Introduction
There’s a lot of information out there about conduit system. Hey, understanding the supplying electric power is a critical part of your home or utility improving strategy. But what about PVC electrical conduit?
Using the right and compliant material in a conduit system is a foundation form in and of itself — and if you don’t do it well, then you may cause fatal accidents. The wrong conduit can damage the conductors in your electrical raceway system. Extreme cases of electric malfunction include electric shock, electric fire and power outages.
Between 2017 and 2021, 628 electrical workers died from electrocution. Workers in the construction industry made up 56% of those deaths. 35% of them had jobs in the installation, maintenance and repair industries. Protect workers on the job by ensuring they’re using the right conduit.

So, let’s see about making it better now, shall we? In this post, I’ll share with you all the basics about PVC electrical conduit.
Key Points
1. What is PVC electrical conduit?
2. What is the difference between PVC conduit and PVC pipe?
3. How PVC conduit works and what are the advantages in applications?
4. What size does PVC conduit come in?
5. Can PVC be recycled?
6. What are PVC conduit fittings and their functions?
1. What is PVC electrical conduit?
PVC stands for Polyvinylchloride which is a tenacious chemically resistant synthetic resin. It has been a widely used plastic material to protect power in houses, telecommunications and utilities since 1932. A PVC electrical conduit is commonly known as a white rigid PVC tube for threading and protecting wires from corrosion and electrical leakage.
The most basic of the home improving is the installation of wire layout. In order to protect the wire when designing the system, we will use PVC electrical conduit. Since the wire thickness is different, PVC electrical conduit is also divided into different size specifications to adapt to the arrangement.
PVC electrical conduit stops burning and electrical leak, resists corrosion, moisture and sunlight, so it is especially suitable for outdoor projects where it is used to protect wires and workers.
2. What is the difference between PVC pipe and PVC conduit ?
These 2 words are fairly similar. Although PVC pipe and PVC conduit are both made from the same plastic, they are not the same thing and should not be used for the same applications. Each of them should only be used in appropriate environment and not be exchangeable. PVC pipes are generally used in plumbing applications and PVC conduits are generally used in electrical applications.
Why is that? The following are 5 main differences between PVC pipe and PVC conduit.
- Pressure test: PVC pipe is tested for pressure and that’s why it is also called as PVC pressure pipe. The pressure rating is normally printed on PVC pipes. Water runs through PVC pipes hence it should withstand water pressure and that’s why are tested and rated for pressure. On the other hand, conduit is the term applied to PVC pipe that are made for electrical wiring and conduits are not tested for pressure. So PVC conduit is not approved for use in the plumbing system because the lack of pressure testing makes the probabilities of leaking higher.
- Wall thickness: PVC pipes have thicker walls compared to PVC conduits. The added thickness ensures that the pipe is strong enough to resist bending and that it will remain undamaged and intact. Whereas PVC conduit is not required to withstand pressure so their walls are not thick and also that simply wouldn’t be a cost effective design for manufacturers.
- Color: PVC pipe that is used for plumbing is usually white whereas electrical PVC conduit is usually grey.
- Ultraviolet degradation: plumbing PVC pipe is mainly situated underground or indoors. It will degrade when exposed to ultraviolet light for prolonged periods of time. Therefore it is not suitable to use it in exposed area applications like rooftops. They tend to become brittle and get cracked when exposed. On the other hand, PVC conduit is tested and rated for UV exposure which means it’s suitable for outdoor applications in which electrical cables need to be run across rooftops or up the sides of buildings.
- Pipe tapering: plumbing PVC pipe requires couples and PVC cement to join individual pieces together. Whereas electrical PVC conduit typically has a flared ends that allows for individual pipes to be easily attached to one another without the use of coupler.
Now you know PVC pipe is used to carry water in plumbing works and PVC conduit is primarily used in house for wiring or can be used in locations where it will be exposed to UV rays.
3. How PVC conduit works and what are the advantages in applications?
Conduit is often used as a term to describe a system that contains a series of electrical conductors. The following are the mechanisms of its capability:
- To connect different conduit sections.
- To provide spaces and create taps and splices in conductors.
- To create 90° bends and taps for conduit runs.
- To provide access for scheduled and accidental maintenance.
- To act as pull outlets for the installed conductors.
PVC electrical conduit is commonly used in corrosive environments. It is installed using PVC fittings that are directly glued in place. The normative glue job makes fittings and conduit watertight hence PVC is really suitable for a quick burial on the grounds and underground.
Here are the advantages of using PVC conduit in applications:
- Commonly available in various wall thicknesses.
- More cost effective than other conduits like EMT (electrical metal tubing) or IMC (intermediate metal conduit).
- More lightweight, versatile, and easy to install.
- Works perfectly in concrete or wet locations.
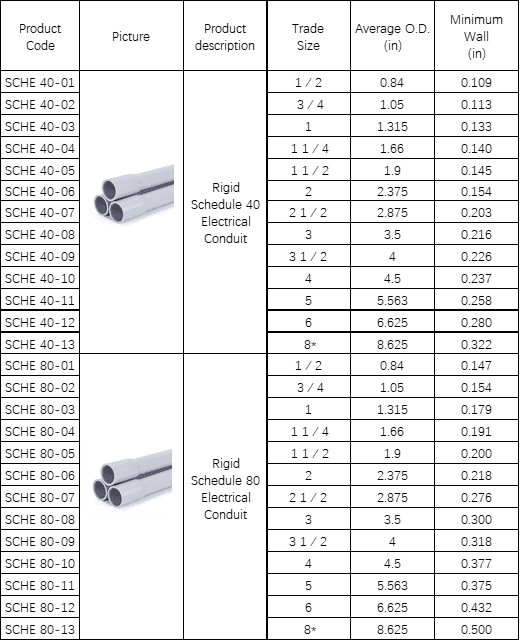
4. What size does PVC conduit come in?
The main dimension of PVC conduit is the wall thickness. Since different wall thicknesses are beneficial in different situations, the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) came up with the schedule 40 and 80 system for classifying the two common types: Schedule 40 and Schedule 80.
In March 1927, the American Standards Association surveyed industry and created a system that designated wall thicknesses based on smaller steps between sizes. The designation known as nominal pipe size replaced iron pipe size, and the term schedule (SCH) was invented to specify the nominal wall thickness of pipe. Under this rule, pipe and conduit are the same.
Ctube offers schedule 40 PVC conduits and schedule 80 PVC conduits as well as fittings and other accessories at highly competitive prices. Here are the Ctube’s product size sheet of Sch. 40 & 80 PVC conduit:
If you plan to do home repair, then Schedule 40 PVC can be the way to go. If your work is industrial or chemical outdoors, you may need to use Schedule 80. These applications may result in higher pressures and stresses on the material, so thicker walls are a must.
Electrical conduit provides a high protection to sealed conductors from impact, moisture, and chemical vapors. To simplify construction, we often pull different quantities, sizes and types of conductors into a single conduit. This design is not only simple, but also reduces the cost of multiple runs and composite cables. If you’re interested in Ctube PVC products, please feel free to contact us and inquiry.
5. Can PVC be recycled?
PVC can be recycled, but the cost of recycling is too high.
PVC, like other plastics, is often accompanied by many impurities after it is eliminated and used, and needs to be sorted before it can be recycled. Earlier methods of physical recycling and combustion recycling have been eliminated. The former recovered plastic materials are not of high quality because they are difficult to sort. The latter is harmful to the environment because many harmful gases are released in the process of burning PVC to pollute the environment. Therefore, only chemical recycling methods can be used to do this at present. Chemical recycling can obtain a higher quality of recovery, but the cost is high.
BTW, the recent crazy increase of crude oil price has greatly affected the price of plastic raw materials, so recycling is a trend in the future.
Secondly, the quality of recycled PVC is not as good as the brand new material. So it can only be used in some low-demand occasions, such as shoe soles, agricultural drainage pipes, etc.
From the electrical PVC conduit industry, recycled material has another layer of meaning. By recycled material we usually mean that after the first injection or extrusion, there may be some quality problems that lead to the scrapping of the product. In order not to waste raw materials, the process of remixing these raw materials for use is called recycling. It is different from the meaning of recycled raw material above, which can be said to be the raw material for the second processing.
Of course, what is described above is an ideal situation. It should be better if the raw materials are only circulated within the factory. Some factories buy this recycled material and mix it with a certain percentage of brand new material, which is indistinguishable in appearance, but its physical properties are very different from the material made of 100% brand new material. This is why Ctube has insisted on using brand new materials for over 10 years of production. We have never had any complaints from our customers in this regard.
6. What are PVC conduit fittings and their functions?
When we need to change the orientation of the PVC conduit, we need to use connectors to attach it to different size boxes or enclosures. Straps and clips are needed when our conduit needs additional support. These parts that are used to connect the wire conduit together and attach the end of the conduit to the box, enclosure or electrical device are collectively called PVC conduit fittings. Their sizes and shapes should comply to the appropriate regulations.
Section 110-3 of the NEC requires that all fittings be labeled and meet the relevant construction and performance standards. If you are in doubt about choosing fittings, feel free to contact us for suggestions.
PVC conduit fittings are listed as follows based on how they function:
Conduit Bodies and Juction Boxes
Conduit bodies and junction boxes are made to fit threaded rigid conduit in every size from half-inch all the way up to 4-inch. These are tubular or square components with openings at each end for admitting conduits, and providing easy access to the cables. It allows more space for electrical conductors to bend (often 90 degrees). They are marked with the purposes they are rated to serve, as well as the internal volume.
Bends and Elbows
PVC bend/elbow is designed to turn the run of a conduit (commonly 45 degrees and 90 degrees). It’s created to save time, equipment and labor cost. You can change the direction of a conduit run with pre-fabricated bends/elbows and they are available in a large range of lengths and curvatures.
Coupling
Conduit couplings securely connect different lengths and diameters of conduits or bends together. They have internal threads. They are small parts that connect or “couple” one part to another, usually permanently. They can connect conduit to conduit and conduit to fittings.
Bushings and Locknuts
Bushings create a smooth entry point to conduits without any sharp edges, protecting the conductors from damage during wire pulls. Locknuts are nuts screwed down hard on another to prevent it from slacking back and threaded on the inside, with teeth on one surface or both, which grip the surface. Both of them protect conductors from damage when pulling. They are also very important when the conduit system enters the enclosure or pull box.
Unions
Unions can come in handy when couplings are difficult to install. They come in three head types, male head, female head or both. The unions can be mounted on the end of a conduit and secured together by nuts.
Reducers
PVC reducer is also a fitting used to connect two different sizes of PVC conduits, connecting the larger one to the smaller one. It is more suitable for conditions where space is tight compared to pull boxes. When connecting two conduits with a reducer, you also need to use adhesive, rubber rings or reducing washer to achieve a leak-free connection. PVC reducers are available in two types: eccentric and concentric.
Straps and Clips
Straps and clips can be useful when we need to fasten conduit to floors, beams, ceilings or walls. If screws and bolts are available, the straps can be used to secure the conduit to the ceiling so that it does not fall due to gravity. Clips are found in all manner of household, industrial and outdoor settings. They’re used as an efficient and tidy way to support, restrain, secure and guide conduit for electrical purposes.
Conclusion
These are all the basics about PVC conduit and fittings. Over 90% of electrical engineers around the world now know these like the back of their hand. Only by knowing these well will you be able to choose the right materials for your electrical projects and thus effectively avoid accidents. Genuinely in the electrical industry, you make the right choice and you save the lives of workers. Of course, there are many credible blogs out there sharing relevant information, try checking and verifying this post.
Why not try to make a DIY project with conduit and fittings? That way you won’t read this post today and forget about it tomorrow. Feel free to challenge. We’re sure you’ll be successful and you’ll be impressed with all of this knowledge. This could be an important milestone on your way to becoming a professional engineer or purchasing manager. Your boss and customers will trust you more because you are skilled in basics.
“Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn.”
– Benjamin Franklin