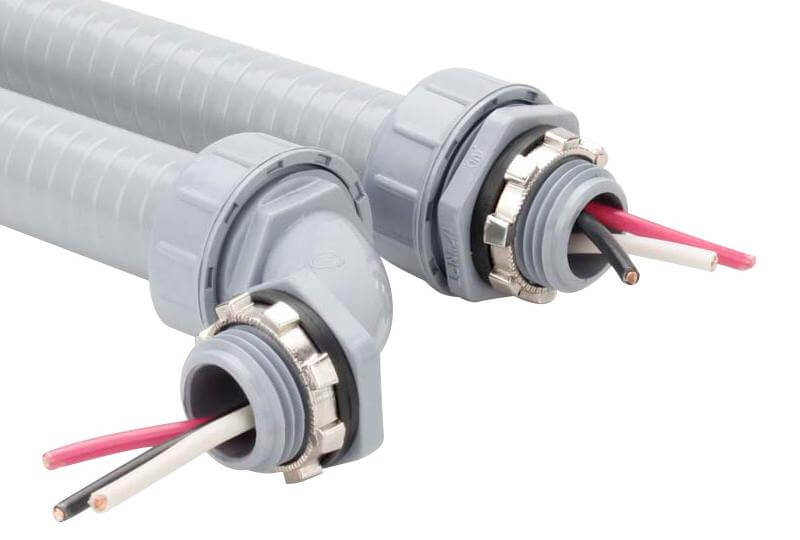
4.4 Fittings for Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit (LFNC)
Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit (LFNC) is designed to protect electrical conductors in both exposed and concealed locations where moisture, vapors, or solids may be present. It is also permitted for outdoor use and direct burial when specifically listed for such purposes. LFNC fittings are essential components to ensure the conduit system remains watertight and mechanically secure.
Types of LFNC and Connector Requirements
LFNC is available in three types:
Type LFNC-A: Features a smooth, seamless inner core and cover, with reinforcement layers in between.
Type LFNC-B: Has a smooth inner wall with integrated reinforcement.
Type LFNC-C: Corrugated inside and outside without internal reinforcement.
Requirements for LFNC fittings: Fittings used with LFNC must comply with UL 1660 – Standard for Liquidtight Flexible Nonmetallic Conduit and adhere to NEC Article 356. The NEC clearly requires that fittings and connectors be used only with the specific wiring methods for which they are designed and listed. This means that only fittings approved and tested for LFNC use should be used, and they must carry the appropriate markings.
It’s also important to note:
Fittings for LFNC should not be used in concealed raceway installations unless specifically listed for that use.
Fittings must ensure a liquidtight seal at entry points into enclosures or equipment.
LFNC fittings may include locknuts and sealing rings to prevent water ingress.
Some fittings may also include an insulated throat to protect conductors from abrasion.
Additionally, LFNC fittings are often identified by trade size, ranging from 3/8 inch to 4 inches, and recent updates have introduced metric size designators that correspond to these trade sizes.
Application Considerations
LFNC fittings may also be used in adverse environments when combined with appropriate enclosures. Compliance with ANSI/NEMA 250 and ANSI/UL 50 standards is required for “Type Rated” applications, ensuring that the entire assembly can perform reliably under specific environmental conditions.
By selecting properly listed LFNC fittings, installers can guarantee that the conduit system is compliant with national electrical standards while providing excellent protection against moisture, dust, and mechanical stress.
5. Guidelines for Choosing the Right Flexible Conduit Connector
Selecting the appropriate flexible conduit connector is crucial to ensure the safety, reliability, and longevity of an electrical installation combined with material. We outlines key considerations and guidelines to help you make an informed decision based on environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, and compliance standards in the following.
5.1 Assess Environmental Conditions
The first step in choosing a flexible conduit connector is to evaluate the environmental factors where the conduit system will be installed. Connectors must be able to withstand exposure to moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes.
5.1.1 Protection Against Moisture and Dust
For environments prone to water exposure, dust, or debris, it is essential to select connectors with appropriate ingress protection (IP) ratings:
- IP67 and IP68 rated connectors offer effective protection against dust and temporary or continuous water immersion.
- Liquid-tight connectors equipped with sealing gaskets are ideal for outdoor or industrial applications, providing superior waterproofing.
5.1.2 Temperature Resistance
Temperature fluctuations can impact the durability of conduit connectors:
- In high-temperature environments, use connectors made from stainless steel or high-temperature-rated nylon to prevent softening or degradation.
- PVC connectors are suitable for installations in moderate temperatures but may not perform well under extreme heat.
5.1.3 Chemical Resistance
Exposure to chemicals requires careful material selection:
- PVC connectors resist mild acids and general industrial chemicals, making them appropriate for laboratories and light industrial settings.
- Stainless steel connectors are recommended for harsh chemical or marine environments due to their high corrosion resistance.
- Nylon-coated connectors provide added protection against oils, solvents, and grease, suitable for automotive, food processing, and similar industries.
5.2 Define Mechanical Requirements
After evaluating environmental factors, the next step is to determine the mechanical stresses the connectors will encounter, such as vibration, movement, or physical impact.
5.2.1 Vibration Resistance
For installations exposed to continuous vibration or movement:
Use corrugated metal connectors or liquid-tight connectors with secure locking mechanisms.
Threaded connectors with locknuts or locking rings prevent loosening in vibration-prone environments.
5.2.2 Flexibility and Movement
In applications where the conduit system requires frequent bending or repositioning:
Choose high-flexibility connectors made from nylon or liquid-tight flexible metal conduit (LFMC) connectors.
Swivel connectors are recommended when rotational movement is needed, reducing stress on the conduit.
5.2.3 Impact Resistance
For environments with a risk of mechanical impact:
- Metallic connectors (such as stainless steel or aluminum) are preferred in heavy-duty environments like construction sites or manufacturing plants.
- Heavy-duty plastic connectors offer good impact resistance while remaining lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
5.3 Verify Compliance and Certifications
The final step is to ensure the selected flexible conduit connectors meet all applicable safety standards and industry regulations.
5.3.1 Relevant Standards
Several standards govern the use and performance of flexible conduit systems and connectors:
- NEC® Article 350 – Specifies requirements for flexible metal conduit (FMC) and associated fittings.
- UL 1 – Defines safety and performance requirements for flexible conduits and fittings.
- IEC 61386 – Provides international standards for conduit systems to ensure global reliability and safety.
5.3.2 Essential Certifications
When selecting connectors, verify the following certifications to ensure compliance:
- UL Listing – Indicates the product has passed safety and performance testing for North American markets.
- CSA Certification – Required for installations in Canada.
- RoHS Compliance – Ensures the product is free from hazardous substances, meeting requirements for the European Union and other global markets.
6. Conclusion
Flexible conduit connectors are an essential component in modern electrical and industrial wiring systems. Their primary function is to provide secure, stable, and protective connections between flexible conduits and electrical equipment, ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical circuits in a wide range of applications. From standard straight connectors to 90-degree elbows, explosion-proof designs, and various material options like stainless steel, galvanized steel, aluminum, PVC, and nylon-coated versions, each connector type serves a specific purpose to meet diverse installation needs.
Choosing the right connector requires careful consideration of environmental conditions, mechanical stresses, and regulatory compliance. Whether it’s for an indoor residential project, an outdoor industrial facility, or a hazardous location, selecting the appropriate connector ensures long-term performance, reduces maintenance needs, and improves overall system safety.
At Ctube, we are committed to providing high-quality flexible conduit systems and accessories tailored to meet the demands of global customers. As a leading manufacturer of electical conduits, Ctube offers a comprehensive range of products such as PVC conduit, solar UPVC conduit and low smoke halogen free conduit. They comply with international standards such as UL, CSA, IEC, and AS/NZS 2053. Our flexible conduit connectors are manufactured with precision, durability, and safety in mind, ensuring excellent performance in even the most challenging environments.
Thanks for reading, and hope this post helpful, any projects requirement, contact us.