جدول المحتويات
تبديل1. التعريف والمقدمة القياسية الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية
في المشهد المتطور باستمرار للبنية التحتية الكهربائية، يعد اختيار الأنابيب الموصلة للكهرباء قرارًا بالغ الأهمية يؤثر على كفاءة ومتانة وسلامة التركيبات. تعمل الأنابيب الموصلة للكهرباء كممرات أساسية، حيث تحمي الأسلاك الكهربائية من التلف المادي والرطوبة والمخاطر البيئية الأخرى. ومن بين خيارات الأنابيب الموصلة للكهرباء المتنوعة المتاحة، حظيت الأنابيب غير المعدنية الكهربائية باهتمام كبير لتعدد استخداماتها وعمليتها.
تهدف هذه المقالة إلى تقديم استكشاف شامل لأنابيب التوصيل الكهربائية، مع تسليط الضوء على خصائصها المميزة وفوائدها وتطبيقاتها المتنوعة. من خلال التعمق في مزاياها مقارنة بأنابيب التوصيل المعدنية التقليدية وتقديم رؤى عملية حول تقنيات التركيب، نهدف إلى تزويد القراء بالمعرفة اللازمة لاتخاذ قرارات مستنيرة في مشاريع البنية التحتية الكهربائية.
1.1 التعريف
تم تصميم ENT لحماية وتمرير الأسلاك الكهربائية في مختلف أنواع المباني، وتتميز ENT بمرونتها وخفة وزنها ومقاومتها للتآكل. كما أن قدرتها على الانحناء والتكيف مع التركيبات المعقدة تجعلها الخيار الأمثل للمشاريع السكنية والتجارية على حد سواء.
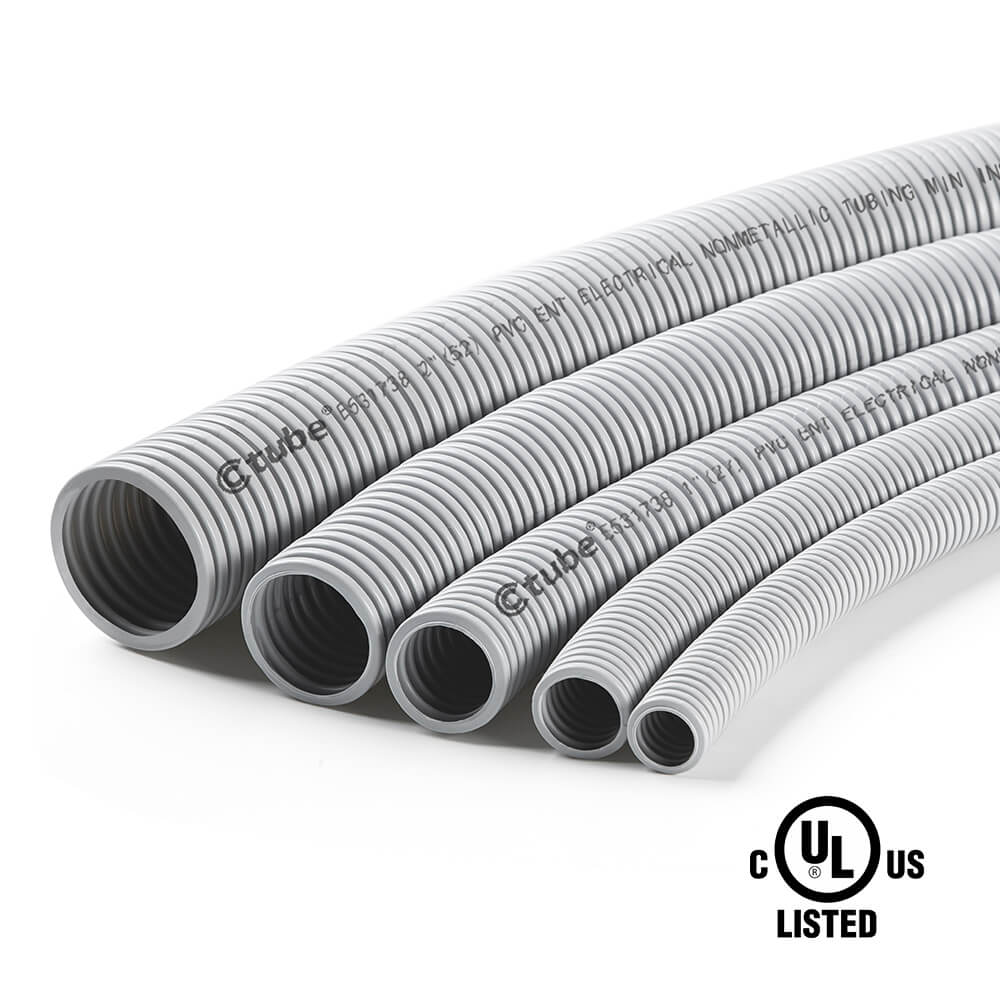
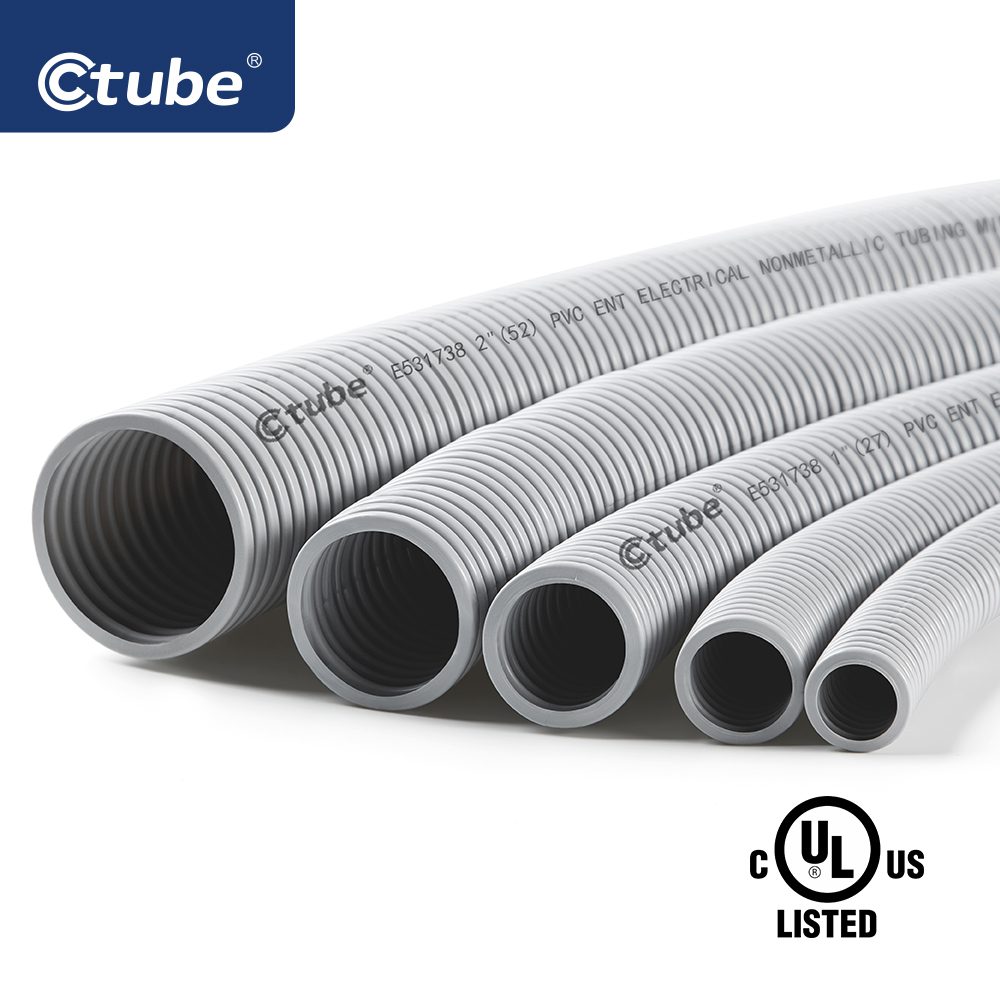
الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT) عبارة عن أنبوب كهربائي مرن ومموج متوفر بأقطار تتراوح من 1/2 بوصة إلى 2 بوصة (13 مم إلى 51 مم)، وعادة ما تكون مصنوعة من مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد. وفقًا لـ NEC، داخل المباني التي يبلغ الحد الأقصى لها ثلاثة طوابق، يتم إخفاء ENT عمومًا داخل الجدران أو الأرضيات أو الأسقف، على الرغم من أنه يمكن تركها مكشوفة إذا لم تكن معرضة لخطر التلف الميكانيكي. بالنسبة للمباني التي يزيد ارتفاعها عن ثلاثة طوابق، يجب إخفاء ENT، ويجب أن يفي هذا الإخفاء بمتطلبات تصنيف التشطيب لمدة 15 دقيقة.
1.2 مقدمة قياسية
قد تختلف معايير الشهادة والاختبار المطلوبة للأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT) حسب المنطقة والرموز الكهربائية المحددة. ومع ذلك، فيما يلي بعض المعايير والاختبارات المرجعية الشائعة للأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT).
1.2.1 يو ال 1653
UL 1653 هو المعيار المعترف به للأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT). يحدد هذا المعيار متطلبات السلامة والأداء لمنتجات الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية، بما في ذلك المواصفات الخاصة بالأبعاد والبناء والمواد ومنهجيات الاختبار.
1.2.2 CSA C22.2 رقم 227.1
CSA C22.2 رقم 227.1 هو معيار كندي يحدد متطلبات الأنابيب غير المعدنية المستخدمة في التركيبات الكهربائية، بما في ذلك الأنابيب الكهربائية الصناعية. يغطي هذا المعيار جوانب مثل المواد والبناء والأبعاد والأداء وطرق الاختبار ذات الصلة.
1.2.3 اختبار اللهب FT4
على الرغم من أن اختبار FT4 لا يقتصر على ENT، إلا أنه اختبار حاسم لمقاومة الحرائق يُستخدم لتقييم خصائص انتشار اللهب للكابلات التي قد يتم تركيبها داخل أو بجانب أنابيب ENT. هذا الاختبار، وهو جزء من معيار جمعية المعايير الكندية (CSA) C22.2 رقم 0.3، يقيم انتشار اللهب من خلال تعريض الكابلات لمصدر اشتعال اللهب الرأسي، وقياس مقاومة الكابل لانتشار اللهب وإمكانية مساهمته في انتشار الحريق في التركيبات الرأسية.
1.2.4 قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC)
إن معيار NEC هو معيار معتمد على نطاق واسع في الولايات المتحدة الأمريكية يوفر إرشادات شاملة للتركيبات الكهربائية. وهو يتضمن متطلبات محددة لاستخدام الأنابيب، بما في ذلك ENT، ويغطي جوانب مثل الحجم المناسب وطرق التركيب والتأريض لضمان أنظمة كهربائية آمنة ومتوافقة.
1.2.5 NEMA TC-13
NEMA TC-13 تعني اللجنة الفنية 13 التابعة للجمعية الوطنية لمصنعي الأجهزة الكهربائية. وهي مسؤولة عن وضع معايير الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT)، وهو نوع من الأنابيب المستخدمة لحماية الأسلاك والكابلات الكهربائية وتوجيهها. الغرض من معايير NEMA TC-13 هو ضمان سلامة وموثوقية منتجات ENT. يستخدم المصنعون والموزعون والمثبتون والمفتشون هذه المعايير لضمان أن منتجات ENT تلبي الحد الأدنى من متطلبات السلامة والأداء.
يعد ضمان الامتثال لهذه المعايير والحصول على الشهادات ذات الصلة أمرًا بالغ الأهمية عند اختيار أنابيب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة. يضمن الامتثال أن تكون منتجات الأنف والأذن والحنجرة آمنة وموثوقة وتعمل كما هو متوقع في ظل ظروف محددة. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، غالبًا ما يكون الالتزام بالرموز والمعايير الكهربائية المحلية والدولية مطلوبًا قانونًا، مما يضمن أن التركيبات تلبي المتطلبات التنظيمية.
ومن خلال استيفاء معايير الشهادة هذه، يمكن للمصنعين ضمان جودة منتجاتهم ومتانتها للعملاء والهيئات التنظيمية، مما يوفر الثقة في استخدامها في مختلف التركيبات الكهربائية.
2. عملية التصنيع ومراقبة جودة أنابيب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة
2.1 عملية إنتاج أنابيب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة
تتضمن عملية إنتاج قنوات الأنف والأذن والحنجرة عملية البثق، باستخدام العديد من المواد والمعدات الرئيسية:
2.1.1 المواد المستخدمة
1. راتينج PVC: المادة الخام الأساسية التي توفر السلامة الهيكلية والقوة للقناة.
2. المثبتات: إضافات تعمل على تعزيز استقرار ومتانة مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد، مما يضمن قدرتها على تحمل الضغوط البيئية والحفاظ على خصائصها بمرور الوقت.
3. الملدنات: مواد تضاف إلى مادة PVC لتحسين مرونتها، مما يسمح لـ ENT بالانحناء والتكيف أثناء التركيب دون تشقق أو كسر.
4. مواد التشحيم: تستخدم لتسهيل عملية البثق، وتقليل الاحتكاك وضمان تدفق المواد بسلاسة عبر الآلات.
5. الأصباغ: إضافات اختيارية للتلوين، تستخدم لتحقيق خيارات الألوان المطلوبة لأنابيب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة.
2.1.2 خطوات الإنتاج
1. التحضير: يتم قياس المواد الخام مثل راتنج PVC، والمثبتات، والملدنات، ومواد التشحيم، والأصباغ بعناية وخلطها وفقًا لصيغ محددة لتحقيق الخصائص المطلوبة.
2. البثق: يتم تغذية المواد المختلطة في آلة بثق البولي فينيل كلوريد، حيث يتم تسخينها وإذابتها حتى تصل إلى حالة منصهرة. ثم يتم دفع البولي فينيل كلوريد المنصهر عبر قالب بثق، والذي يشكله في شكل الأنبوب المطلوب، مثل الأشكال الدائرية أو البيضاوية.
3. التبريد: عندما يخرج الأنبوب المبثوق من القالب، فإنه يمر عبر نظام تبريد. يعمل هذا النظام على تبريد مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد بسرعة لتصلبها في شكل الأنبوب النهائي، مما يضمن سلامة البنية ودقة الأبعاد.
4. القطع والقياس: بعد التبريد، يتم قطع الأنابيب إلى الأطوال المطلوبة باستخدام معدات القطع وتخضع لعمليات القياس لتلبية مواصفات القطر الدقيقة. وهذا يضمن التوافق مع التركيبات ويسهل عملية التركيب.
5. الطباعة (إن أمكن): إذا كانت معلومات المنتج أو المواصفات أو العلامات مطلوبة على القناة، فيمكن استخدام معدات الطباعة لتطبيق هذه التفاصيل، وتوفير معلومات التعريف والامتثال اللازمة.
2.2 تدابير مراقبة الجودة
لضمان موثوقية وسلامة أنابيب الكهرباء غير المعدنية، يتم تطبيق تدابير صارمة لمراقبة الجودة طوال عملية التصنيع. تم تصميم هذه التدابير للتأكد من أن كل منتج يفي بمعايير الصناعة ويعمل بشكل موثوق في ظل ظروف مختلفة:
2.2.1 فحوصات الأبعاد
- قياسات دقيقة: يخضع كل أنبوب لعمليات تفتيش صارمة باستخدام أدوات قياس متقدمة للتحقق من الامتثال لمتطلبات القطر والطول المحددة.
- أخذ العينات بشكل منتظم: يتم أخذ عينات من القنوات على فترات منتظمة أثناء الإنتاج لضمان الامتثال المستمر للمعايير الأبعادية.
2.2.2 اختبار الأداء
- قوة الشد: يتم اختبار عينات من مادة الأنابيب لمعرفة قوة الشد للتأكد من قدرتها على تحمل الضغوط الميكانيكية التي تواجهها أثناء التركيب والاستخدام.
- المرونة: يتم إجراء اختبارات المرونة للتأكد من أن الأنابيب يمكن أن تنحني وتنثني دون أن تتشقق أو تنكسر، مما يضمن إمكانية تركيبها في تكوينات مختلفة.
- مقاومة الصدمات: تخضع الأنابيب لاختبارات مقاومة الصدمات للتأكد من قدرتها على تحمل الصدمات والتأثيرات المادية دون التعرض لأضرار.
2.2.3 الاختبار البيئي
– التعرض للأشعة فوق البنفسجية: يتم اختبار الأنابيب بحثًا عن مقاومتها للأشعة فوق البنفسجية (UV) للتأكد من أنها يمكنها تحمل التعرض لأشعة الشمس لفترات طويلة دون أن تتدهور.
- مقاومة الرطوبة: يتم إجراء الاختبارات لتقييم مقاومة الأنابيب للرطوبة وتسرب المياه، والتأكد من بقائها صالحة للعمل في البيئات الرطبة أو المبللة.
- التقلبات في درجات الحرارة: تتعرض الأنابيب لتغيرات شديدة في درجات الحرارة لتقييم أدائها في الظروف الساخنة والباردة، مما يضمن عدم تعرضها للكسر أو التشوه.
– التعرض للمواد الكيميائية: يتم إجراء اختبارات مقاومة المواد الكيميائية للتأكد من أن الأنابيب يمكنها تحمل التعرض للمواد الكيميائية الشائعة دون تدهور، مما يجعلها مناسبة للتطبيقات الصناعية.
2.2.4 التحقق من الامتثال
– معايير الصناعة: يتم تقييم المنتجات النهائية بدقة وفقًا لمعايير الصناعة، مثل تلك الموضحة في UL 1653 وCSA C22.2 رقم 227.1، للتأكد من أنها تلبي جميع معايير السلامة والأداء المطلوبة.
- المتطلبات التنظيمية: يتم التحقق من الامتثال للمتطلبات التنظيمية، بما في ذلك تلك المنصوص عليها في قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC)، لضمان الموافقة على استخدام الأنابيب في التركيبات الكهربائية.
2.3 احتياطات التثبيت
يجب أن يتوافق تركيب الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية (ENT) مع إرشادات محددة لضمان السلامة والامتثال للكود المحلي. وفقًا للكود الكهربائي الوطني (NEC)، يلزم تركيب الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية كنظام كامل وفقًا للشروط.
2.3.1 أحجام وعدد الموصلات
يجب أن تكون الأحجام المختارة وفقًا للكود ومتطلبات المشروع الفعلية، مع عدم تجاوز عدد الموصلات المسموح بها بنسبة الملء.
2.3.2 مثبتة بشكل آمن
يجب تثبيت ENT بشكل آمن على فترات لا تزيد عن 900 مم (3 أقدام). بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يجب تثبيته على مسافة 900 مم (3 أقدام) من كل صندوق مخرج أو صندوق جهاز أو صندوق توصيل أو خزانة أو أي تركيب ينتهي فيه الأنبوب.
هناك ثلاثة استثناءات لهذه القاعدة:
1. يُسمح بالأطوال التي تصل إلى 1.8 متر (6 أقدام) من توصيل طرف المصباح إلى توصيلات الصنبور لمصابيح الإضاءة دون تأمينها.
2. لا تتطلب الأطوال التي تصل إلى 1.8 متر (6 أقدام) من نقطة التثبيت الأخيرة، عند استخدام المسار للتوصيلات داخل سقف يمكن الوصول إليه بمصابيح أو معدات أخرى، تثبيتًا إضافيًا.
3. بالنسبة للأعمال المخفية في المباني النهائية أو ألواح الجدران النهائية حيث يكون التأمين غير عملي، يُسمح بصيد أطوال غير منقطعة من ENT (بدون وصلات).
2.3.3 الدعم
يجب أن تلتزم المسارات الأفقية لأنابيب التهوية والتهوية المدعمة بفتحات في عناصر الإطار بنفس متطلبات الفواصل الزمنية. يجب دعم هذه المسارات على فترات لا تتجاوز 900 مم (3 أقدام) ويجب تثبيتها بشكل آمن في غضون 900 مم (3 أقدام) من نقاط النهاية.
2.3.4 الانحناءات
يجب أن يتم عمل الانحناءات بحيث لا تتلف الأنابيب ولا يتم تقليل القطر الداخلي للأنابيب بشكل فعال. يجب السماح بعمل الانحناءات يدويًا بدون معدات مساعدة، ويجب أن يكون نصف قطر المنحنى إلى خط الوسط لهذه الانحناءات وفقًا للعمود.
لا يجوز أن يكون هناك أكثر من ما يعادل أربعة أرباع الانحناءات (360 درجة في المجموع) بين نقاط السحب، على سبيل المثال، أجسام الأنابيب والصناديق.
2.3.5 البطانات والتشذيب
في حالة دخول أنبوب إلى صندوق أو تركيب أو حاوية أخرى، يجب توفير جلبة أو محول لحماية السلك من التآكل ما لم يوفر تصميم الصندوق أو التركيب أو الحاوية حماية مكافئة. يجب تقليم جميع الأطراف المقطوعة من الداخل والخارج لإزالة الحواف الخشنة.
3. مميزات وفوائد الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية
3.1 المرونة والمتانة
– القدرة على التكيف: تسمح المرونة المتأصلة للأنابيب الكهربائية بالانحناء والتكيف مع أشكال ومساحات مختلفة، مثل الزوايا الضيقة والمنحنيات والجدران. وهذا مفيد بشكل خاص في تصميمات المباني المعقدة حيث يصعب تركيب الأنابيب الصلبة.
– سهولة التركيب: تقلل مرونة ENT من الحاجة إلى تركيبات وموصلات إضافية، مما يبسط عملية التركيب. تعمل هذه القدرة على التكيف على تبسيط توجيه الأسلاك الكهربائية، مما يوفر الوقت والجهد أثناء التركيب.
– قوة المادة: صُمم ENT المصنوع من مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد القوية ليتحمل الصدمات والتآكل والتلف. تضمن طبيعته المتينة قدرته على تحمل الظروف القاسية والإجهاد البدني دون المساس بخصائصه الوقائية.
- مقاومة الرطوبة: التركيبة غير المعدنية لـ ENT تعني أنها لا تصدأ أو تتآكل عند تعرضها للرطوبة، مما يجعلها مناسبة للاستخدام في البيئات الرطبة أو المناطق ذات مستويات الرطوبة العالية، مثل الأقبية والمنشآت الخارجية.
3.2 خفيفة الوزن وغير موصلة للكهرباء
- المناولة والنقل: إن طبيعة أنابيب ENT خفيفة الوزن تجعل من السهل التعامل معها ونقلها مقارنة بالأنابيب المعدنية. تعمل سهولة المناولة هذه على تقليل الضغط البدني على العمال وتعزيز كفاءة عملية التركيب.
- التأثير الهيكلي: نظرًا لوزنها الأخف، تفرض ENT حمولة هيكلية أقل على المباني، وهو أمر مفيد في الإنشاءات حيث يكون تقليل الوزن أمرًا بالغ الأهمية، مثل المباني الشاهقة والإطارات خفيفة الوزن.
– السلامة الكهربائية: نظرًا لكونها غير معدنية، فإن ENT لا توصل الكهرباء، وبالتالي تقلل من خطر حدوث تماس كهربائي ومشاكل التأريض. تعمل هذه الخاصية غير الموصلة على تعزيز السلامة، خاصة في البيئات ذات الرطوبة العالية أو التعرض للمواد الكيميائية.
3.3 فعالية التكلفة
– تكاليف المواد: تعتبر أنابيب ENT أكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة من الأنابيب المعدنية التقليدية. وتجعل تكاليف المواد المنخفضة أنابيب ENT خيارًا اقتصاديًا لمجموعة متنوعة من المشاريع، من المشاريع السكنية الصغيرة إلى المنشآت التجارية الكبيرة.
– توفير المال عند التركيب: تساهم عملية التركيب البسيطة والحاجة المنخفضة إلى تجهيزات إضافية في خفض تكاليف العمالة وتسريع أوقات إكمال المشروع، مما يوفر المزيد من المدخرات.
3.4 خيارات الألوان والأحجام
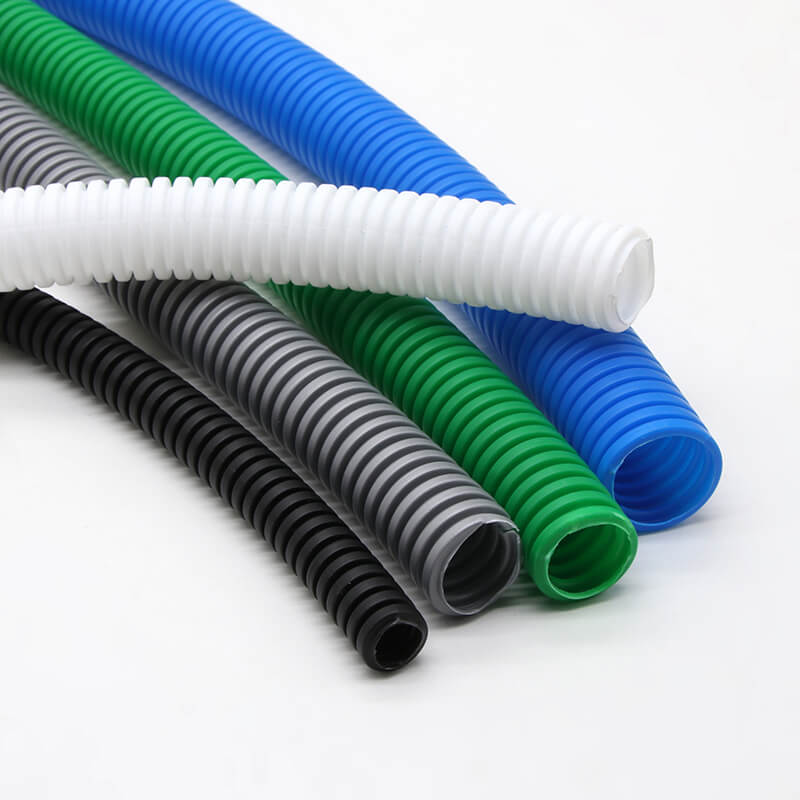
– التعريف والجماليات: يتوفر أنبوب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة بمجموعة من الألوان، بما في ذلك البرتقالي والأبيض والرمادي والأسود والأخضر والأحمر. تسهل خيارات الألوان هذه التعرف على الدوائر الكهربائية المختلفة وتحسين التكامل الجمالي في تصميمات المباني. يجب أن يتبع اختيار الألوان أكواد الكهرباء المحلية.
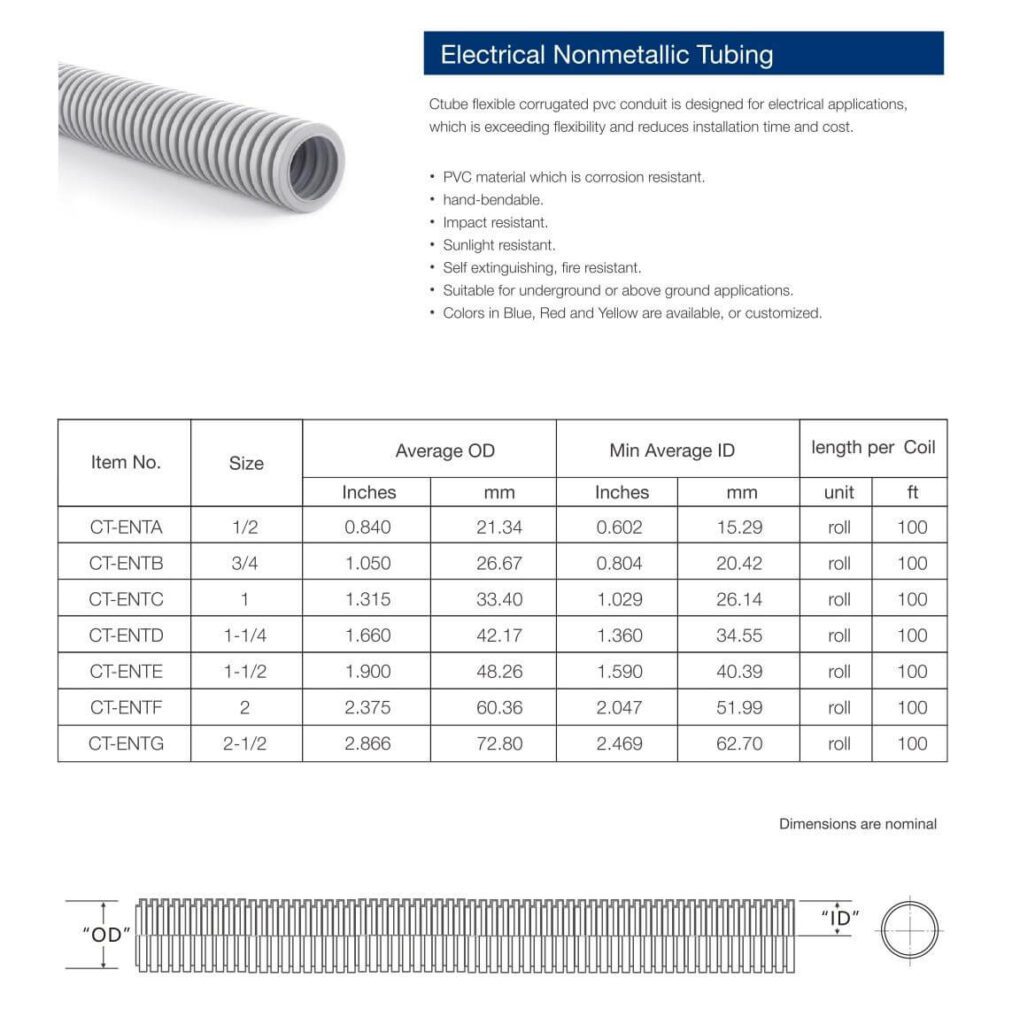
يتوفر أنبوب الأنف والأذن والحنجرة بمجموعة متنوعة من الأحجام لتلبية احتياجات الأسلاك المختلفة. توفر Ctube أحجامًا شائعة تشمل:
- 1/2 بوصة
- 3/4 بوصة
- 1 بوصة
- 1-1/4 بوصة
- 1-1/2 بوصة
- 2 بوصة
- 2-1/2 بوصة
تسمح هذه الأحجام بالمرونة في التوجيه ويمكنها استيعاب أعداد مختلفة من الأسلاك حسب الحاجة لتطبيقات محددة، بدءًا من الأسلاك السكنية البسيطة إلى التركيبات الصناعية المعقدة.
3.5 مقاومة البيئة
– تحمل درجات الحرارة: يمكن لأنابيب ENT تحمل مجموعة من درجات الحرارة، مما يجعلها مناسبة للبيئات الساخنة والباردة. تضمن هذه المقاومة أن الأنابيب تظل وظيفية ووقائية في ظل الظروف المناخية المختلفة.
- مقاومة المواد الكيميائية: إن ENT مقاوم لمجموعة متنوعة من المواد الكيميائية، مما يجعله مناسبًا للاستخدام في البيئات الصناعية حيث قد يحدث التعرض لمواد قاسية.
4. تطبيقات الأنابيب الكهربائية غير المعدنية
4.1 التركيبات السكنية
– الأسلاك الكهربائية المنزلية: تُستخدم الأسلاك الكهربائية الصناعية على نطاق واسع في الأماكن السكنية للقيام بمهام الأسلاك الكهربائية المختلفة. وتتيح لها مرونتها المتأصلة التنقل عبر الجدران والأسقف والأرضيات بسلاسة، مما يجعلها الخيار الأمثل لكل من مشاريع البناء الجديدة والتجديد. وفي المنازل الجديدة، تساعد الأسلاك الكهربائية الصناعية في تبسيط عملية التركيب، بينما يمكن توصيلها في المنازل القديمة عبر الهياكل القائمة بأقل قدر من الاضطراب. وتضمن هذه المرونة دمج الأنظمة الكهربائية بكفاءة وأمان في المباني السكنية، مع الحفاظ على المعايير الجمالية والوظيفية.
– التجديدات والترقيات: إن مرونة أنابيب ENT وسهولة تركيبها تجعلها ذات قيمة خاصة في مشاريع التجديد. عند ترقية الأنظمة الكهربائية في المنازل القديمة، يمكن تركيب أنابيب ENT دون هدم أو إعادة تشكيل مكثف. وهذا مفيد بشكل خاص في الحفاظ على سلامة المباني التاريخية أو ذات الأهمية المعمارية. يمكن إدخال الأنابيب بسهولة في الجدران والأسقف والأرضيات الموجودة، مما يسمح بالترقيات الكهربائية الحديثة دون المساس بالتصميم الأصلي للهيكل.
4.2 التطبيقات التجارية
– المباني المكتبية: في بيئات المكاتب التجارية، يتم استخدام الأنابيب الكهربائية لتنظيم وحماية الكابلات الكهربائية وكابلات البيانات. إن طبيعة الأنابيب خفيفة الوزن ومرونتها تجعلها مناسبة للتركيب في الأسقف المعلقة وتحت الأرضيات المرتفعة، وهي سمات شائعة في تصميمات المكاتب الحديثة. وهذا يسهل إعداد الأسلاك بشكل أنيق وفعال، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية للحفاظ على بيئة عمل منظمة وضمان سهولة الوصول للصيانة والترقيات.
4.3 الإعدادات الصناعية
– المصانع والمستودعات: في البيئات الصناعية مثل المصانع والمستودعات، توفر ENT حماية قوية للأسلاك الكهربائية المعرضة لظروف قاسية مثل الغبار والرطوبة والتأثير الميكانيكي. خصائصها غير الموصلة قيمة بشكل خاص، حيث تقلل من خطر حدوث تماس كهربائي وتعزز السلامة في المناطق التي تحتوي على آلات ومعدات ثقيلة. تضمن متانة ENT بقاء الأنظمة الكهربائية عاملة وآمنة حتى في الظروف الصناعية الصعبة.
– مصانع التصنيع: إن مقاومة ENT للتآكل والمواد الكيميائية المختلفة تجعلها خيارًا مثاليًا لبيئات التصنيع. غالبًا ما تنطوي هذه البيئات على التعرض للمواد المسببة للتآكل والمتطلبات الكهربائية العالية. تضمن ENT حماية الأنظمة الكهربائية من هذه العناصر القاسية، والحفاظ على الوظائف والسلامة. تضمن قدرتها على تحمل التعرض للمواد الكيميائية والإجهاد الميكانيكي الموثوقية طويلة الأمد في هذه البيئات القاسية.
4.4 التطبيقات المتخصصة
– الأنابيب عالية الحرارة: تُستخدم الأنابيب عالية الحرارة في البيئات المعرضة لدرجات حرارة عالية، مثل بالقرب من الآلات الصناعية والعمليات التي تولد حرارة كبيرة. تضمن المواد مثل البولي بروبلين والنايلون أن تتحمل هذه الأنابيب الحرارة الشديدة دون أن تتدهور. يعد هذا التطبيق بالغ الأهمية في الحفاظ على سلامة وأداء الأنظمة الكهربائية في البيئات ذات درجات الحرارة العالية.
– كابلات البيانات والاتصالات: تُستخدم ENT على نطاق واسع لتوجيه وحماية كابلات البيانات والاتصالات، وضمان سلامتها وحمايتها من التلف المادي. في تركيبات الاتصالات، تمنع خصائص ENT غير الموصلة التداخل الكهربائي، وهو أمر بالغ الأهمية للحفاظ على نقل إشارة واضح. وهذا يجعل ENT أصلًا لا يقدر بثمن في مراكز البيانات وغرف الخوادم والبيئات الأخرى حيث يكون توصيل البيانات عالي الأداء أمرًا ضروريًا.
5. أنابيب ENT مقابل أنابيب PVC الصلبة
5.1 المتانة والحماية
توفر كل من أنابيب PVC الصلبة والمرنة مزايا مميزة من حيث المتانة والحماية:
أنابيب PVC الصلبة:
- يوفر حماية مادية فائقة ومقاومة للصدمات.
- مثالي للتركيبات التي قد تتعرض فيها الأسلاك لأضرار محتملة.
- مناسب للبيئات التي تتطلب حماية قوية ضد الضغوط الميكانيكية.
أنابيب PVC المرنة:
- على الرغم من أنها ليست صلبة، إلا أنها توفر حماية جيدة ضد الرطوبة وأشعة الشمس.
- متعدد الاستخدامات للتطبيقات التي تتطلب مرونة في الأنابيب.
- أكثر ملاءمة للتركيبات الكهربائية الداخلية.
5.2 سهولة التثبيت
إن سهولة التركيب تؤثر بشكل كبير على كفاءة المشروع الكهربائي:
أنابيب PVC الصلبة:
- يتطلب قياسات دقيقة وقطع وتجهيز المقاطع الصلبة.
- عادةً لا يكون الانحناء ممكنًا بدون تركيبات إضافية أو تقنيات الانحناء بالحرارة.
- قد يكون التثبيت مستهلكًا للعمالة ويستغرق وقتًا طويلاً.
أنابيب PVC المرنة:
- طبيعتها المرنة تسمح بسهولة الانحناء والتوجيه.
- يقلل من الحاجة إلى تجهيزات إضافية.
- تبسيط عملية التثبيت، خاصة في الأماكن الضيقة أو المعقدة.
5.3 التكلفة والصيانة
إن التكاليف المترتبة والصيانة طويلة الأمد تشكل اعتبارات أساسية:
أنابيب PVC الصلبة:
- تتمتع عمومًا بتكلفة مادية أقل مقارنةً بأنابيب PVC المرنة.
– قد يتطلب التثبيت تجهيزات وأدوات إضافية، مما يزيد من التكلفة الإجمالية.
- متطلبات الصيانة ضئيلة.
أنابيب PVC المرنة:
- قد تكون تكلفة المواد أعلى قليلاً.
- سهولة التركيب والمرونة يمكن أن تقلل من تكاليف العمالة.
- متطلبات الصيانة أيضًا قليلة.
5.4 اعتبارات الدفن المباشر
تعتبر ملاءمة الدفن المباشر عاملاً حاسماً في اختيار القنوات لتطبيقات محددة:
تنص قواعد قانون الكهرباء الوطني (NEC) على أن ENT غير مناسب للدفن المباشر.
يمكن دفن الأنابيب الصلبة المصنوعة من مادة البولي فينيل كلوريد المتوافقة جزئيًا بشكل مباشر، مثل أنبوب توصيل DB2/ES2 PVC.
يعتمد الاختيار بين أنابيب PVC الصلبة وأنابيب ENT على المتطلبات المحددة لمشروعك. عند اتخاذ قرارك، ضع في اعتبارك الظروف البيئية ومستوى الحماية المادية المطلوبة وسهولة التركيب والتكلفة الإجمالية لضمان أفضل ملاءمة لمشروعك.

6. الخاتمة
يُجسّد أنبوب ENT التطورات الحديثة في التركيبات الكهربائية من خلال توفير المرونة والمتانة وخصائص السلامة المحسنة. تضمن عملية إنتاجه، جنبًا إلى جنب مع تدابير مراقبة الجودة الصارمة، أن يظل أنبوب ENT خيارًا موثوقًا به لمجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات. من ترقيات الأسلاك السكنية إلى المشاريع الصناعية المعقدة، يوفر أنبوب ENT حلاً فعالاً وآمنًا لحماية البنية التحتية الكهربائية.
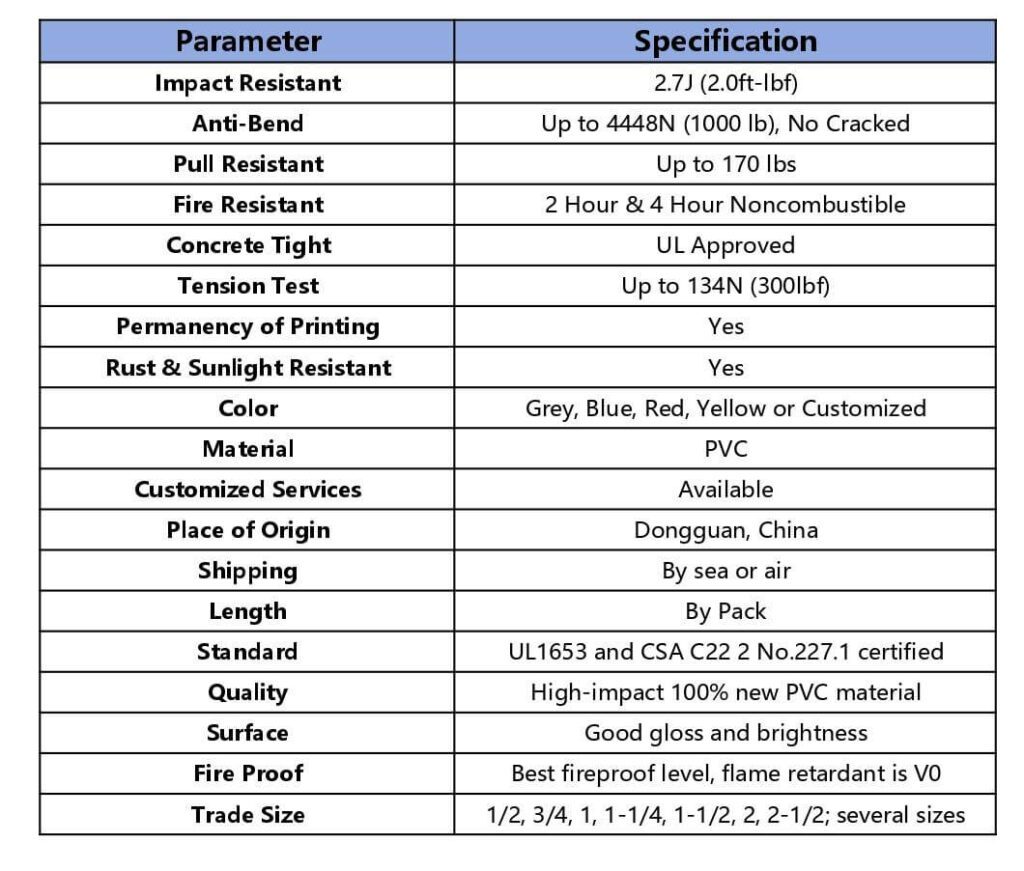
Ctube هي واحدة من الشركات المصنعة المهنية للأنابيب البلاستيكية في الصين. نحن متخصصون في تطوير وإنتاج الأنابيب البلاستيكية المبتكرة ومنتجات التركيب لإدارة الكابلات وحمايتها. منتجاتنا من الأنابيب البلاستيكية حاصلة على شهادة UL1653 وCSA C22.2 رقم 227.1، مما يجعلها مناسبة للسوقين الأمريكية والكندية.
تفتخر شركة Ctube بتصنيع أنابيب عالية الجودة باستخدام مادة PVC الجديدة 100%، مما يضمن مقاومة فائقة للصدمات والمتانة. تتميز أنابيبنا بسطح نهائي ممتاز مع لمعان وسطوع جيدين. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تتميز أنابيب PVC المموجة لدينا بأفضل مستوى مقاومة للحريق مع تصنيف V0 لمقاومة اللهب. متوفرة بألوان قياسية مثل الرمادي والأحمر والأزرق، كما نقدم التخصيص لتلبية متطلبات محددة. تتراوح أحجام التجارة لدينا من 1/2 إلى 2-1/2 بوصة، لتلبية مجموعة متنوعة من احتياجات التركيب.
لمزيد من التفاصيل، مرحبا بكم في موقعنا: https://www.ctube-gr.com/