Table of Contents
Toggle1. Introduction
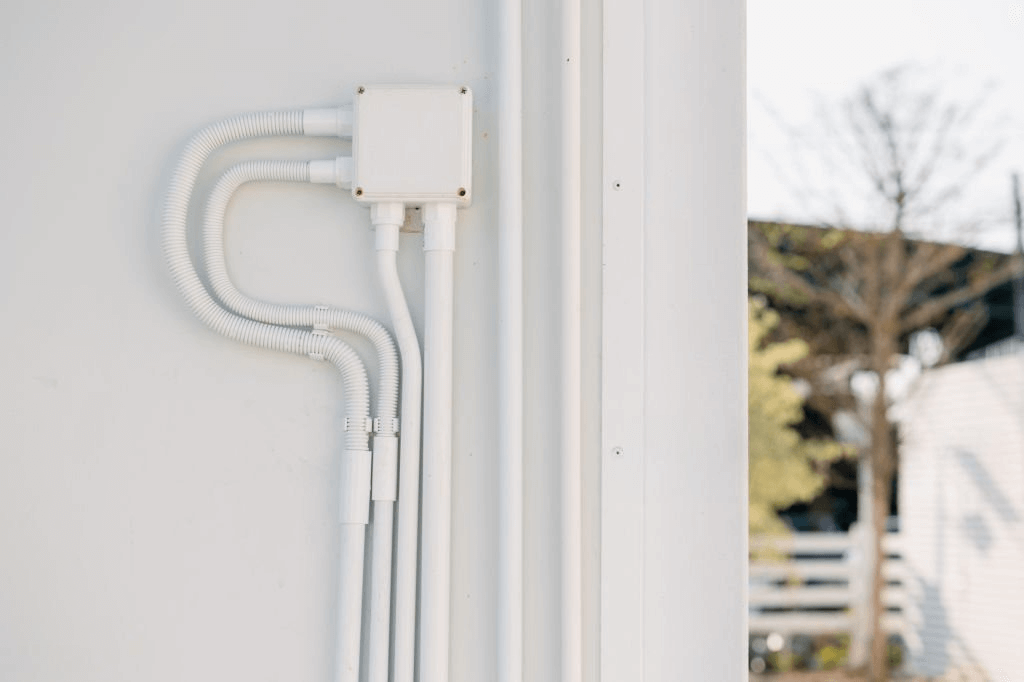
Outdoor electrical conduit systems play a vital role in protecting and supporting electrical wiring in environments where exposure to the elements is a concern. These conduit systems are designed to shield electrical cables from weather conditions such as rain, snow, wind, and extreme temperatures, ensuring the safety, longevity, and reliability of electrical installations.
The purpose of this post is to offer a detailed and comprehensive guide on outdoor electrical conduit systems, helping readers fully understand their importance, how to choose the right type, and how to properly install and maintain these systems. Whether you are an electrician, contractor, homeowner, or someone involved in outdoor electrical projects, this guide aims to equip you with all the necessary information to make informed decisions.
2. Understanding Functions of Outdoor Electrical Conduits
Outdoor electrical conduits are protective tubes or channels used to encase and protect electrical wires and cables from environmental hazards. These conduits are typically made from various materials, including plastic (such as PVC), metal (like steel), or specialized coatings, and are designed to shield electrical wiring from external factors such as weather, mechanical damage, and chemical exposure.
In outdoor environments, electrical wiring is often exposed to conditions that can cause rapid deterioration, resulting in safety risks, electrical failures, and potential system downtime. Outdoor conduits act as a safeguard, ensuring that electrical systems remain functional, safe, and compliant with relevant safety regulations and codes.
- Protection Against Physical Damage: One of the most important functions of outdoor electrical conduits is providing physical protection to cables and wires. Whether the conduit is placed above ground or underground, it acts as a shield against external forces, such as impact from falling debris, pressure from construction activities, or animal interference. For example, in high-traffic areas, an outdoor conduit can protect wiring from accidental cuts or punctures that might otherwise expose live wires.
- Resistance to Weather and Environmental Conditions: Unlike indoor installations, outdoor electrical wiring is subjected to various environmental stressors, including direct sunlight, rain, snow, freezing temperatures, and humidity. These conditions can cause degradation of electrical insulation, corrosion of wiring, and potential short circuits. Outdoor electrical conduits are designed to resist these weather-related challenges. For instance, PVC conduits often have UV-resistant properties to prevent degradation from exposure to the sun’s harmful rays, while metal conduits provide an added layer of defense against extreme temperatures and moisture.
- Prevention of Electrical Hazards: Conduits are crucial for electrical safety. They prevent accidental contact with live electrical wires by containing the cables within a protective enclosure. This is especially critical in outdoor environments where electrical systems might be exposed to humans, animals, or conductive materials. For example, if a conduit were to be damaged, the wires inside would still be contained and insulated, reducing the risk of electrical shocks or fires. Many outdoor conduit systems are also built with grounding capabilities, ensuring that if a fault occurs, the electrical current is safely directed to the ground.
- Compliance with Electrical Codes and Regulations: In most regions, the installation of electrical conduits, particularly in outdoor settings, is required by law to meet specific safety standards and codes, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States or local equivalent standards in other countries. These codes dictate how wiring systems should be installed to minimize risks such as fire, electrical shock, and damage due to environmental factors. The use of outdoor conduits ensures that electrical installations comply with these regulations and provide a higher level of safety for both the installation crew and the end-users.
- Organizational Benefits: Outdoor conduits also provide an organizational benefit by neatly bundling multiple cables and wires. This is particularly beneficial in environments where numerous electrical systems, such as lighting, security systems, irrigation, and more, need to be integrated into the same space. A well-organized conduit system can make maintenance easier by consolidating and protecting cables, reducing the chance of tangles, and simplifying repairs or upgrades when necessary.
- Aesthetic Considerations: In certain residential or commercial applications, outdoor conduits can also play a role in improving the aesthetic appeal of an installation. Instead of having exposed wires running along walls, ceilings, or fences, the wires can be routed through conduits that hide them from view, resulting in a cleaner, more professional appearance. This is particularly relevant in outdoor spaces like gardens, patios, or rooftops, where aesthetics and functionality must be balanced.
3. Criteria for Classifying Outdoor Electrical Conduits
Outdoor electrical conduits can be classified based on various environmental conditions and use scenarios.
3.1 Outdoor Above-Ground Use
- Conduits designed for above-ground use are exposed to the elements and must withstand conditions such as UV radiation, high temperatures, and varying weather conditions.
- Requirements: Conduits in this category must have UV protection to prevent degradation from sunlight, as well as the ability to endure temperature fluctuations and moisture from rain or humidity.
3.2 Outdoor Underground Use
- Burial Requirements: Conduits used underground may either be directly buried or require additional protection such as concrete encasement. The burial depth and method depend on the type of conduit and local regulations.
- Direct Burial: Some conduits are suitable for direct burial, typically requiring a minimum depth of 18 inches.
- Concrete Encapsulation: Other conduits, especially metal ones, may need to be wrapped in concrete to protect them from soil pressure, moisture, and mechanical damage.
- Depth of Burial: Conduits for underground use have specific depth requirements, which can vary based on conduit material and application (e.g., shallow vs. deep burial).
3.3 Exposure to Strong Ultraviolet (UV) Light
- Conduits in areas with high exposure to UV light, such as rooftops or coastal regions, must be able to resist the damaging effects of sunlight, which can cause cracking, brittleness, or degradation over time.
- Requirement: UV-resistant coatings or special additives in the conduit material are needed for long-lasting durability.
3.4 High-Temperature Environments
- Conduits installed in areas that experience extreme heat, such as deserts or near industrial plants, need to be capable of withstanding high temperatures without warping or degrading.
- Requirement: The conduit material should be rated for high-temperature resistance to maintain its integrity in these conditions.
3.5 Humid or Wet Environments
- In locations prone to heavy rainfall, high humidity, or water exposure (e.g., basements, coastal areas), the conduit material should provide waterproofing and prevent moisture penetration.
- Requirement: Waterproof, rust-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials are needed to ensure that the conduits do not degrade in these conditions.
3.6 Corrosion and Rust Resistance
- Conduits exposed to corrosive elements such as salty air, chemicals, or industrial pollutants require special protection against rust and corrosion.
- Requirement: Conduits made from corrosion-resistant materials, such as galvanized steel, stainless steel, or specially treated PVC, are required for such environments.
4. Different Types of Outdoor Electrical Conduits
Selecting the right electrical conduit based on the specific environmental conditions is critical for ensuring an electrical system’s safety, longevity, and efficiency. The choice of material determines how well the conduit performs under various stresses, such as exposure to moisture, UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and physical impacts.
In the following, we introduce different materials used for electrical conduits, comparing their advantages and disadvantages to provide readers with practical guidance for making the best choice.
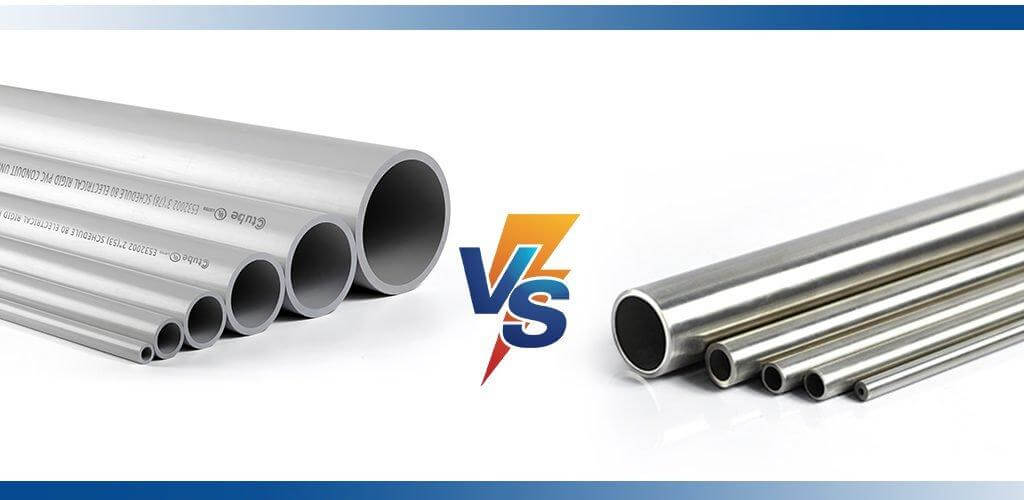
4.1 PVC Electrical Conduit
4.1.1 Rigid PVC Conduit
Key Features: Rigid PVC conduit is one of the most commonly used types of electrical conduit due to its excellent durability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of installation. It is designed to provide robust protection for electrical wiring systems in various outdoor environments.
- Durability and Strength: Rigid PVC conduit is highly resistant to physical damage, including impacts, which makes it ideal for protecting electrical cables in exposed areas.
- Corrosion Resistance: Unlike metal conduits, PVC is not prone to rust or corrosion, making it suitable for installations in coastal regions or wet environments.
- Cost-Effective and Easy to Install: Rigid PVC is affordable compared to metal conduits, and its lightweight nature makes it easy to transport and install, even for DIY projects.
- UV Resistance: While PVC is naturally susceptible to UV degradation, modern formulations include UV stabilizers to enhance its outdoor durability.
Ideal Applications: Rigid PVC conduit is typically used in residential and light commercial installations where a balance between strength, cost, and ease of installation is required. It is ideal for outdoor areas where electrical cables need to be protected from physical damage but aren’t exposed to extreme UV or moisture conditions.
Distinguishing Feature: The most notable advantage of rigid PVC conduit is its cost-efficiency, offering a robust solution for general outdoor use while being easy to handle and install.
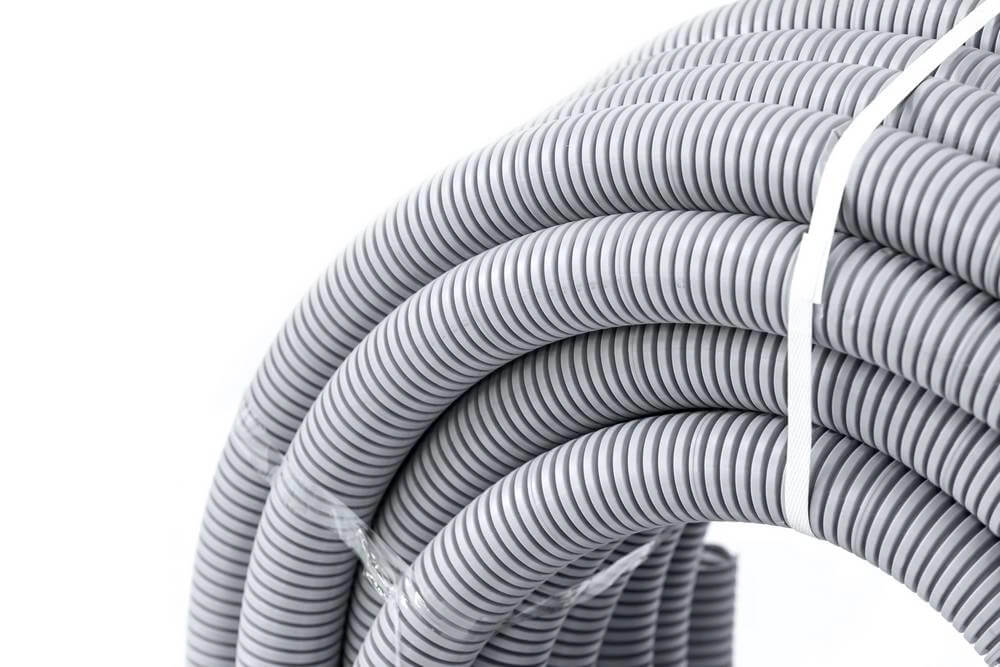
4.1.2 Flexible PVC Conduit
Key Features: Flexible PVC conduit is designed for installations that require adaptability and easy routing. Its flexibility allows it to bend around obstacles and fit into tight spaces, offering a unique set of advantages over rigid conduits.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:Flexible PVC can be bent around corners and obstacles without the need for special fittings, making it ideal for installations that involve tight turns or complex routing.
- Moisture and UV Resistance:Flexible PVC conduit comes with UV-resistant formulations, enabling it to withstand direct sunlight exposure and outdoor weather conditions.
- Lightweight and Easy to Install:Similar to rigid PVC, flexible PVC conduit is lightweight, making it easy to install in a variety of outdoor applications.
- Protection in Constrained Spaces:Its flexibility makes it an excellent choice for installations where traditional rigid conduit might be difficult to install.
Ideal Applications: Flexible PVC conduit is commonly used in residential and industrial applications where adaptability and ease of installation are essential. It is particularly useful in areas that require frequent adjustments or tight turns, such as in garden lighting, HVAC systems, or temporary outdoor setups.
Distinguishing Feature: The key feature of flexible PVC conduit is its outstanding flexibility, which makes it perfect for installations that need to be routed around corners or adjusted frequently.
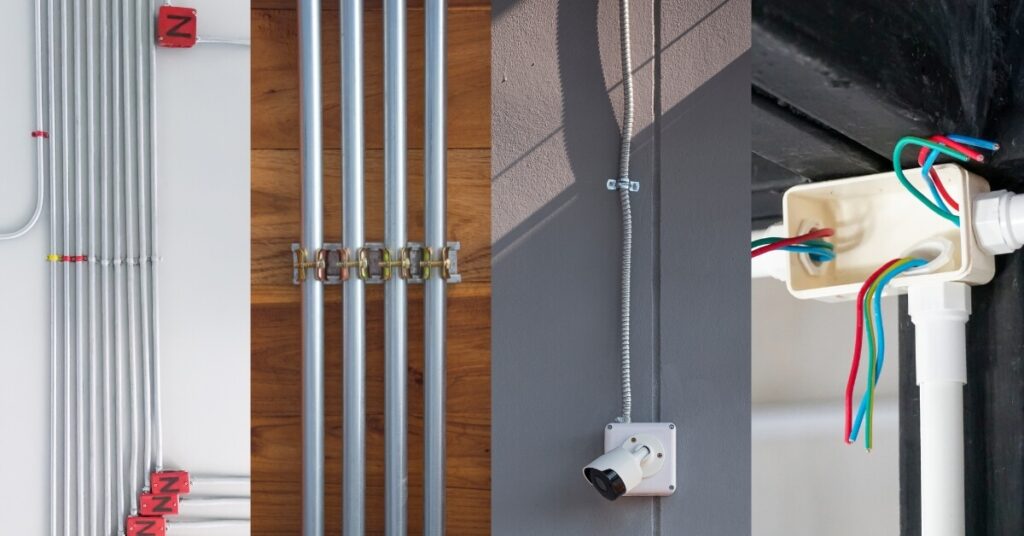
4.2 Metal Conduits
Metal conduits offer the most robust protection for electrical systems, making them ideal for installations that need to endure physical stress, high temperatures, or corrosive environments.
4.2.1 Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT)
Key Features:
- Lightweight and Thin-Walled:EMT is thinner and lighter than other metal conduits, which makes it easier to handle and install.
- Cost-Effective:EMT is an affordable option compared to heavier metal conduits like RMC or IMC.
- Corrosion Resistance:Although not as resistant to corrosion as other metal conduits, EMT can be galvanized to offer some protection against rust.
Ideal Applications: EMT is commonly used in dry locations and areas where physical protection is needed without significant exposure to moisture or harsh outdoor elements. It is ideal for indoor applications or for residential and light commercial installations where cost and ease of installation are priorities.
Distinguishing Feature: EMT is preferred for light-duty outdoor applications where physical strength is required but the installation environment is not exposed to extreme weather or corrosive conditions.
4.2.2 Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC)
Key Features:
- Stronger Than EMT:IMC is more robust and thicker than EMT, offering increased protection for electrical cables.
- Corrosion Resistance:Galvanized IMC provides strong protection against rust and corrosion, making it ideal for use in coastal or industrial environments.
- Versatility for Outdoor Use:IMC is versatile and can be used in both indoor and outdoor applications, offering protection against mechanical damage.
Ideal Applications: IMC is suitable for industrial, commercial, and residential applications where superior strength and corrosion resistance are required. It is often used in exposed outdoor installations or areas exposed to chemicals and moisture.
Distinguishing Feature: IMC provides a combination of strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh outdoor environments where higher levels of protection are needed.
4.2.3 Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC)
- Heavy Duty and Thick-Walled:RMC is the most robust metal conduit, offering superior protection for wiring systems in extreme conditions.
- Fire-Resistant:RMC is highly resistant to fire, making it ideal for high-risk industrial areas.
- Corrosion Resistance:Galvanized RMC is resistant to rust and corrosion, offering durability in challenging environments like coastal areas or locations with high humidity.
Ideal Applications: RMC is used in high-risk industrial and commercial environments, as well as outdoor areas where electrical wiring needs maximum protection from physical damage, extreme weather, and potential fire hazards.
Distinguishing Feature: RMC is the strongest and most durable metal conduit, offering the highest level of protection against both mechanical damage and environmental stresses.
4.3 Liquidtight Conduit
- Waterproof Protection:Liquidtight conduit is specifically designed to provide protection against water and moisture, making it ideal for wet environments.
- Flexibility:It combines flexibility with excellent water resistance, allowing it to be installed in areas prone to moisture or flooding.
- Corrosion Resistance:Liquidtight conduit is resistant to oils, chemicals, and moisture, which extends its lifespan in harsh industrial or outdoor environments.
Ideal Applications: Liquidtight conduit is ideal for wet or damp environments, such as in coastal regions, industrial settings, or areas exposed to frequent water exposure.
Distinguishing Feature: The standout feature of liquidtight conduit is its waterproofing capabilities, which make it perfect for installations in moisture-prone areas.
4.4 Fiberglass Conduit (RTRC)
Fiberglass conduit, also known as Reinforced Thermosetting Resin Conduit (RTRC), is a lightweight yet durable solution designed to handle extreme environmental and industrial conditions. It is valued for its strength, corrosion resistance, and adaptability in specialized applications.
- Chemical Resistance:Fiberglass conduit excels in environments exposed to harsh chemicals, including solvents, oils, and corrosive gases, making it ideal for industrial and petrochemical settings.
- Weatherproofing:Its high resistance to UV radiation and moisture makes fiberglass conduit suitable for outdoor use, even in areas with prolonged exposure to harsh sunlight or heavy rain.
- Thermal Stability:With a wide temperature tolerance range, fiberglass conduit remains stable in both extremely high and low temperatures, offering reliability in demanding climates.
- Electrical Properties:As a non-conductive material, fiberglass conduit provides excellent insulation, eliminating risks of electrical conductivity or interference in sensitive installations.
- Durability and Lightweight:Despite its strength, fiberglass conduit is significantly lighter than metal alternatives, reducing transportation and installation effort and cost.
Installation Considerations:
Fiberglass conduit is easy to handle and can be joined using adhesive or mechanical fittings. It can be cut with standard tools, and its lightweight nature simplifies installation in overhead or remote locations. Proper sealing of joints is essential to maintain its watertight integrity in wet or underground installations.
Ideal Applications:
- Petrochemical plants and industrial facilities where exposure to corrosive agents is prevalent.
- Outdoor installations in regions with intense UV exposure or fluctuating temperatures.
- Underground electrical systems in coastal areas prone to saltwater corrosion.
- Power generation and renewable energy projects, including wind and solar farms.
Distinguishing Feature:
Fiberglass conduit stands out for its exceptional resistance to both chemical and environmental factors, making it the popular choice for demanding industrial and outdoor applications requiring long-term durability and reliability.
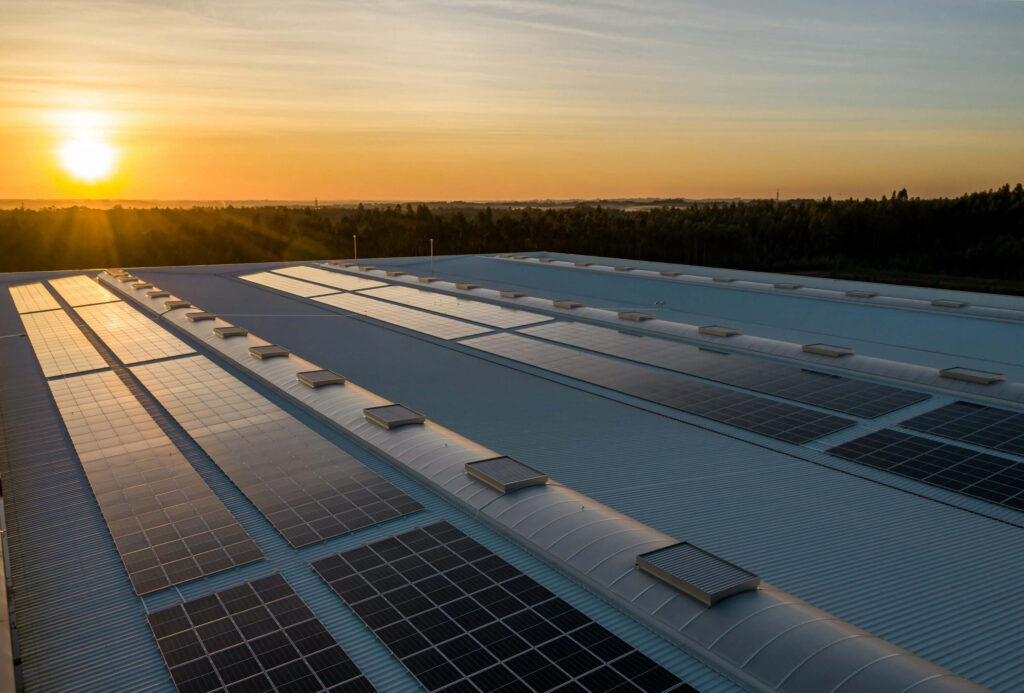
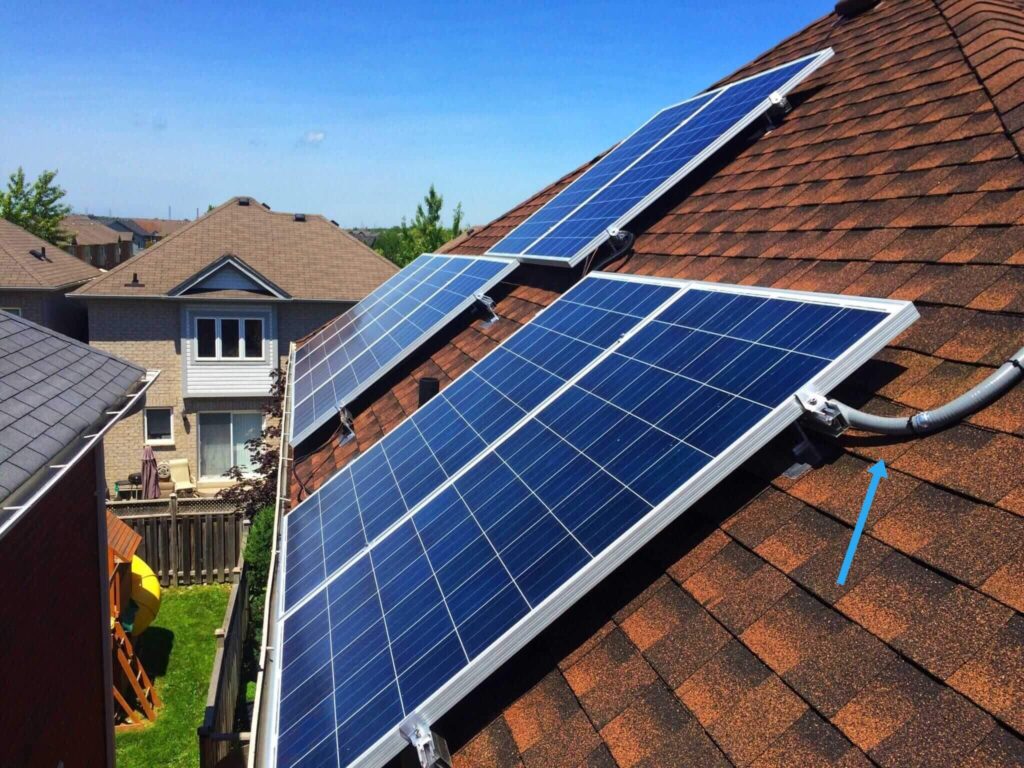
4.5 Photovoltaic (Solar) Conduit
- UV and Heat Resistance:Photovoltaic conduit is engineered to handle high UV exposure and temperature fluctuations, which are typical for solar panel installations.
- Durability for Outdoor Use:Designed to withstand expansion and contraction due to sunlight exposure, ensuring long-lasting protection for solar system components.
- Weatherproofing:Photovoltaic conduit is resistant to weather extremes, including UV rays and high temperatures, ensuring continuous protection for solar panels in all climates.
Ideal Applications: Photovoltaic conduit is designed for solar energy installations, offering robust protection for wiring systems in solar power setups exposed to harsh outdoor conditions.
Distinguishing Feature: Photovoltaic conduit is specifically formulated for solar power systems, offering protection against UV rays and temperature extremes, making it essential for outdoor solar installations.
5. Choosing the Right Outdoor Conduit
5.1 Factors to Consider
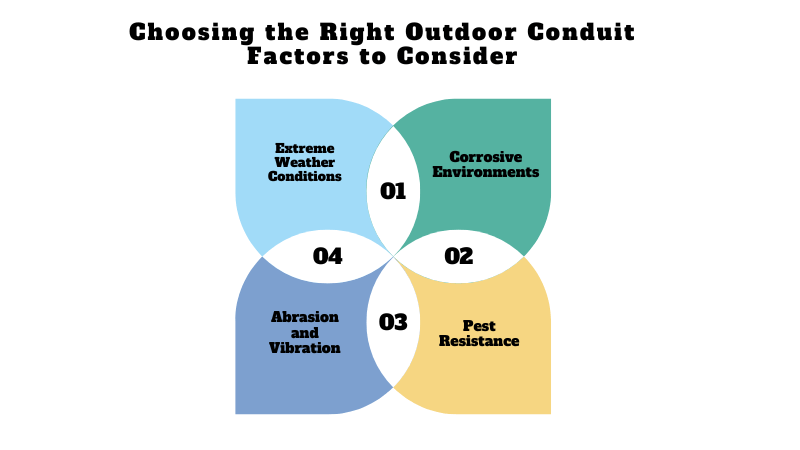
5.1.1. Environmental Considerations
Extreme Weather Conditions: Outdoor conduits must withstand temperature fluctuations, from freezing winters to scorching summers. Materials like RMC or specially formulated PVC are ideal for such conditions.
Corrosive Environments: In coastal or industrial regions, conduits face exposure to saltwater or chemical fumes. Corrosion-resistant materials, like PVC or coated metal, are essential.
Abrasion and Vibration: Outdoor installations near machinery, railroads, or high-traffic areas may require conduits with high abrasion resistance or flexibility to tolerate vibrations without cracking.
Pest Resistance: Underground installations in rural areas might face pest intrusion. Metal conduits or rigid PVC conduits can prevent damage caused by rodents or insects.
5.1.2. Compliance with Local Codes and NEC Standards
Specific Depth Requirements: Depending on the type of conduit, burial depths can range from shallow (PVC at 6–12 inches) to deep installations requiring encasement in concrete.
Special Zone Regulations: Conduits in flood-prone areas must meet stricter moisture-resistance standards, while areas with frequent lightning storms may require metal conduits for grounding.
5.1.3. Functionality and Maintenance
Ease of Installation: Flexible conduits reduce installation time in complex environments, while rigid conduits ensure fewer points of failure over time.
Maintenance Needs: Materials like PVC, which are resistant to rust and require minimal upkeep, are preferred in remote areas where regular maintenance is difficult.
Aesthetic Considerations: In visible outdoor installations, the color or finish of the conduit might need to blend with the surroundings or meet aesthetic standards, such as UV-stabilized finishes.
5.2 Material Selection
5.2.1 PVC vs. Metal Conduit Selection
PVC Conduits:
Newer formulations include low-smoke halogen-free PVC, ideal for areas requiring minimal toxic gas emission in case of fire.
Advances in UV-resistant PVC ensure better performance for long-term outdoor use.
While lightweight and flexible, PVC is less effective in areas requiring grounding unless paired with grounding wires.
Metal Conduits:
Stainless Steel Conduits: Offering superior corrosion resistance, these are ideal for marine environments but are significantly more expensive.
Aluminum Conduits: Lighter than steel and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is suitable for installations requiring reduced weight without compromising durability.
Specialized Coatings: Galvanized or epoxy-coated conduits provide additional protection against rust and wear.
5.2.2 Flexible vs. Rigid Conduit Options
Flexible Conduits:
Polyethylene-Based Flexible Conduits: A modern alternative that is lightweight, water-resistant, and suitable for above-ground use in low-impact areas.
Shielded Flexible Conduits: Provide added electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for installations near sensitive electronics.
Rigid Conduits:
Pre-Cut Rigid Conduits: Save time during installation and ensure consistency in alignment for industrial-scale projects.
Customized Lengths and Diameters: Manufacturers often offer tailor-made rigid conduits to suit specific project needs, such as oversized diameters for high-capacity cables.
5.3 Specialized Conduit Options
Adding to the traditional categories of PVC and metal, specialized conduits cater to niche needs:
- Liquidtight Flexible Metal Conduits (LFMC): A hybrid solution combining flexibility with moisture resistance, commonly used in areas with intermittent water exposure.
- Fiberglass Conduits: Lightweight and non-conductive, ideal for projects requiring non-metallic materials with high strength and durability.
- Photovoltaic Conduits: Designed specifically for solar energy installations, these conduits resist UV, high temperatures, and outdoor exposure over decades.
6. Conclusion
The process of choosing the right outdoor conduit extends beyond basic material comparisons. By evaluating factors like environmental challenges, regulatory requirements, maintenance considerations, and specialized project demands, you can select the most effective and reliable conduit. With innovations in materials and designs, modern conduits now offer tailored solutions for diverse scenarios, from residential landscapes to industrial complexes. By making informed choices, you not only ensure safety and compliance but also optimize performance and longevity in outdoor electrical systems.
Ctube is a professional manufacturer specializing in high-quality PVC electrical conduits and fittings designed to meet the diverse needs of residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Outdoor electrical conduits are critical for protecting wiring against environmental challenges such as UV exposure, temperature fluctuations, moisture, and physical impacts. Ctube specializes in manufacturing a diverse range of conduit types, ensuring there is a solution for every outdoor application, whether above ground, underground, or in extreme weather conditions.
Ctube offers a comprehensive range of products, including PVC Rigid Conduit, Electrical Non-Metallic Tubing (ENT), Low Smoke Halogen-Free (LSZH) conduits, Photovoltaic (Solar) conduits, and a variety of conduit fittings.
What sets Ctube apart is its focus on durability and compliance. All products undergo rigorous testing to ensure exceptional performance, including resistance to UV rays, corrosion, and environmental stress. Ctube’s conduits are designed to meet international safety and quality standards, such as UL certification, ASTM, and NEC compliance, guaranteeing customers products they can trust.
In addition to its standard offerings, Ctube provides tailored solutions for specific project requirements, such as customized conduit colors and sizes. If your have projects requirements, feel free to contact us.
Thanks for your reading and good luck with your projects.
FAQs
1. Can PVC conduits be used for underground installations?
Yes, PVC conduits are widely used for underground installations, particularly in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. Schedule 40 PVC conduit is the most common choice for general underground applications due to its cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and resistance to environmental factors like moisture and corrosion. It is suitable for direct burial as long as it is installed at the proper depth—typically 18 to 24 inches—depending on local codes and environmental conditions. In areas with heavy traffic or high impact, Schedule 80 PVC conduit, with thicker walls, is recommended for enhanced durability.
2. What depth should underground conduits be buried?
The burial depth for different types of conduit varies based on the material and its specific application. PVC conduits (Schedule 40 and Schedule 80) are typically buried between 18 to 24 inches, with Schedule 80 offering more protection for areas with higher impact or traffic. Metal conduits like EMT are usually buried at 6 to 18 inches, while IMC and RMC can be buried deeper, ranging from 6 to 24 inches, depending on environmental factors.
3. Do outdoor conduits require special maintenance?
Yes, outdoor conduits require special maintenance to ensure their longevity and optimal performance, especially when exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for signs of wear, damage, or degradation caused by elements like UV radiation, extreme temperatures, or physical impact. PVC conduits, for example, can become brittle over time when exposed to prolonged UV exposure, so it is important to check for cracks or fading and replace sections as necessary. Metal conduits like EMT or RMC may be prone to corrosion, especially in humid or coastal areas, so periodic inspections for rust or oxidation are crucial. Applying anti-corrosion coatings can help extend their lifespan.